Chapter: Biochemistry: Carbohydrates
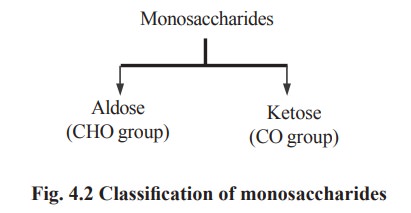
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are defined as polyhydroxy
aldehydes or ketones, which cannot be further hydrolysed to simple sugars.
Monosaccharides are divided into two groups according to their functional
groups (Fig. 4.2).
They are also classified based on the number of
carbon atoms present in the monosaccharides
1. Aldotriose eg: Glycerose 1. Ketotriose :eg.Dihydroxy acetone
2. Aldotetrose eg : Erythrose 2. Ketotetrose : eg : Erythrulose
3. Aldopentose eg : Ribose 3. Ketopentose : eg. Ribulose
4. Aldohexose eg: Glucose 4. Ketohexose : eg. Fructose
1. Aldoses are sugars containing aldehyde group
eg : glucose, galactose, mannose.
2. Ketoses are sugars containing ketone group
eg : fructose and sorbose.
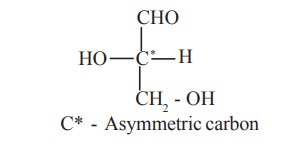
Carbohydrates posses asymmetric carbon atoms. A
carbon atom to which four different atoms or groups of atoms are attached is
said to be an asymmetric carbon.
Vant Hoff’s Rule of ‘n’
The number of possible isomers of any given
compound depends upon the number of asymmetric carbon atoms the molecule
posses.
According to this rule, 2n equals the possible
isomers of that compound, where ‘n’ - represents the number of asymmetric carbon
atoms in a compound.
Hexoses
Hexoses are monosaccharides containing 6 carbon
atoms. The molecular formula of hexose is C6H12O6.
Aldohexoses contain asymmetric carbon atoms at position 2,3,4 and 5. Hence an
aldohexose can exist in 16 isomeric forms. (2n = 24 =
16).
The ketohexoses contain 3 asymmetric carbon
atoms at position 3,4 and 5. Hence, it exist in 8 isomeric forms (2n
= 23 = 8).
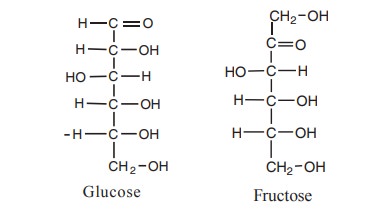
Structure of glucose and fructose
Glucose is a simple sugar. It is a
monosaccharide. It cannot be hydrolysed further.
Glucose is an important sugar of blood.
Human blood contains 60-100 mg of glucose in
100 ml of blood in fasting. It serves as the major metabolic fuel in cells and
tissues. Oxidation of glucose quickly provides energy for the cells.Hence,
glucose is described as the chief source of energy.
1. The empirical formula of glucose is CH2O
and the molecular formula is C6H12O6. The
molecular formula of fructose is C6H12O6 .
Glucose has aldehyde group whereas fructose has ketone group.
Related Topics