Chapter: Microprocessor and Microcontroller
Microcontroller Chips
Microcontroller Chips
Broad
Classification of different microcontroller chips could be as follows:
·
Embedded (Self -Contained) 8 - bit Microcontroller
·
16 to 32 Microcontrollers
·
Digital Signal Processors
Features of Modern Microcontrollers
·
Built-in Monitor Program
·
Built-in Program Memory
·
Interrupts
·
Analog I/O
·
Serial I/O
·
Facility to Interface External Memory
·
Timers
Internal Structure of a Microcontroller
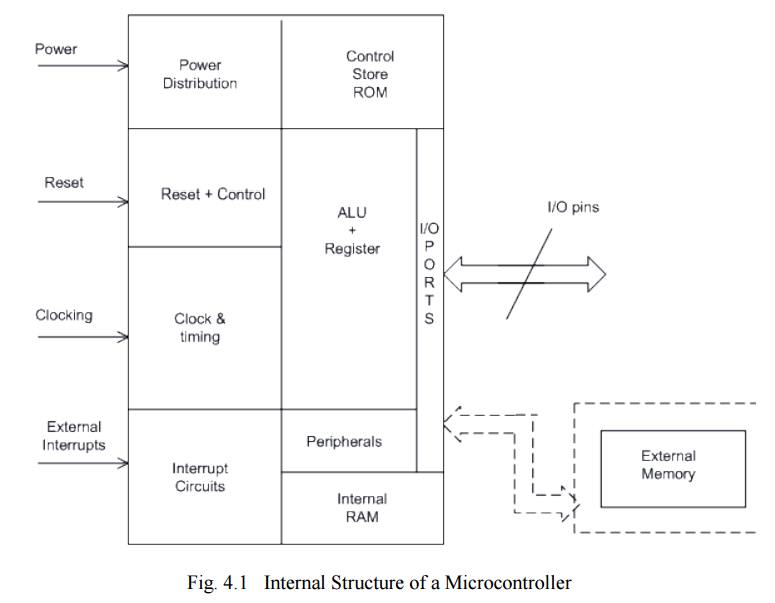
At times,
a microcontroller can have external memory also (if there is no internal memory
or extra memory interface is required). Early microcontrollers were
manufactured using bipolar or NMOS technologies. Most modern microcontrollers
are manufactured with CMOS technology, which leads to reduction in size and
power loss. Current drawn by the IC is also reduced considerably from 10mA to a
few micro Amperes in sleep mode(for a microcontroller running typically at a
clock speed of 20MHz).
Harvard Architecture (Separate Program and Data Memory
interfaces)
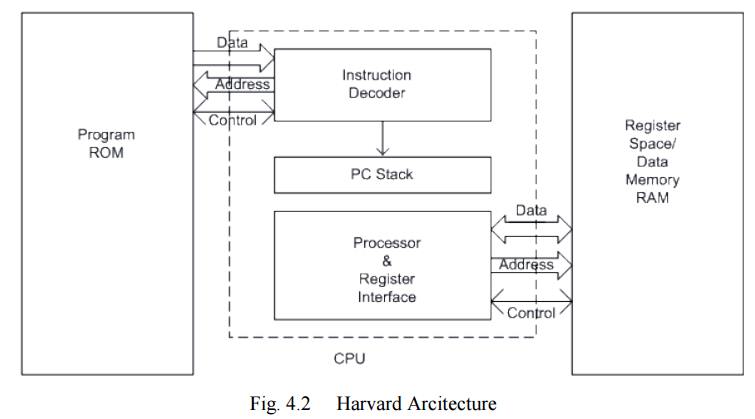
The same
instruction (as shown under Princeton Architecture) would be executed as
follows:
Cycle 1
- Complete
previous instruction
- Read the
"Move Data to Accumulator" instruction
Cycle 2
- Execute
"Move Data to Accumulator" instruction
- Read next
instruction
Hence
each instruction is effectively executed in one instruction cycle, except for
the ones that modify the content of the program counter. For example, the
"jump" (or call) instructions takes 2 cycles. Thus, due to
parallelism, Harvard architecture executes more instructions in a given time
compared to Princeton Architecture.
Memory organization:
In the
8051, the memory is organized logically into program memory and data memory
separately. The program memory is read-only type; the data memory is organized
as read-write memory. Again, both program and data memories can be within the
chip or outside.
Related Topics