Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school
Leaf Modification
Leaf Modification
The primary functions of leaf are photosynthesis and transpiration. But in many plants the leaves are modified to perform some additional functions. These are called as leaf modifications Some of the leaf modifications are:
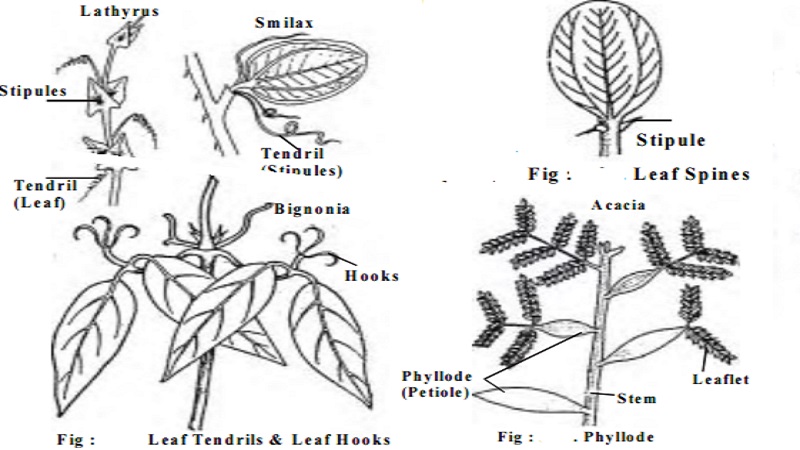
1. Leaf tendrils (eg. Wild pea)
2. Leaf hooks (eg. Bignonia)
3. Leaf spines (eg.Zizyphus)
4. Phyllode (eg. Acacia)
5.Pitcher (Nepenthes)
6. Bladder eg. Stipules (Utricularia)
1. Leaf tendrils : Here the stem is very weak and hence they have some special organs for attachment to the support. Tendril is a slender wiry coiled structure which helps in climbing the support. In Lathyrus the entire leaf is modified into tendril. In Smilax the stipules become modified into tendril.
2. Leaf hooks: In this the leaves are modified into hooks and help the plant to climb the support. In Bignonia unguiscati , the three terminal leaflets of the compound leaves become stiff, corved and claw like hooks.
3. Leaf-spines : In this type the leaves become wholly or partially modified into sharp pointed structures known as spines. This modification helps the plant to cut down transpiration and also protects the plants against the attacks of grazing animals. Any part of the leaf may get modified in to spine. e.g. Zizyphus
4. Phyllode: In Acacia the petiole or any part of the rachis becomes flattened or winged taking the shape of the leaf and turning green in colour. This flattened
or winged petiole or rachis is known as the phyllode. The normal leaf which is pinnately compound develops in the young stage, but soon falls off. The phyllode then performs all the functions of the leaf. The wing of the phyllode normally develops in the vertical
direction so that sunlight cannot fall on its surface; this reduces evaporation of water. There are about 300 species of Australian Acacia, all showing the phyllode.
5. Pitcher
In the pitcher plant (Nepenthes) the leaf becomes modified into a pitcher. There is a slender stalk which coils like a tendril holding the pitcher vertical and the basal portion is flattened like a leaf. The pitcher is provided with a lid which covers the mouth. The function of the pitcher is to capture and digest insets. The lamina is modified into pitcher. The rim of the pitcher is beautifully coloured and it is provided with a row of nectar glands for attracting insects. The inner wall of the pitcher is provided with glands secreting a watery fluid.
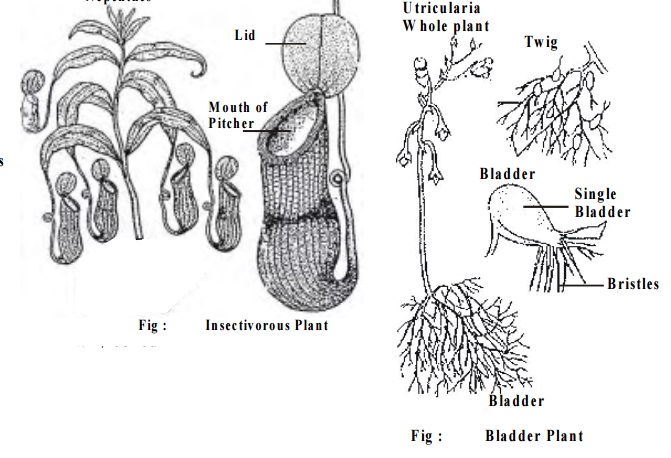
pointed downwards below the rim. This arrangement prevents the insects entering the pitcher from escaping out. The insects get drowned in the fluid and it is digested by the enzymes secreted by the glands. Thus the plant is able to get nitrogenous food.
6. Bladder
In utricularia some of the much dissected leaves are modified into bladders.
These bladders serve as floats for the aquatic plants and for trapping the insects.
Related Topics