In many plants in addition to the normal functions mentioned above the stem performs certain additional functions. In these plants they show structural modifications. The additional functions may be 1. Storage of food 2. Perennation 3. Vegetative propagation 4. Photosynthesis.
Modified stems are grouped into the following three categories.
1. Aerial modifications 2. Sub aerial modifications 3. Under ground modifications
Modifications of stem
In many plants in addition to the normal functions mentioned above the stem performs certain additional functions. In these plants they show structural modifications. The additional functions may be 1. Storage of food 2. Perennation 3. Vegetative propagation 4. Photosynthesis.
Modified stems are grouped into the following three categories.
1. Aerial modifications 2. Sub aerial modifications 3. Under ground modifications
1. Aerial modifications
In some plants, stem undergoes modification to a great degree to perform certain special functions. These are
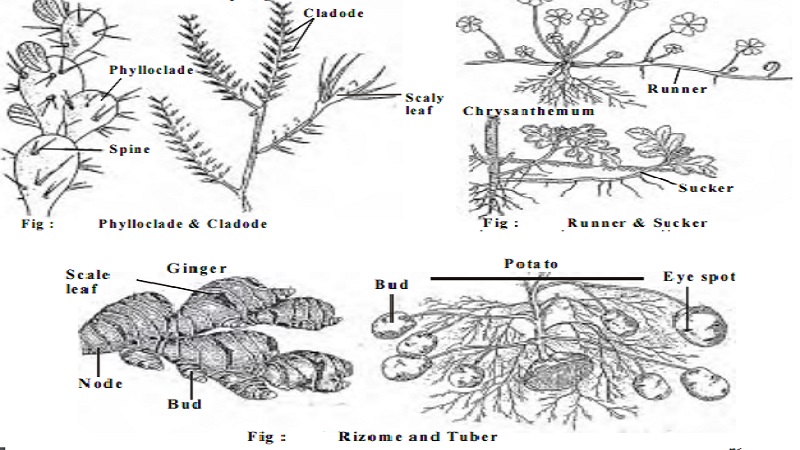
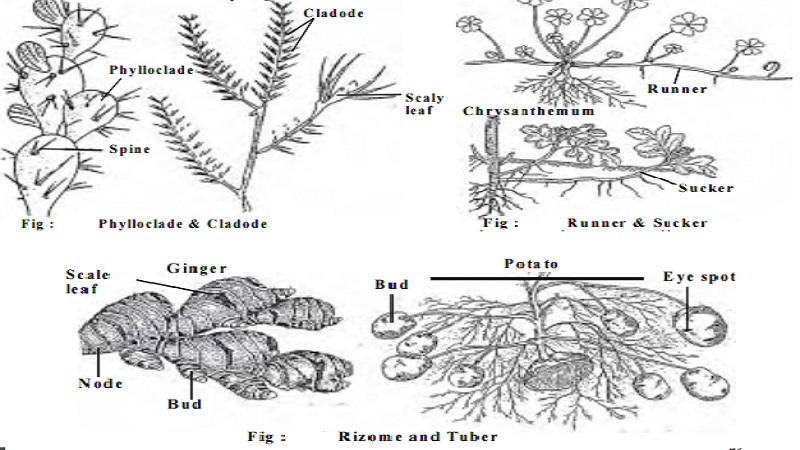
1. Tendrils 2. Thorns 3. Phylloclade 4. Cladode 5. Bulbil. We will discuss about phylloclade and cladode in detail.
Phylloclade: These are green, flattened or cylindrical stems with nodes and internodes. The leaves are reduced to spines to reduce the loss of water by transpiration since these plants grow in xerophytic conditions. The stem becomes flat like a leaf and performs the functions of photosynthesis. eg. Opuntia. In this the phylloclade i.e. the stem performing the function of leaf becomes succulent due to storage of water and food.
Cladode: These are green, cylindrical or flattened stem branches of limited growth. These are usually of one internode as inAsparagus. Their stem nature is evident by the fact that they bear buds, scales and flowers.
2. Sub-aerial modifications:
This type of modification is found in many herbaceous plants with a thin, delicate and weak stem. In such plants a part of the stem is aerial and the remaining part lives underground. These plants bear adventitious roots and aerial branches at their nodes. They propagate quickly by vegetative methods. Sub-aerial modified stems are of the following types:
1. Runner 2. Sucker 3. Stolon 4. Offset
We will discuss about Runner and Sucker.
Runner : It has long and thin internodes and the branches creep over the surface of the soil. They develop adventitious roots from the lower sides of the nodes. From the axil of the scale leaves at the nodes arise aerial branches. Runners grow in all directions from the mother plant. On detachment from the mother plant the daughter plant propagate in a similar manner. Thus very soon a whole area is covered by many plants from a single plant. Eg. Doob grass, oxalis
Sucker: It is a modified runner. In this the runner originates as a lateral branch from the underground axillary bud of an aerial shoot. It grows down in to the soil obliquely for some distance and then grows upwards. The sucker has nodes and internodes and in the nodal region it bears scale leaves and axillary buds above and adventitious roots below. Eg. Chrysanthemum
3. Underground modifications:
Some plants develop non-green underground stem which are perennial i.e they live for many years. These store reserve food, and are adapted for perennation. During favorable conditions underground stems give rise to aerial shoots. With the onset of unfavourable conditions the aerial shoots die. During this period the underground stems remain dormant.
These underground stems can be following.
1. Presence of nodes and internodes2. Presence of scale leaves and adventitious roots arising from the nodes. 3. Presence of axillary and terminal bud.
The four different types of underground stem.
Corm
Rhizome: Rhizomes are horizontal, thick, stout underground stems. They are swollen with the storage of food materials. They have nodes and internodes. The nodes have brown scaly leaves which protect the axillary buds. The nodes bear adventitious roots on the lower side. At the onset of favourable condition the axillary and terminal buds grow into aerial shoots. These aerial shoots die on the approach of unfavourable condition. eg.Ginger, Turmeric
Advantages of Rhizomes: Rhizomes are very good means of perennation. They help to tide over the unfavourable conditions like drought etc. They serve as store houses of food which is safely protected from the grazing of animals. Since aerial shoots arise from the buds of the rhizome they are useful in vegetative propagation also.
Tuber: Tubers are the swollen tips of special underground branches. They are different from rhizomes in that they are stouter, with slender internodes and the adventitious roots are generally absent. The tuber bears many scale leaves with axillary buds in the nodes. Potato is a common example for a tuber. It has got small depressions on it called the eye of the potato. It bears the bud. When the tuber is planted in the soil the buds develop into branches at the expense of the food material stored in the tuber. Some of these branches become aerial and green and erect while others grow horizontally underground and their tips become swollen with food materials.
Study Material, Lecturing Notes, Assignment, Reference, Wiki description explanation, brief detail
11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school : Modifications of stem : 1. Aerial modifications 2. Sub aerial modifications 3. Under ground modifications |