Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school
Types of Root System And Functions of roots
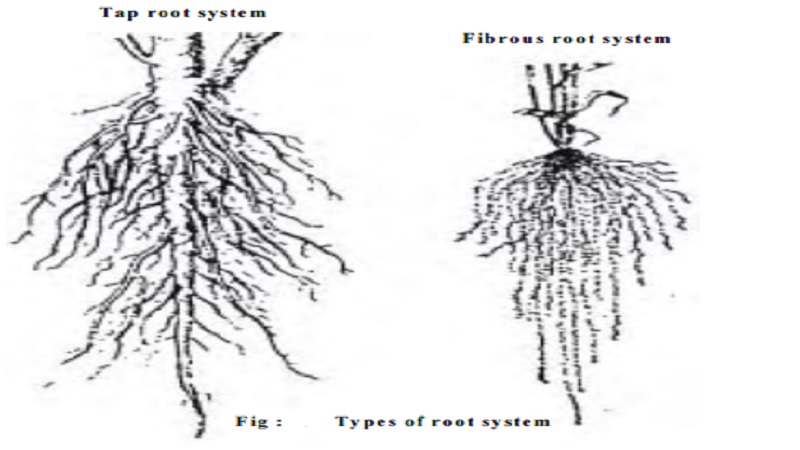
Types of Root System
There are two types of root system
1. Tap root system
2. Adventitious root system
Tap root system
It develops from the radicle of the embryo. The radicle grows in to the primary or tap root. It produces branches called secondary roots. These branch to produce what are called tertiary roots. This may further branch to produce fine rootlets. The tap root with all its branches constitutes the tap root system. Tap root system is the characteristic feature of most of the dicot plants.
Adventitious root system
Root developing from any part of the plant other than the radicle is called adventitious root. It may develop from the base of the stem or nodes or internodes. The adventitious roots of a plant along with their branches constitute the adventitious root system.
In most of the monocots the primary root of the seedling is short lived and lateral roots arise from various regions of the plant body. They are thread like and are of equal size and length. These are collectively called fibrous root system. It is commonly found in monocot plants like maize, sugarcane and wheat.
Functions of roots
Roots perform two kinds of function namely primary and secondary function. The primary functions are performed by all the roots in general. In some plants the roots perform certain additional functions in order to meet some special needs. These are called secondary functions of the roots. In order to perform these special functions the roots show modification in their structure accordingly.
Primary functions
Absorption: The main function of any root system is absorption of water and minerals from the soil with the help of root hairs.
Anchorage: The roots help to fix the plant firmly in the soil.
Secondary functions:
The following are some of the secondary functions performed by the roots in addition to the primary functions mentioned above.
1. Storage of food
2. Additional support
3. Haustorial function
4. Assimilation
5. Respiration
6. Symbiosis
Related Topics