Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school
Plant Cell Mitochondria - Power house of the cell
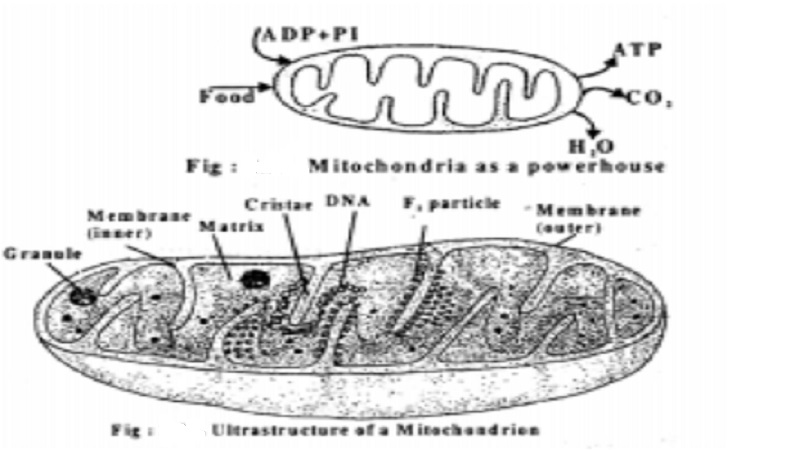
Mitochondria
A Mitochondrion is also called as the 'Power house of the cell' because it stores and releases the energy of the cell. The energy released is used to form ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate ) Mitochondria are the principal sites of ATP production in aerobic cells.
Most eukaryotic cells contain many mitochondria, which occupy up to 25 percent of the volume of the cytoplasm. These complex organelles are among the largest organelles generally exceeded in size only by the nucleus, vacuoles and chloroplasts. Typically the mitochondria are sausage-shaped but these may be granular, filamentous, rod-shaped, spherical or thread like.
Mitcohondria contain two very different membranes an outer one and an inner one, separated by the inter membrane space.
The outer membrane is composed of about half lipid and half protein. The inner membrane is less permeable. It is composed of about 20 percent lipid and 80 percent protein. The surface area of the inner membrane is greatly increased by a large number of infoldings, or cristae that protrude into the matrix.
Structure of the cristae membrane
The inner of the cristae membrane (i.e the surface towards the matrix) is covered with numerous (infinite) stalked particles. These are called F1 Particles, elementary particles or sub units. These particles project into the matrix. Each F1 particle has 3 parts, viz, the head piece, the stalk and the base piece. The respiratory chain consists of enzymes and co-enzymes which constitute the Electron Transport System, (ETS) in the mitochondrion. These enzymes and co-enzymes of the ETS act as the electron acceptors in the aerobic respiration reaction. (Oxidative Phosphorylation).
In non photosynthetic cells the principal fuels for ATP synthesis are fatty acids and glucose. The complete aerobic degradation of glucose to CO2 and H2O is coupled to synthesis of as many as 38 molecules of ATP. In eukaryotic cells, the initial stages of glucose degradation occur in the cytosol, where 2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule are generated. The terminal stages including those involving phosphorylation coupled to final oxidation by oxygen are carried out by exzymes in the mitochondrial matirix and cristae. As many as 36 ATP molecules per glucose molecule are generated in mitochondria although this value can vary because much of the energy released in mitochondrial oxidation can be used for other purposes (e.g heat generation and the transport of molecules into or out of the mitochondrion) making less enery available for ATP synthesis. Similarly, virtually all the ATP formed during the oxidation of fatty acids to CO2 is generated in the mitochondrion. Thus the mitochondrion can be regarded as the 'Power plant' of the cell.
Mitochondria as semi-autonomous organelles
Mitochondria are self perpetuating semi autonomous bodies. These arise new by the division of existing mitochondria. These are also regarded as intra cellular parasitic prokaryotes that have established symbiotic relationship with the cell. The mitochondrial matrix contains DNA molecules which are circular and 70s ribosomes, tRNA and enzymes for functioning of mitochondrial genes.
Related Topics