Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school
Morphology of flowering plants or Angiosperms - short notes
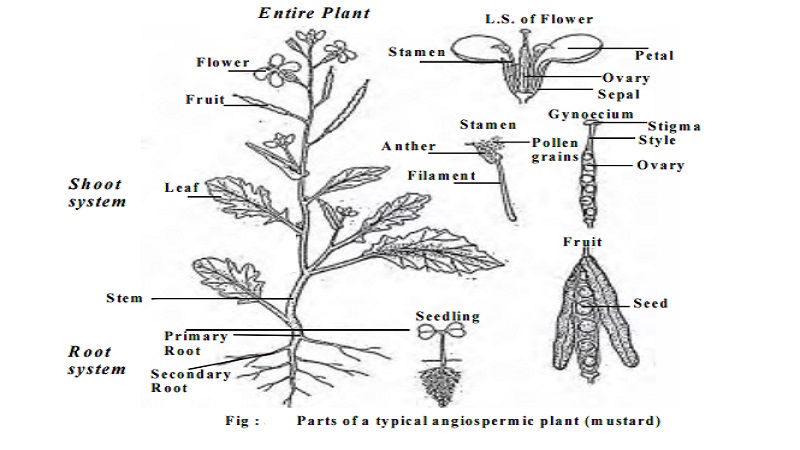
PLANT MORPHOLOGY
Root, Stem and Leaf
Morphology is the branch of biology that deals with form, size and structure of various organs of the living organisms. Each and every living organism has a definite form. Study of the external structure or morphology helps us to identify and distinguish living organisms. Knowledge of morphology of plants is also helpful in the study of various other fields such as genetics, plant breeding, genetic engineering, horticulture, crop protection and others.
Morphology of flowering plants or Angiosperms.
The plants which we commonly see in the gardens and road-side belong to the largest group of plants called flowering plants or Angiosperms. (angio=box sperm=seed). The word derives its origin from the fact that the ovules are enclosed in a box like organ called ovary. Hence the seeds are enclosed in the fruit. Angiosperms include more than 2,20,000 species exhibiting a wide spectrum of forms and occupying a wide range of habitats. Such a wide range of flowering plants are identified, described and classified based on their morphology and anatomy.
Parts of a Flowering Plant
Any common flowering plant consists of a long cylindrical axis which is differentiated into an underground root system and an aerial shoot system. The root system consists of root and its lateral branches. The shoot system has a stem, a system of branches andleaves. Root, stem and leaves together constitute the vegetative organs of the plant body and they do not take part in the process of reproduction. The flowering plants on attaining maturity produce flowers, fruits and seeds. These are called the reproductive organsof the plant.
Related Topics