Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Bacteriology: Nonsporing Anaerobes
Laboratory Diagnosis of Proteus Infections
Laboratory Diagnosis
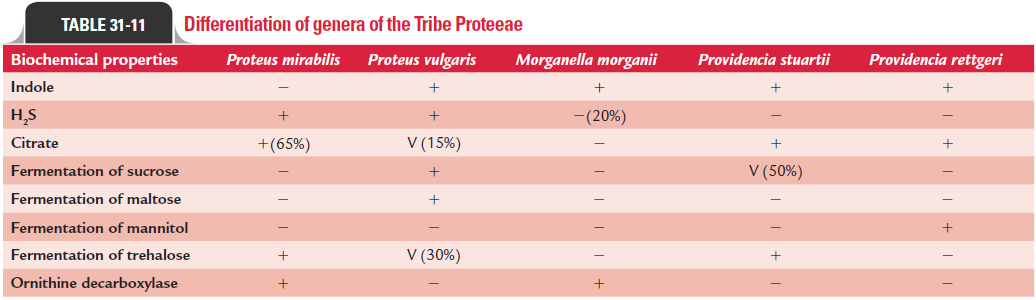
Urine is the specimen of choice for diagnosis of UTIs. Urine is collected in the same way as described earlier for UTI caused by E. coli. Other specimens are collected depending on the natureof infections. These include pus for wound infections, blood for septicemia, CSF for meningitis, etc. Definitive diagnosis is based on the isolation of Proteus spp. from various clinical specimens by culture. Urine culture is carried out in the same way as described earlier for E. coli and other Gram-negative bac-teria. After incubation overnight at 37°C, pale, nonlactose-fer-menting colonies of Proteus on the MacConckey agar and those on blood agar are identified by various biochemical tests and agglutination reactions (Table 31-11). Culture of blood, CSF, and other specimens is also carried out depending on the clini-cal diseases caused by Proteus.
Related Topics