Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Bacteriology: Nonsporing Anaerobes
Cell Wall Components and Antigenic Structure - Escherichia coli
Cell Wall Components and Antigenic Structure
◗ Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
The heat-stable lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is the major cell wall antigen of E. coli. The LPS consists of three components: (a) the genus-specific somatic O polysaccharide, (b) a core polysaccha-ride common to all Enterobacteriaceae (common antigen), and (c) lipid A.
E. coli organisms possess four major antigens (Fig. 31-3): Hor flagellar antigen, O or somatic antigen, K or capsular anti-gen, and F or fimbrial antigens.
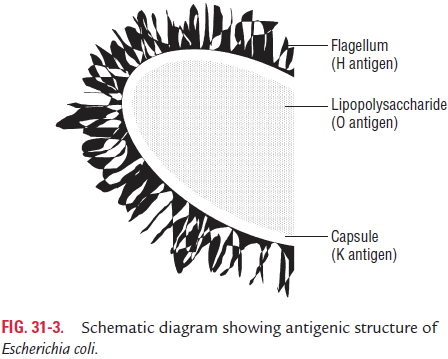
H or flagellar antigen: The H antigens are heat- andalcohol-labile proteins present on the flagella. The H antigens are genus specific and usually are not shared by other entero-bacteria. All of the H antigens are present as monophasic, but very rarely as diphasic. A total of 75 “H” antigens have been recognized so far.
O or somatic antigen: O antigens occur on the surface ofthe outer membranes and are determined by specific sugar sequences on the cell surface. O antigen is an LPS complex and is an integral part of the cell wall. It is heat stable, resistant to boiling up to 2 hours and 30 minutes. Till now, 173 (1, 2, 3, etc. up to 173) O antigens have been described.
· Somatic O polysaccharide antigen shows cross-reactions with related genera (Shigella, Salmonella, Yersinia, and Citro-bacter) in the family Enterobacteriaceae.
· The O antigen also shows cross-reaction with individual E. coli O antigens. The O antigens are detected by agglutina-tion with specific antibodies.

K or capsular antigen: The heat-labile K antigen is the acidicpolysaccharide antigen present in the “envelope” or microcap-sule (K for Kapsel, German for capsule) of the bacteria.
· K antigen encloses the O antigen and may interfere with detection of the O antigens. This problem is overcome by boiling of the bacterial suspension to remove the K antigens
· K antigens may also contribute to virulence by inhibiting phagocytosis. The K antigens are poor activators of com-plement. A total of 103 “K” antigens have been recognized.
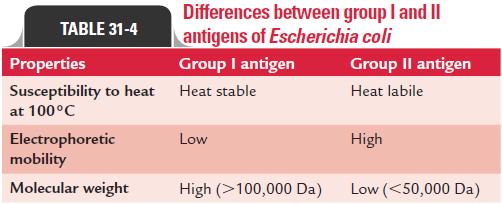
· The K antigens are of two types: I and II. E. coli K I antigen shows cross-reaction with Neisseria meningitidis and Haemoph-ilus influenzae capsular antigens. Differences between the twogroups are summarized in Table 31-4.
F or Fimbrial antigens: These antigens are present on thefimbriae and are heat-labile proteins. A number of filamentous protein structures resembling fimbriae have been described in E. coli. These are K88, K99 antigens in E. coli strains causing diar-rhea in animals or colonization factor antigens (CFA) in entero-toxigenic E. coli (ETEC) causing diarrhea in humans. These fimbrial antigens also contribute to virulence of the bacteria.
◗ Antigenic typing
The serotyping of E. coli is based on three major groups of antigens: O antigens, K antigens, and H antigens. E. coli strains on the basis of O antigens are initially divided into a number of O groups. Each O group is then further divided into subgroups on the basis of K antigens. Finally, each of the subgroup includes strains with different H antigens. The antigenic pat-tern of a strain is recorded depending on the number of the particular antigen it carries (e.g., E. coli O111:K58:H2).
Different serotypes of E. coli are found in the normal intes-tine of humans and they do not have K antigens.
· The normal colon strains belong to the “early” O groups (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.).
· Enteropathogenic strains responsible for intestinal diseases belong to the “later” O groups (55, 86, 111, 112, etc.).
Related Topics