OstwaldŌĆÖs dilution law | Ionic Equilibrium | Chemistry - Ionisation of weak acids | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 8 : Ionic Equilibrium
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 8 : Ionic Equilibrium
Ionisation of weak acids
Ionisation of weak acids
We have already learnt that weak acids are partially dissociated in
water and there is an equilibrium between the undissociated acid and its
dissociated ions.
Consider the ionisation of a weak monobasic acid HA in water.
HA + H2O Ōåö H3O+
+ A-
Applying law of chemical equilibrium, the equilibrium constant Kc is
given by the expression

The square brackets, as usual, represent the concentrations of the
respective species in moles per litre.
In dilute solutions, water is present in large excess and hence, its
concentration may be taken as constant say K. Further H3O+
indicates that hydrogen ion is hydrated, for simplicity it may be replaced by H+
. The above equation may then be written as,

The product of the two constants KC and K gives another
constant. Let it be Ka

The constant Ka is called dissociation constant of the acid.
Like other equilibrium constants, Ka also varies only with
temperature.
Similarly, for a weak base, the dissociation constant can be written as
below.

OstwaldŌĆÖs dilution law
OstwaldŌĆÖs dilution law relates the dissociation constant of the weak
acid (Ka ) with its degree of dissociation (╬▒) and the
concentration (c). Degree of dissociation (╬▒) is the fraction of the total number of moles of a
substance that dissociates at equilibrium.
╬▒= Number
of moles dissociated / total number of moles

We shall derive an expression for ostwald's law by considering a weak
acid, i.e. acetic acid (CH3COOH). The dissociation of acetic acid
can be represented as
CH3COOH Ōåö H+ + CH3COO-
The dissociation constant of acetic acid is,
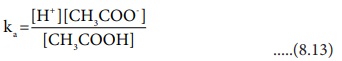
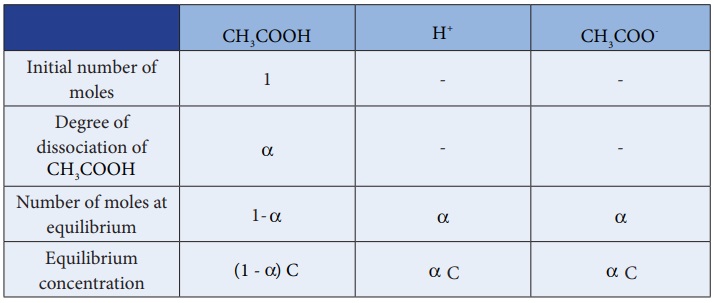
Substituting the equilibrium concentration in equation (8.13)

We know that weak acid dissociates only to a very small extent. Compared
to one, ╬▒ is so
small and hence in the denominator (1 - ╬▒) 1. The above expression (8.14) now becomes,
Ka =╬▒2C

Let us consider an acid with Ka value 4 ├Ś 10-4
and calculate the degree of dissociation of that acid at two different
concentration 1 ├Ś 10-2M
and 1 ├Ś 10-4M
using the above expression (8.15)
For 1 ├Ś 10-2M ,
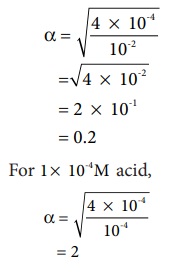
i.e, When the dilution increases by 100 times, (Concentration decreases
from 1 ├Ś 10-2M
to 1 ├Ś 10-4M
), the dissociation increases by 10 times.
Thus, we can conclude that, when dilution increases, the degree of
dissociation of weak electrolyte also increases. This statement is known as
OstwaldŌĆÖs dilution Law.
The concentration of H + (H 3O+ ) can be
calculated using the Ka value as below.
[ H+]= ╬▒C (Refer table) .....(8.16)
Equilibrium molar concentration of [H+ ] is equal to ╬▒C
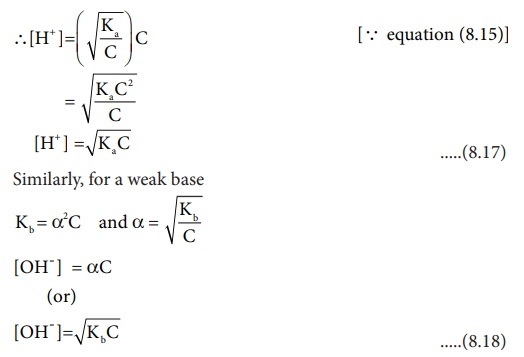
Example 8.4
A solution of 0.10M of a weak electrolyte is found to be dissociated to
the extent of 1.20% at 25oC . Find the dissociation constant of the acid.
Given that ╬▒=1.20%=1.20/100
= 1.2 ├Ś 10-2
Ka = ╬▒2c
= (1.2 ├Ś 10-2
)2 (0.1) = 1.44 ├Ś10-4
├Ś10-1
= 1.44 ├Ś 10-5
Example 8.5
Calculate the pH of 0.1M CH3COOH solution. Dissociation
constant of acetic acid is 1.8 ├Ś10-5
.
pH=-log[H+ ]
For weak acids,
[H+ ]= ŌłÜ [Ka
├Ś C]
= ŌłÜ (1.8 ├Ś10-5 ├Ś 0.1)
=1.34 ├Ś10-3M
pH=-log (1.34 ├Ś10-3)
= 3 - log1.34
= 3 - 0.1271
= 2.8729 Ōēł2.87
Evaluate yourself ŌĆō 7
Kb for NH 4 OH is 1.8 ├Ś 10-5 . Calculate the percentage of ionisation of
0.06M ammonium hydroxide solution.
Answer:
╬▒ = ŌłÜ(Kb / C) = 1.8 ├Ś10-5 / 6 ├Ś 10-2
= ŌłÜ 3├Ś10-4
= 1.732 ├Ś 10-2
= 1.732 / 100 = 1.732%
Related Topics