Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : General Anesthetics
Inhaled Anesthetics
INHALED
ANESTHETICS
A
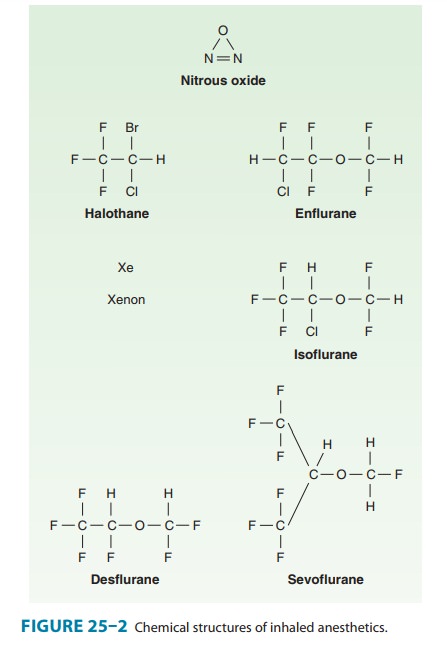
clear distinction should be made between volatile and gaseous anesthetics, both
of which are administered by inhalation. Volatile anesthetics (halothane,
enflurane, isoflurane, desflurane, sevoflu-rane) have low vapor pressures and
thus high boiling points so that they are liquids at room temperature (20oC)
and sea-level ambient pressure, whereas gaseous anesthetics (nitrous oxide,
xenon) have high vapor pressures and low boiling points such that they are in
gas form at room temperature. Figure 25–2 shows the chemical structures of
important, clinically used, inhaled anesthetics.
Related Topics