Chapter: Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Fundamentals and Applications : Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Peptide and Protein Drugs
Indirect Response PK/PD Models - Pharmacodynamics of Protein Therapeutics
Indirect Response PK/PD Models
The effect of most protein therapeutics, however, is not mediated via a
direct interaction between drug concentration at the effect site and response
systems, but frequently involves several transduction processes that include at
their rate-limiting step the stimulation or inhibition of a physiologic
process, for example the synthesis or degradation of a molecular response
mediator like a hormone or cytokine. In these cases, the time courses of plasma
concentration and effect are also dissociated resulting in counterclockwise
hysteresis for the concentration–effect relationship, but the underlying cause
is not a distributional delay as for the indirect link models, but a
time-consuming indirect response mechanism (Meibohm and Derendorf, 1997).
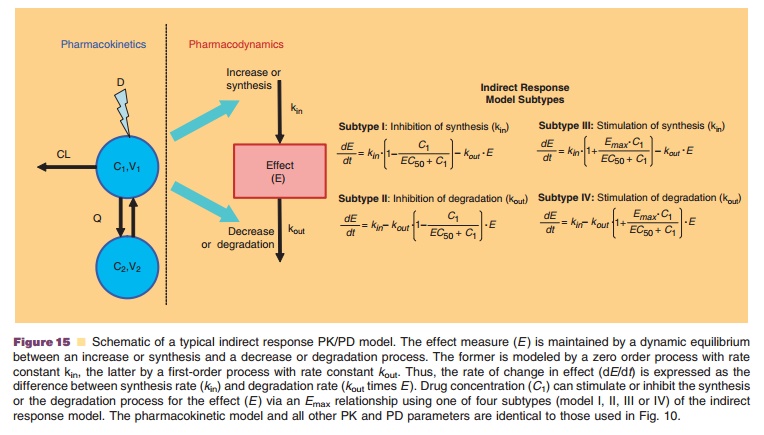
Indirect response models generally describe the effect on a
representative response parameter via the dynamic equilibrium between increase
or synthesis and decrease or degradation of the response, with the former being
a zero-order and the latter a first-order process (Fig. 15). The response
itself can be modulated in one of four basic variants of the models. In each
variant, the synthesis or degradation process of the response is either
stimulated or inhibited as a function of the effect site concentration. A
stimulatory or inhibitory Emax model is used to describe the drug effect on the synthesis or
degradation of the response (Dayneka et al., 1993; Sharma and Jusko, 1998; Sun
and Jusko, 1999).
As indirect response models appreciate the underlying physiological
events involved in the elaboration of the observed drug effect, their applica-tion
is often preferred in PK/PD modeling as they have a mechanistic basis on the
molecular and/or cellular level that often allows for extrapolating the model
to other clinical situations.
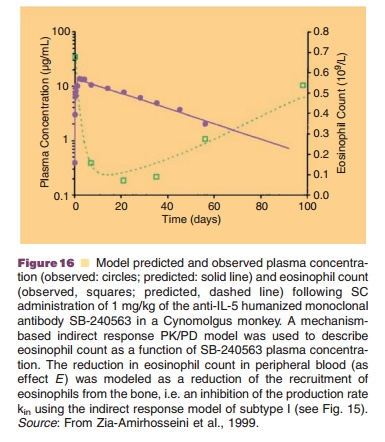
An indirect response model was for example used in the evaluation of SB-240563, a humanized monoclonal antibody directed towards IL-5 in mon-keys (Zia-Amirhosseini et al., 1999). IL-5 appears to play a significant role in the production, activation, and maturation of eosinophils. The delayed effect of SB-240563 on eosinophils is consistent with its mechanism of action via binding to and thus inactivation of IL-5. It was modeled using an indirect response model with inhibition of the production of response (eosinophils count) (Fig. 16). The obtained low EC50 value for reduction of circulating eosino-phils combined with a long terminal half-life of the protein therapeutic of 13 days suggests the possibility of an infrequent dosing regimen for SB-240563 in the pharmacotherapy of disorders with increased eosinophil function, such as asthma.
Indirect response models were also used for the effect of growth hormone
on endogenous IGF-1 concentration (Sun et al., 1999), as well as the effect of
epoetin-a on two response parameters, free ferritin concentration and soluble
transferrin receptor concentration (Bressolle et al., 1997). Similarly, a
modified indirect response model was used to relate the concentration of the
humanized anti-factor IX antibody SB-249417 to factor IX activity in Cynomolgus
monkeys as well as humans (Benincosa et al., 2000; Chow et al., 2002). The drug
effect in this model was introduced by interrupting the natural degradation of
Factor IX by sequestration of Factor IX by the antibody.
Related Topics