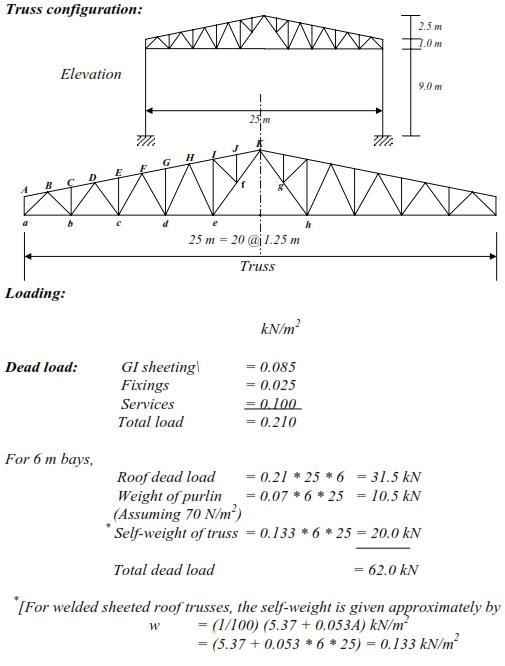
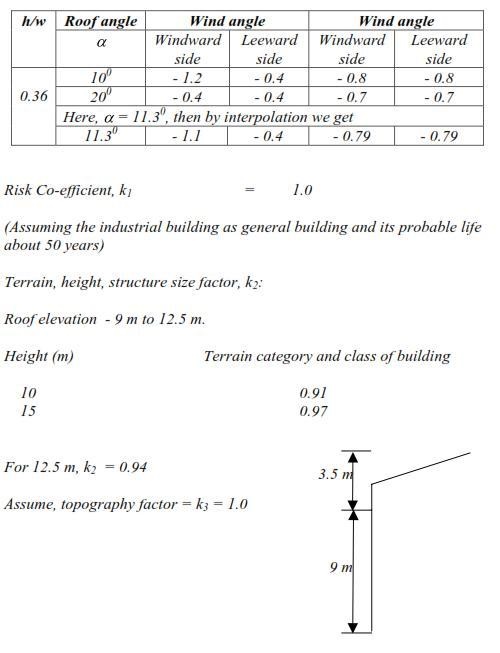
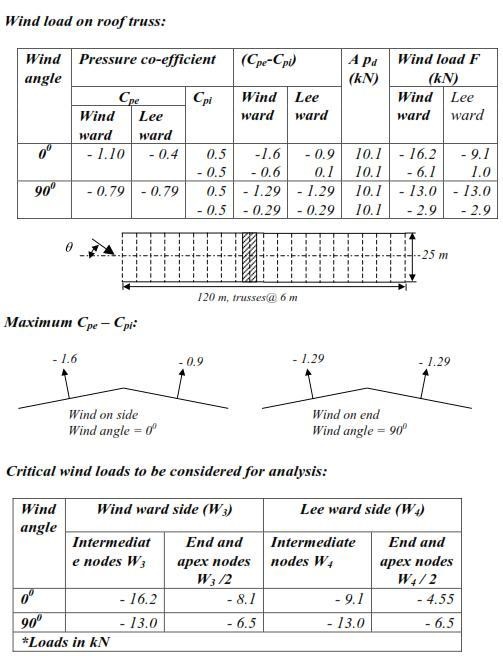
Chapter: Civil : Design Of Steel Structures
Important Question And Problems With Answer: Roof Trusses And Industrial Buildings
Important
Question And Problems With Answer: Roof
Trusses And Industrial Buildings
1. Name the types of roofing systems.
Flat roofing consists of either RCC
construction or RSJ slab construction Sloping roofing
2. Where the steel roof trusses are used?
Industrial buildings, workshop
buildings, storage godowns, warehouse and even for residential buildings,
school buildings, offices
where the construction work is to
be completed in a short duration of time.
3. Mention the advantages of a roof truss.
Its mid-span depth is the greatest
specially where bending moment in the span is the maximum Great economy.
Sloping faces of trusses facilitate in
easy drainage of rainwater.
4. What is the factor that is considered in
the roof truss and why?
The factor, which is considered in the
roof truss, is pitch, it is defined as the ratio of the span length to
the depth of the truss,
is governed by the roofing material and other requirements such as ventilation
and light.
5. How the trusses are classified according
to the pitch?
Small pitch - span depth ratio is more than 12 m
Medium pitch - span depth ratio is between 5m to 12 m
Large pitch - span depth ratio is 5 or less.
8. What is gantry girder and what are the
forces that are acting on it?
A gantry girder, having no lateral
support in its length, has to withstand vertical loads from the weight of the
crane, hook load and impact and horizontal loads from crane surge.
9. What is meant by purlins?
Purlins are structural members which
are supported on the principal rafter, and which run transverse to the trusses.
The span of the purlins is equal to the center-to- center spacing of the trusses.
The purlins support
the roof covering either
directly or through common rafters. They are usually
made of either
an angle section
or a channel section
and are therefore subjected to
unsymmetrical bending.
10. Why the bracings are provided?
Bracing is
required to resist
horizontal loading in
pin-jointed buildings, including
roof trusses. Bracing of roof trusses and supporting columns
provide still rigid structure.
When wind blows normal to the inclined surface of the trusses, it is efficiently resisted
by all the
members of the
truss and the
wind forces are transferred to the supports at the ends
of the truss.
11.
Name the most common roof covering materials.
Slates Glass
Tiles Corrugated aluminium sheets
Lead Galvanized corrugated iron sheets (G.I.
sheets)
sheets Asbestos cement sheets (A.C. sheets)
Zinc
sheets
13.
Mention some of the requirements of a good joint.
The
line of thrust should pass through the C.G of the rivet group and the riv ets
should be symmetrically arranged about this line.
For
a tensio n member, the rivets should be so arranged that the area of the member
joined is not reduced more than necessary.
The
numbe r and the diameter of rivets should be suffici ent to develop the maximum
stresses induced in all the members at the connection. Members s hould be
straight and bolts used to draw th em together before the rivets are driven.
14. What are the cond itions that to be
satisfied for the end supports?
The
size of base plate should be
sufficient so that the bearing
pressure
does not exceed the permissible value.
Anchor
bol ts should be provided at one end to accomm odate the thermal expansion of
the truss.
The
lines of forces in rafter, bottom tie and vertical end reaction meet at a
point.
15.
Where the gantry girders are used?
Gantry girders
or crane girders
carry hand operated
or electric over head
cranes in ind ustrial buildings
such as factories,
worksh ops, steel works etc.,
to lift heavy
materials, equipment etc., to carry them fro m one location to the other,
within the building.
17.
What is drag force?
This is
caused due to
the starting and
stopping of the
crane bridge moving over
the crane rails
as the crane
m0oves longitudinally, i.e.
in the direction of gantry
girders.
18.
What is the permissible deflection where the electrically overhead cranes
operated over 500kN?
The maximum
vertical deflection for
crane girder, under
dead and imposed loads shall not exceed L/1000, where L is the
span of the crane runway girder.
19.
Define shoe angle.
It
is a supporting angle provided at the junction of the top and bottom chords of a
truss. The reaction
of the truss
is transferred to
the supports through the shoe
angle. It is supported on the base plate.
20.
What is panel point?These are the prominent points along the principal rafter,
at which various members (i.e. ties and struts) meet. The distance of the
principal rafter between any two panel point is termed as panel.
This is
caused due to
the starting and
stopping of the
crane bridge moving
over the crane rails as the crane
m0oves longitudinally, i.e. in the direction of gantry girders.
18.
What is the permissible deflection where the electrically overhead
cranes operated over 500kN?
The
maximum vertical deflection for crane girder, under dead
and imposed



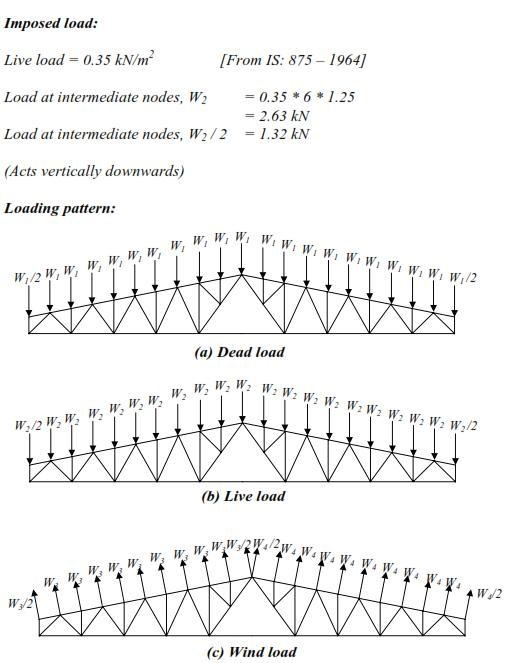
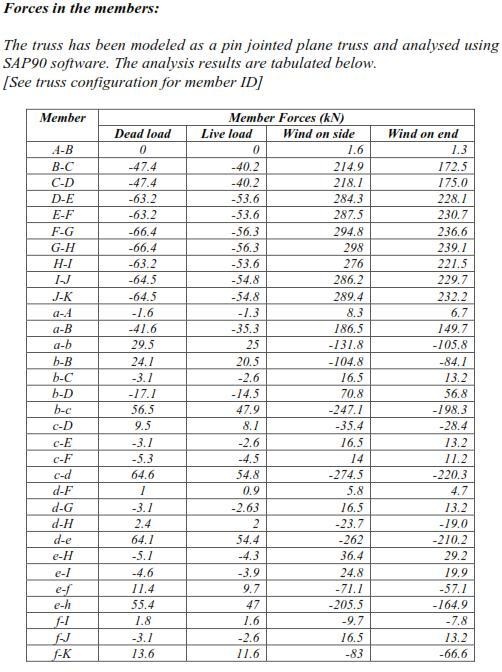
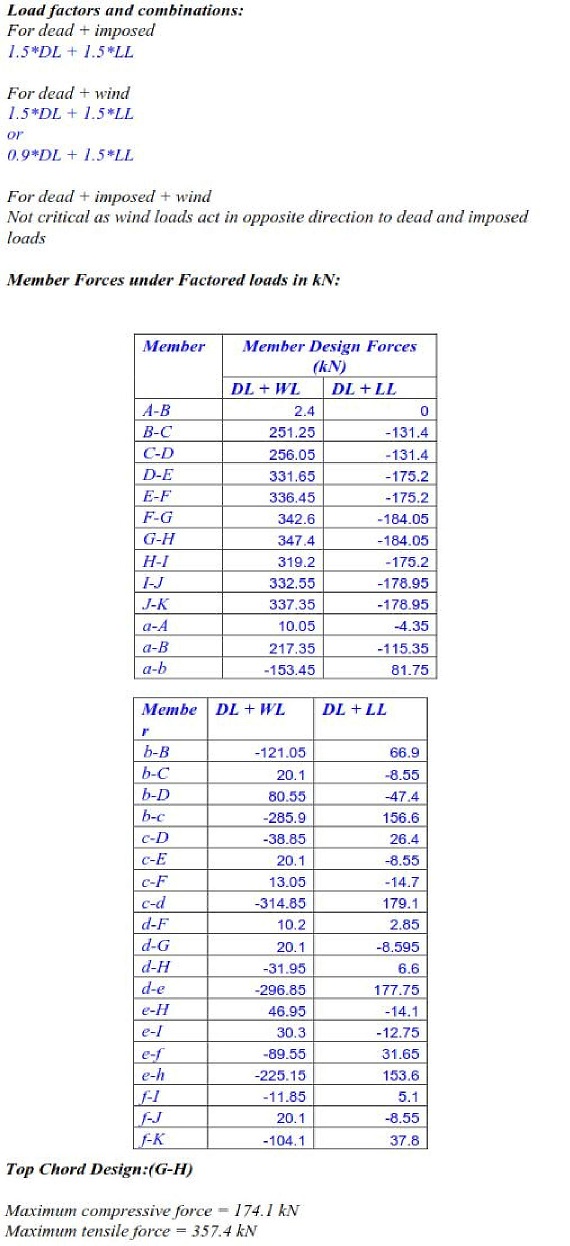

Related Topics