Chapter: civil : Design Of Steel Structures
Classification Of Bolts
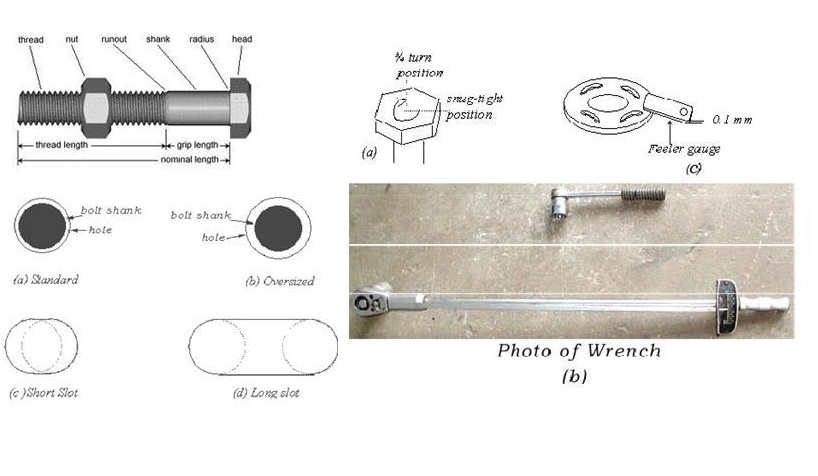
BOLTED CONNECTIONS
Bolt is a
metal pin with a head at one end and a shank threaded at other end to receive a
nut, as shown in Figure 6. Steel washers are usually provided under the bolt
head and nuts to prevent the treaded portion of the bolt from bearing on the
connecting pieces and to distribute the clamping pressure on the bolted member.
A bolt connection can be used for
end connections in tension and compression members. They can also hold down
column bases in position and as separator for purlins and beams in foundations.
Bolts are having the following advantages over rivets and pins: (a) the
erection of the structures can be speeded up. (b) Less skilled labour can be
employed. (c) Overall cost of bolted connection is lesser than the other
alternatives. However the following shortcomings are also associated with the
bolted connections: (a) Cost of material is high, about double than that of
rivets. (b) The tensile strength of bolt is reduced due to the reduced area at
the root of the thread and stress concentration. (c) Normally strength
reduction will be there for loose fit bolts. (d) Bolts may get loose when
subjected to vibrations.
CLASSIFICATION OF BOLTS
Bolts used in steel structures
are of three types:
1) Black Bolts
2) Turned and Fitted Bolts and
3) High Strength Friction Grip
(HSFG) Bolts.
The International Standards
Organisation designation for bolts, also followed in India, is given by Grade
x.y. In this nomenclature, x indicates one-tenth of the minimum ultimate
tensile strength of the bolt in kgf/mm2 and the second number, y,
indicates one-tenth of the ratio of the yield stress to ultimate stress,
expressed as a percentage. Thus, for example, grade 4.6 bolt will have a
minimum ultimate strength 40 kgf/mm2 (392 MPa) and minimum yield
strength of 0.6 times 40, which is 24 kgf/mm2 (235 MPa).
5.1.1. Black bolts
Black bolts are unfinished and
are made of mild steel and are usually of Grade 4.6. Black bolts have adequate
strength and ductility when used properly; but while tightening the nut snug
tight ('Snug tight'
is defined as the tightness that exists when all plies in a joint are
in firm contact) will twist off
easily if tightened too much.
5.1.2. Turned and fitted bolts
Turned and fitted bolts have uniform shanks and are inserted
in close tolerance drilled holes and made snug tight by box spanners. The
diameter of the hole is about 1.5 to 2.0 mm larger than the bolt diameter for
ease in fitting. High strength black bolts (grade 8.8) may also be used in
connections in which the bolts are tightened snug fit. In these bearing type of
connections, the plates are in firm contact but may slip under loading until
the hole surface bears against the bolt .The load transmitted from plate to
bolt is therefore by bearing and the bolt is in shear. Under dynamic loads, the
nuts are liable to become loose and so these bolts are not allowed for use
under such loading. In situations where small slips can cause significant
effects as in beam splices, black bolts are not preferred. However, due to the
lower cost of the bolt and its installation, black bolts are quite popular in
simple structures subjected to static loading. Turned and fitted bolts are
available from grade 4.6 to grade 8.8. For the higher grades there is no
definite yield point and so 0.2% proof stress is used.
5.1.3. High Strength Friction Grip bolts (HSFG)
High Strength Friction Grip bolts
(HSFG) provide extremely efficient connections and perform well under
fluctuating/fatigue load conditions. These bolts should be tightened to their
proof loads and require hardened washers to distribute the load under the bolt
heads. The washers are usually tapered when used on rolled steel sections. The
tension in the bolt ensures that no slip takes place under working conditions
and so the load transmission from plate to the bolt is through friction and not
by bearing. However, under ultimate load, the friction may be overcome leading
to a slip and so bearing will govern the design. HSFG bolts are made from
quenched and tempered alloy steels with grades from 8.8 to 10.9. The most
common are the so-called, general grade of 8.8 and have medium carbon content,
which makes them less ductile. The 10.9 grade have a much higher tensile
strength, but lower ductility and the margin between the 0.2% yield strength
and the ultimate strength is also lower. The tightening of HSFG bolts can be
done by either of the following methods (IS 4000):
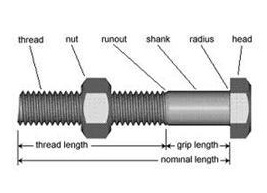
• Turn-of-nut
tightening method: In this method the bolts are first made snug tight and then
turned
by specific amounts (usually either half or three-fourth turns) to induce
tension equal to the proof load (Figure 7(a)).
•
Calibrated wrench tightening method: In
this method the bolts are tightened by a wrench
(Figure 7(b)) calibrated to produce the required tension.
• Alternate
design bolt installation: In this method special bolts are used which indicate
the bolt
tension. Presently such bolts are not available in India.
• Direct tension indicator
method: In this method special washers with protrusions are used
(Figure
7(c)). As the bolt is tightened, these protrusions are compressed and the gap
produced by them gets reduced in proportion to the load. This gap is measured
by means of a feeler gauge, consisting of small bits of steel plates of varying
thickness, which can be inserted into the gap.
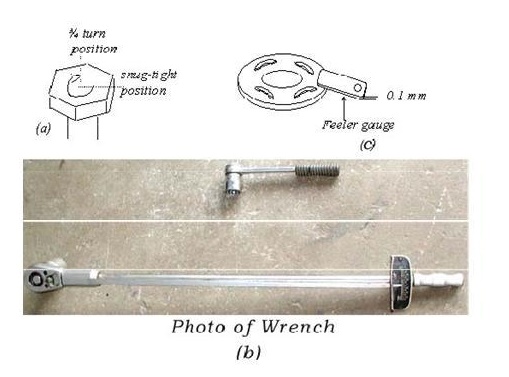
Since
HSFG bolts under working loads, do not rely on resistance from bearing, holes
larger than usual can be provided to ease erection and take care of
lack-of-fit. Typical hole types that can be used are standard, extra large and
short or long slotted. These are shown in Figure 8. However the type of hole
will govern the strength of the connection. Holes must also satisfy pitch and
edge/end distance criteria (Cl.10.2 of IS 800:2007). A minimum pitch is usually
specified for accommodating the spanner and to limit adverse interaction
between the bearing stresses on neighbouring bolts. A maximum pitch criterion
takes care of buckling of the plies under compressive loads.
Related Topics