Chapter: Microprocessor and Microcontroller
INTEL 8259A Programmable Interrupt Controller
INTEL 8259A Programmable Interrupt Controller
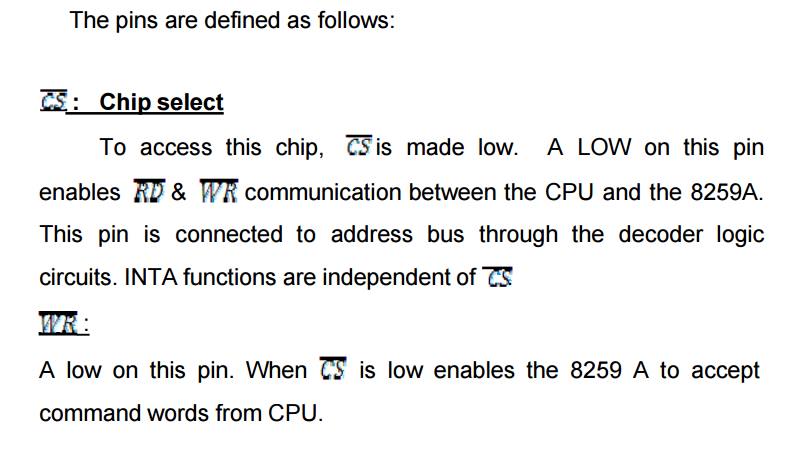
The 8259A is a programmable interrupt controller
designed to work with Intel microprocessor 8080 A, 8085, 8086, 8088. The 8259 A
interrupt controller can
1) Handle eight interrupt inputs. This is
equivalent to providing eight interrupt pins on the processor in place of one
INTR/INT pin.
2) Vector an interrupt request anywhere in the
memory map. However, all the eight interrupt are spaced at the interval of
either four or eight location. This eliminates the major
drawback, 8085 interrupt, in which all
interrupts are vectored to memory location on page 00H.
3) Resolve eight levels of interrupt priorities in
a variety of modes.
4) Mask each interrupt request individually.
5) Read the status of pending interrupts, in
service interrupts, and masked interrupts.
6) Be set up to accept either the level triggered
or edge triggered interrupt request.
7) Mine 8259 as can be cascade in a master slave
configuration to handle 64 interrupt inputs.
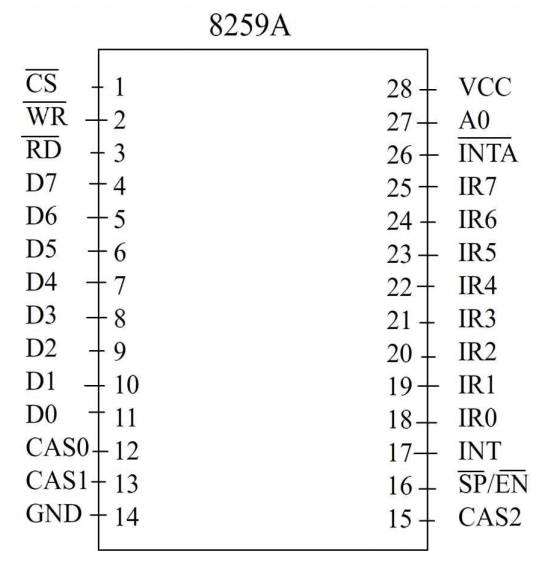
The 8259 A is contained in a 28-element in line
package that requires only a compatible with 8259. The main difference between
the two is that the 8259 A can be used with Intel 8086/8088 processor. It also
induces additional features such as level triggered mode, buffered mode and
automatic end of interrupt mode. The pin diagram and interval block diagram is
shown below:
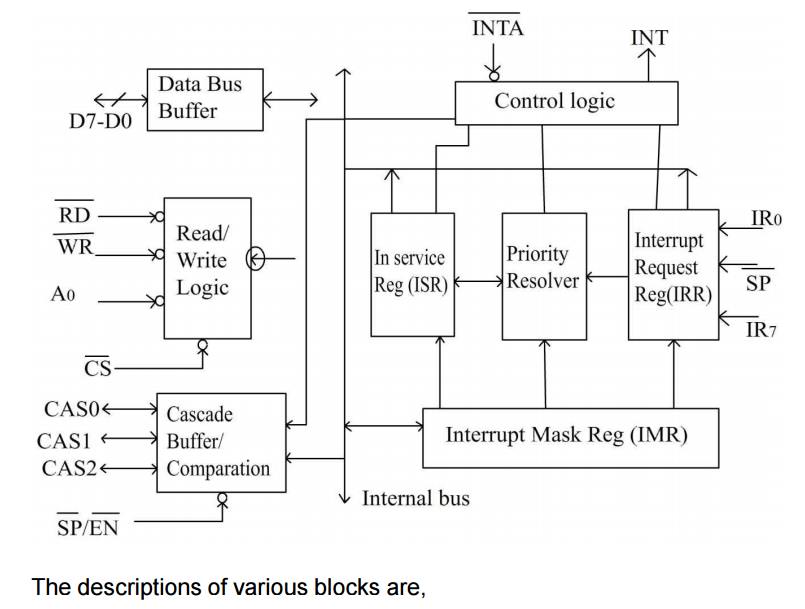
Data bus buffer:
This 3- state, bidirectional 8-bit buffer is
used to interface the 8259A to the system data bus. Control words and status
information are transferred through the data bus buffer.
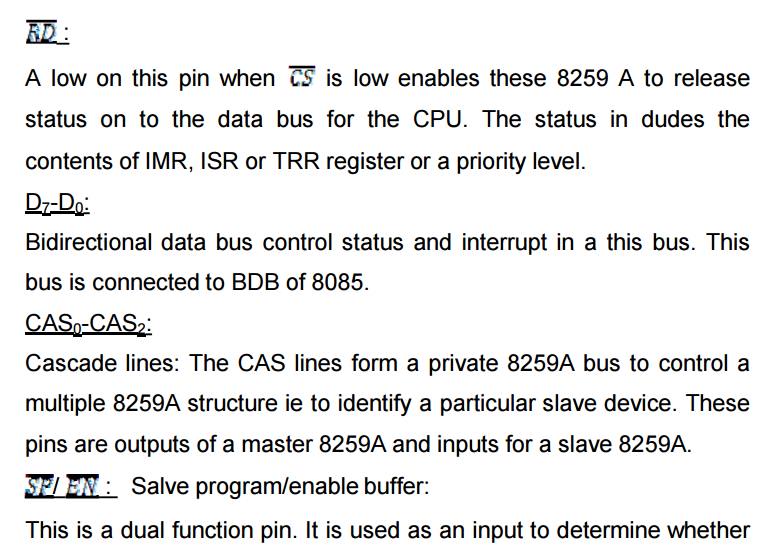
Read/Write & control logic:
The function of this block is to accept OUTPUT
commands from the CPU. It contains the initialization command word (ICW)
register and operation command word (OCW) register which store the various
control formats for device operation. This function block also allows the
status of 8159A to be transferred to the data bus.
Interrupt request register (IRR):
IRR stores all the interrupt inputs that are
requesting service. Basically, it keeps track of which interrupt inputs are
asking for service. If an interrupt input is unmasked, and has an interrupt
signal on it, then the corresponding bit in the IRR will be set.
Interrupt mask register (IMR):
The IMR is used to disable (Mask) or enable
(Unmask) individual interrupt inputs. Each bit in this register corresponds to
the interrupt input with the same number. The IMR operation on the IRR. Masking
of higher priority input will not affect the interrupt request lines of lower priority.
To unmask any interrupt the corresponding bit is set ‘0’.
In service register (ISR):
The in service registers keeps tracks of which
interrupt inputs are currently being serviced. For each input that is currently
being serviced the corresponding bit will be set in the in service register.
Each of these 3-reg can be read as status reg.
Priority Resolver:
This logic block determines the priorities of
the set in the IRR. The highest priority is selected and strobed into the
corresponding bit of the ISR during  ^(INT A) pulse.
^(INT A) pulse.
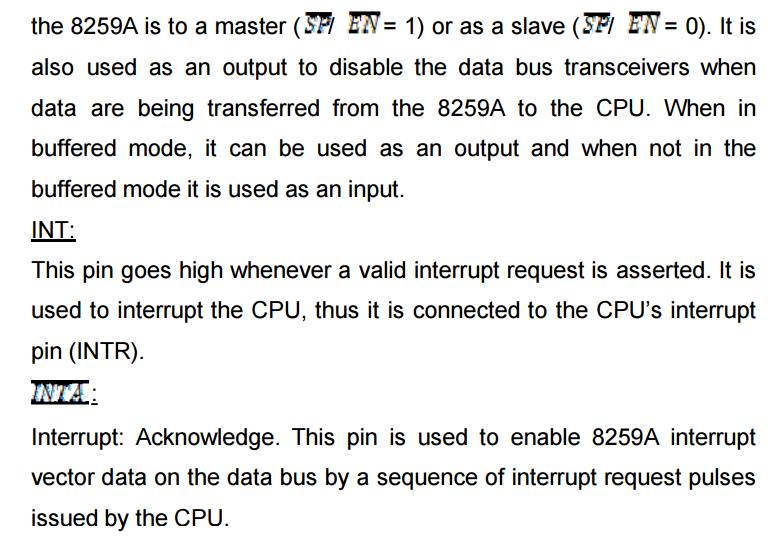
Cascade buffer/comparator:
This function blocks stores and compare the IDS
of all 8259A’s in the reg. The associated 3-I/O pins (CAS0-CAS2) are outputs
when 8259A is used a master. Master and are inputs when 8259A is used as a
slave. As a master, the 8259A sends the ID of the interrupting slave device
onto the cas2-cas0. The slave thus selected will send its pre-programmed
subroutine address on to the data bus during the next one or two successive
^(INT A)  pulses.
pulses.
Related Topics