Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Gastro-Intestinal
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C
·
An enveloped ssRNA virus (used to
be called non A non B). 6 geneotypes
identified.
·
Damage is caused by immune
response – not virus
Presentation
·
Incubation to onset of symptoms
average 7 weeks (range 3 – 20)
·
HCV RNA detectable within 1 – 3
weeks of exposure. Rises rapidly to 10E6
– 10E8 per ml
·
Only 1/3 have symptoms. . Clinical illness (if any) lasts 2- 12 weeks
·
ALT elevation to 300 – 800
·
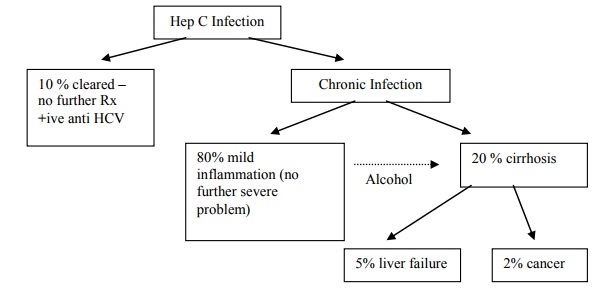
50% go on to chronic infection
(ie higher than Hep B)
· May present with end stage liver disease (e.g. may present for first time with variceal bleeding)
·
Hepatocellular carcinoma found in
1/3, test with ultrasound. ?Evidence that interferon for 6 months ÂŻrisk of
HCC
Risk Factors
·
NZ prevalence: 0.47%
·
Low infectivity: mainly
transmitted by blood
·
Transfusion
·
IV drugs (40-60% of cases)
·
Sexual contact (very low risk)
·
Maternal transmission to neonate
in 5% of maternal infection (ie low risk)
Viral Serology
·
Acute HCV: Anti-HCV doesn’t appear for 3 months. Can do PCR.
Exclude HAV, HBV, EBV, and
·
CMV
·
Chronic HCV: Anti-HCV antibody
·
Indications for HCV test:
o Chronic hepatitis (raised ALT over 6 months)
o History of Non-A, Non-B hepatitis but at least 3 months after acute
infection
o At risk groups: IV users, haemophiliacs
o Donors: blood and organs
·
Indications for HCV RNA test.
Test if indeterminate Anti-HCV results, diagnosis in neonates and monitoring of
interferon therapy.
·
80% of chronically infected have
persisting viraemia
Tests
·
LFT: bilirubin, Albumin
·
FBC: platelets
·
APTT/INR
·
Anti HCV antibodies
·
PCR for HCV RNA
· Ultrasound for size (& to guide biopsy)
·
?Biopsy ® degree
of fibrosis ® prognosis
·
Exclude: Hep A, Hep B, Iron
studies, ANA
Progression
·
If self-limiting HCV RNA
undetectable and ALT back to normal in 1 – 3 months
·
Wide spectrum: 1/3 persistently
normal ALT. Majority fluctuating ALT (Ăž immune system active and causing
hepatocyte death). ALT height doesn‟t correlate with histological severity.
Acute – ALT 10 times normal
·
Non-hepatic manifestations:
arthritis, dry membranes, lichen planus (white plaques in mouth),
glomerulonephritis, cryoglobulinaeamia, porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT – blisters
on skin)
Prognosis
·
Contributing to progression:
o Alcohol ® Âfibrosis
o HBV
o Age at infection - younger have
longer period of time with infection
o Mode of acquisition: transfusion worse (?greater viral load)
o Genotype of virus: effects interferon treatment. Type 1 ® severe
disease and poor response to interferon
Management
· ¯Alcohol
·
Have liver biopsy before
commencing drug treatment. Also, intravenous drug users should have drug free
urines (otherwise risk of reinfection)
·
Need strong motivation/compliance
·
Interferon - best for:
o High ALT
o Disease < 5 years
o Non-cirrhotic
o Not genotype 1
o Low viral load
o No history of depression (interferon can cause this)
o Causes flu like symptoms: ÂŻappetite, fever, myalgia. Largely resolves after 1-2 weeks. Given it up-regulates the immune system can also cause Âautoimmune diseases (e.g. thyroid)
o On it‟s own only 15% are PCR negative 6 months after completing
treatment
·
Combination interferon/Ribavirin
o Ribavirin is teratogenic: contraception needs to be VERY reliable
o Purine nucleoside analogue
o Stored and transported in red cells.
Dose dependent haemolysis Ăž monitor HB and reticulocytes
o Only useful in addition to interferon
o After 3 months, 35% non-responders. 65% complete responders. For
geneotypes 2 & 3 most of these go on to be sustained responders
·
Transplantation:
o Hep C most common indication
o Recurrent (usually mild) infection of graft
o Survival: 65% at 5 years
Related Topics