Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Gastro-Intestinal
CrohnŌĆÖs Disease
CrohnŌĆÖs Disease
┬Ę
= Chronic granulomatous
inflammation of the gut
Epidemiology
┬Ę
Incidence increasing. Peaks in 2nd to 3rd decade
┬Ę
1 per 1000 in UK
┬Ę
F > M, W > B
Symptoms & Signs:
┬Ę
Malaise, weight loss (65 ŌĆō 75%),
failure to thrive, malabsorption
┬Ę
Diarrhoea (70 ŌĆō 90%)
┬Ę
Rectal bleeding (45%)
┬Ę
Pain (50%, from inflammation,
infection, obstruction, colicky from intermittent obstruction of terminal
ileum)
┬Ę
Perianal disease (50 ŌĆō 80%)
┬Ę
Mild fever (30 ŌĆō 40%)
┬Ę
Anaemia, glossitis (due to
malabsorption)
┬Ę
Aphthous ulcers in mouth
┬Ę
Erythema nodosum (painful red
nodular lesions on shins), pyoderma gangrenosum (recurring skin ulcers ŌĆō 10 cm),
clubbing
┬Ę
Asymptomatic periods for
weeks-months
┬Ę
Attacks may be precipitated by
emotional/physical stress
┬Ę
Risk factors: genetic, smoking,
high sugar/low fibre
Aetiology
┬Ę
Type 4 immune reaction: trigger
unknown. Cause: ?immune hyper-reactivity
┬Ę
Proposed agents: viruses,
disordered immunologic response to ingested antigen
┬Ę Genetic susceptibility. 10-fold risk in first-degree relatives
┬Ę
├× Multifactorial ┬« abnormal regulation of inflammatory mediators
Investigations
┬Ę
Bloods: check for anaemia
(including anaemia of chronic disease), malabsorption, inflammatory
measurements, ┬ŁESR and acute phase proteins
┬Ę
Deficiencies: folate, iron, B12,
etc, electrolyte abnormalities
┬Ę
Culture to exclude infective
causes
┬Ę
Sigmoidoscopy/colonoscopy +
biopsy
┬Ę
Upper GI endoscopy
┬Ę
Barium contrast of small &
large bowel: strictures, fistula, cobblestone appearance, skip lesions etc
Differential
┬Ę
Ileal disease: Tb, Lymphoma
┬Ę
Colonic disease: colitis
(ulcerative, ischaemic, radiation, collagenous), infection (salmonella,
shigella, campylobacter), cancer
┬Ę
Malabsorption: lactose
intolerance, coeliac disease
Pathology
┬Ę
Location:
o 75% terminal ileum
o 50% also involves colon
o 25% colon only (predominantly right side)
o <5% oesophagus, mouth
┬Ę
Macroscopic appearance:
o Skip lesions
o Transmural inflammation
o Thickened, inflexible (resembles rubber hose) with narrow lumen
o Thickened, fibrosed mesentery and enlarged regional lymph nodes
o Strictures, fistulas, abscesses
o Mucosa: varying degrees of erythema and oedema. Cobblestone mucosa
┬Ę
Microscopic appearance:
o Submucosal and subserosal inflammation with only secondary mucosal
involvement (ie glands may be straight, unaffected)
o Aphthoid ulceration of the mucosa
o Lymphocytic infiltrate, fibrosis
o Multifocal granulomatous vasculitis
o Non-caseating granulomata (only 60%): can have some Langhans/giant cells
(horseshoe pattern of nuclei around periphery of a giant cell), but usually
granulomas poorly circumscribed
Treatment
┬Ę Aim: suppress activity, restore quality of live, prevent complications
┬Ę Diet: nutritional supplements. Malnutrition a real risk, ┬« growth retardation in kids. May need enteral or TPN feeding for ŌĆ×Bowel RestŌƤ ┬« ┬»antigen load (controversial)
┬Ę
Corticosteriods e.g. prednisone:
symptomatic relief
┬Ę 5-aminosalicylic acids e.g. mezalazine
┬Ę
Antibiotics (mainly colonic and
perianal disease, ¯antigen load): metronidazole
┬Ę Steroid sparing immunosuppressives: azathioprine
┬Ę Cholestyramine: absorbs bile (normally absorbed in the terminal ileum) to stop it getting into the large bowel, where it causes irritation
┬Ę
Surgery
┬Ę
Monitor: inflammatory markers
Complications
┬Ę
Episcleritis (reddened sclera)
┬Ę
Stricture, obstruction, fistulas
(to bowel, bladder, vagina)
┬Ę
Malnutrition
┬Ę
Large & small bowel cancer
(5% at 10 years ŌĆō ie small risk ŌĆō not screened for)
┬Ę
Ankylosing Spondylitis
┬Ę
Pyoderma gangrenosum
┬Ę
Iritis
┬Ę
Arthritis
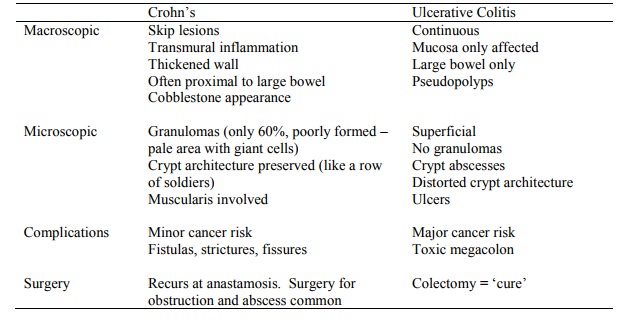
Comparison with Ulcerative Colitis
Related Topics