Chapter: Mechanical : Engineering Thermodynamics : Basic Concepts And Definitions
Heat
Heat
Heat is the interaction
between systems which occurs by virtue of their temperature difference when
they communicate.
If a system, at a given
temperature is brought in contact with another system (or surroundings) at a
lower temperature, it can be observed that heat is transferred from the system
at the higher temperature to the system at lower temperature. This heat
transfer occurs solely because of the temperature difference between the two
systems. Another important aspect of the definition of heat is that a body
never contains heat. Rather, heat can be identified only as it crosses the
boundary. Similar to work, heat is also a form of energy transfer occurring at
the boundary of the system and is a path function.
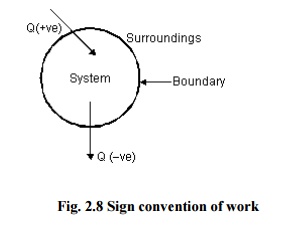
Sign Convention of Heat
· Heat given into a system is positive
· Heat coming out of the system is
negative
Modes of
Heat Exchange
Conduction, convection
and radiation are the three possible modes of heat transfer between systems and
between system and its surroundings.
Conduction occurs
without bulk movement of molecules. Energy transfer in conduction is due to
lattice vibration and free electron movement. It is the predominant mode of
heat transfer in solids.
Convection occurs with
bulk movement of molecules and therefore, occurs in gases and liquids. If the
bulk movement or flow is due to an external device, it is known as forced
convection. In the absence of an external device the flow is due to the
difference in density caused by the temperature difference. This mode is known
as natural convection.
Bodies separated by a
distance may exchange heat in the form of electromagnetic waves without the
participation of the intervening medium. It is known as radiation. It is
generally a surface phenomenon. Sometimes as in the case of gas mixtures
containing carbon dioxide and water vapour it is a volume phenomenon.
Related Topics