Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Home Science Maintain Basic Knowledge for family life Higher secondary school College
Functions and Structure of Digestive System
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Digestion is the process by which the complex form of food materials are broken down into simpler form of food materials suitable for absorption. Once the food is digested, it must be transferred to the blood stream and the process by which this transfer occurs is called absorption. Digestion and absorption are the two chief functions of the digestive system.
Functions of Digestive System
1. Break down the food substances into small particles.
2. Digestion of food substances.
3. Absorption of food substances.
4. Excretion of undigested food and toxic substances.
The digestive system may be divided into two groups of organs:
The alimentary canal which is a continuous passage way beginning at the mouth, where the food is taken in and terminating at the anus, where the solid products of digestion which are not absorbed are expelled from the body.
The accessory organs such as salivary glands, pancreas, liver and biliary tract which are vitally necessary for the digestive process, do not happen to be the part of the alimentary canal.
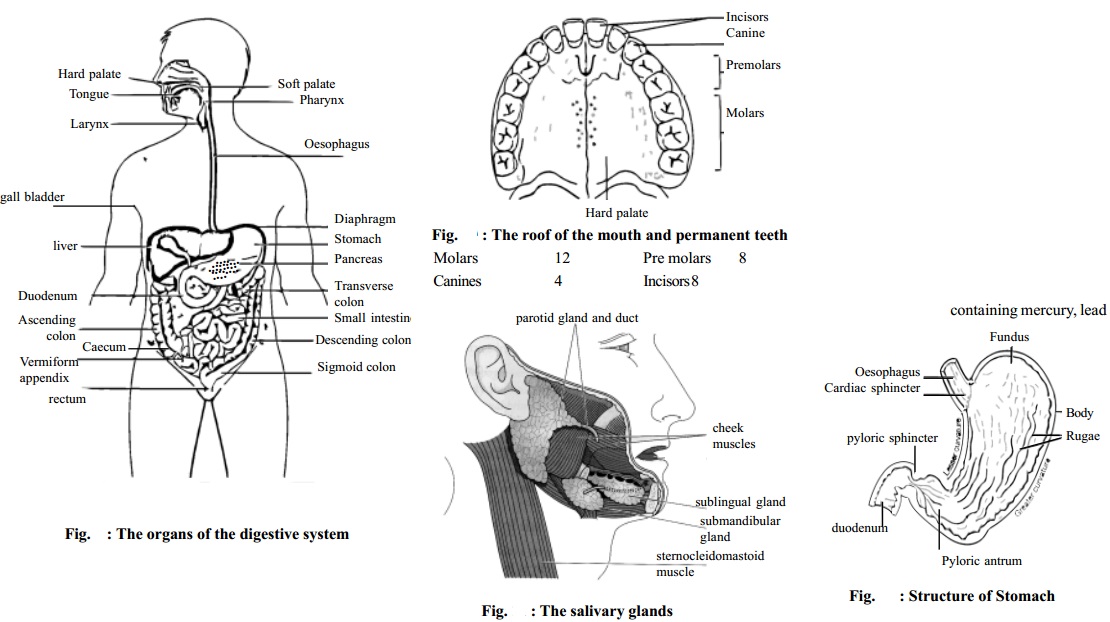
The Alimentary Canal
The alimentary canal is a long muscular digestive tube extending through the body. It is about 750 cm in length. It consists of the following parts.
The mouth
Oesophagus
Stomach
Small intestine
Large intestine
Rectum
Anal Canal
The gastrointestinal tract consists of a tube composed of four principal layers. From outside onwards:
Tunica Adventitia or serous coat - in the abdomen the organs are covered by a serous membrane called peritoneum.
The muscular coat.
The submucous coat.
The Mucous coat.
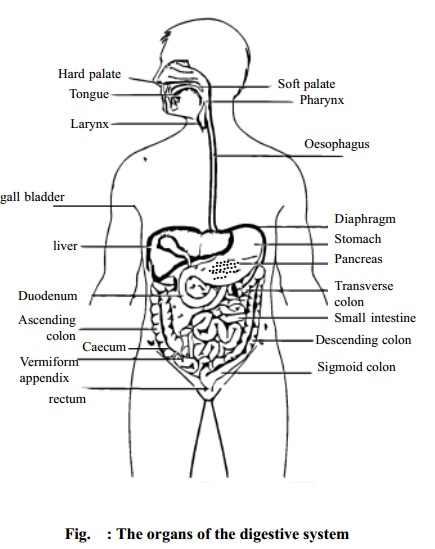
Mouth
The mouth is also called the oral cavity. In the mouth there are about 32 teeth. They are:
The teeth helps to break down the food substances into small particles. Into this space there projects a muscular organ called the tongue. It helps in chewing and swallowing and is one of the principal organs of speech. The tongue has on its surface a number of taste buds by means of which we can differentiate sensation of taste (bitter, sweet, sour and salty).
In chewing, the teeth grind the food into pieces while the secretion of saliva moistens and lubricates the food.
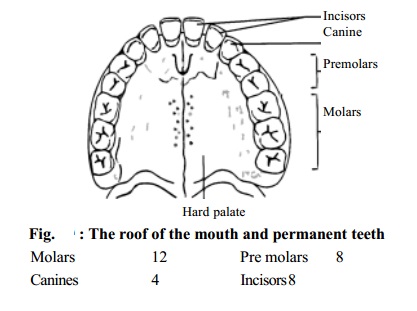
Saliva is a juice secreted by three pairs of salivary glands in the mouth. They are (a) the parotid (b) the sub-mandibular and (c) sub-lingual gland.
Parotid - located in front and below each external
ear.
b. Sub-mandibular - located between the mandible and the
muscle of the floor of the mouth.
c. Sublingual - located in the floor of the mouth.
Salivary secretion is a reflex process, both conditioned and unconditioned reflexes are involved. A new born infant salivates when food is placed in its mouth. But the sight and smell of food does not produce any reaction. Later by associating the sight and smell of food with its taste, the child learns that the food has certain qualities and these very qualities are afterward capable of eliciting salivary secretion.
Functions of Saliva
1. It keeps the mouth moist and helps in speech.
2. It helps in the process of mastication of the food stuff and in preparing it into a bolus suitable for digestion.
3. It dilutes hot, irritant substances and thus prevents injury to the mucous membrane.
4. Saliva contains two enzymes. Ptyalin and Maltase which converts starchy foods into sugars.
5. Saliva helps in the sensation of taste.
6. It helps heat loss. This is mainly found in animals. When they become hot, more saliva is secreted causing greater heat loss.
7. It helps in the excretion of certain substances like drugs containing mercury, lead and iodine.
Oesophagus
The Oesophagus is a tube connecting the pharynx and the stomach. It conveys the food from the mouth to the stomach.
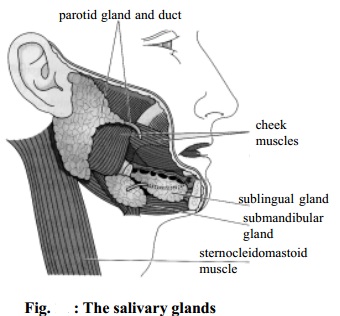
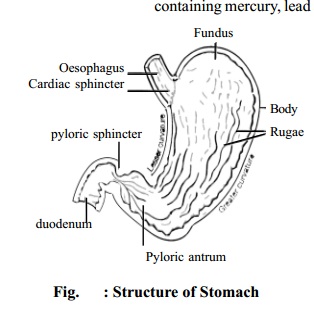
Stomach
The stomach is an enlarged section of the alimentary tube. The stomach is divided into three regions: the fundus, the body and the antrum. Both ends of the stomach are guarded by valves which normally permit the passage of substances in only one direction.
The proximal end is guarded by cardiac sphincter and the distal end of the stomach is guarded by pyloric sphincter. Stomach acts as a pouch for holding large quantities of food so that frequent feeding can be avoided. The stomach mixes up the food thoroughly by its movements. It also destroys bacteria by high acidity.
Small Intestine
The small intestine is about 600 cm long in the adult extending from the pyloric sphincter of the stomach to large intestine. The first 25 cm or 30 cm of the small intestine is called the duodenum, followed by the jejunum and the remainder is the ileum.
Large Intestine
The large intestine is as the name implies has the larger diameter than the small intestine. It is about 150 cm. in length. The small intestine opens into the large intestine. There is a small pouch at the beginning part of the large intestine. This pouch is called the caecum. To the caecum is attached a small tube called the vermiform appendix. Large intestine consists of ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon and the sigmoid colon.
Rectum and Anal Canal
The descending colon of large intestine opens into the last part. The rectum and anal canal. It is about 15 cm to 20 cm long. The rectum serves as a temporary storage area for the undigestible and nonabsorbable substances. The narrow portion of the distal part of the large intestine is called the anal canal which leads to the outside through an opening called the anus.
Related Topics