Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Perioperative & Critical Care Medicine: Acid-Base Management
Conjugate Pairs & Buffers
Conjugate Pairs & Buffers
As discussed above, when the weak acid HA is in solution, HA can act as
an acid by donating an H+, and A− can act as a base by taking up H+. A− is there-fore often referred to as the conjugate base of HA. A similar
concept can be applied for weak bases. Consider the weak base B, where
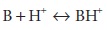
BH+ is therefore the conjugate acid of B.
A buffer is a solution that contains a weak
acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its con-jugate acid (conjugate
pairs). Buffers minimize any change in [H+] by readily accepting or giving up hydrogen ions. It is readily
apparent that buffers are most efficient in minimizing changes in the [H+] of a solution (ie, [A−] = [HA]) when pH = pK. Moreover, the conjugate
pair must be present in significant quantities in solution to act as an
effective buffer.
Related Topics