Chapter: Digital Signal Processing : Signals and System
Classification of Signals
CLASSIFICATION OF SIGNALS
1. Single
channel and Multi-channel signals
2. Single
dimensional and Multi-dimensional signals
3. Continuous
time and Discrete time signals.
4. Continuous
valued and discrete valued signals.
5. Analog
and digital signals.
6. Deterministic
and Random signals
7.
Periodic
signal and Non-periodic signal
8. Symmetrical(even)
and Anti-Symmetrical(odd) signal
9. Energy
and Power signal
If signal
is generated from single sensor or source it is called as single channel
signal. If the signals are generated from multiple sensors or multiple sources
or multiple signals are generated from same source called as Multi-channel
signal. Example ECG signals. Multi-channel signal will be the vector sum of
signals generated from multiple sources.
2. Single Dimensional (1-D) and
Multi-Dimensional signals (M-D)
If signal
is a function of one independent variable it is called as single dimensional
signal like speech signal and if signal is function of M independent variables
called as Multi - dimensional signals. Gray scale level of image or Intensity
at particular pixel on black and white TV is examples of M-D signals.
3. Continuous time and Discrete
time signals.
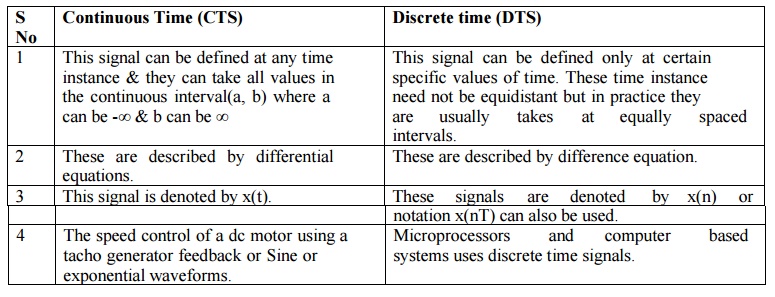
Continuous Time (CTS)
1.
This signal can be defined at any time instance
& they can take all values in the continuous interval(a, b) where a can be
-∞ & b can be ∞
2.
These are described by differential equations.
3.
This signal is denoted by x(t).
4.
The speed control of a dc motor using a tacho
generator feedback or Sine or exponential waveforms.
Discrete time (DTS)
1.
This signal can be defined only at certain specific
values of time. These time instance need not be equidistant but in practice they
are usually takes at equally spaced intervals.
2.
These are described by difference equation.
3.
These signals are denoted by x(n) or notation x(nT) can also be used.
4.
Microprocessors and computer based systems uses
discrete time signals.
4. Continuous valued and Discrete
Valued signals.
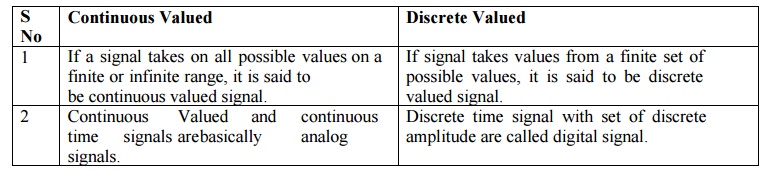
Continuous Valued
1.
If a signal takes on all possible values on a
finite or infinite range, it is said to be continuous valued signal.
2.
Continuous Valued
and continuous time signals are
basically analog signals.
Discrete Valued
1.
If signal takes values from a finite set of
possible values, it is said to be discrete valued signal.
2.
Discrete time signal with set of discrete amplitude
are called digital signal.
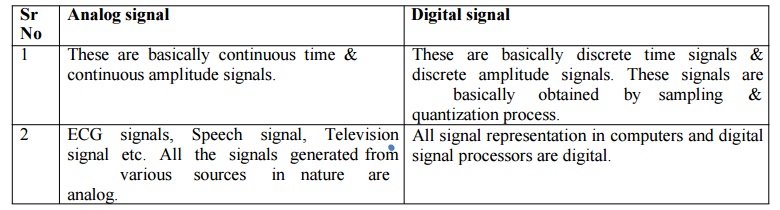
Analog signal
1.
These are basically continuous time &
continuous amplitude signals.
2.
ECG
signals, Speech signal,
Television signal etc. All the signals generated from various sources
in nature are analog.
Digital signal
1.
These are basically discrete time signals &
discrete amplitude signals. These signals are basically obtained
by sampling & quantization
process.
2.
All signal representation in computers and digital
signal processors are digital.
Note:
Digital signals (DISCRETE TIME &
DISCRETE AMPLITUDE) are obtained by sampling the ANALOG signal at discrete instants of time, obtaining DISCRETE TIME signals and then by
quantizing its values to a set of discrete values & thus generating DISCRETE AMPLITUDE signals.
Sampling
process takes place on x axis at regular intervals & quantization process
takes place along y axis. Quantization process is also called as rounding or
truncating or approximation process.
6. Deterministic and Random
signals
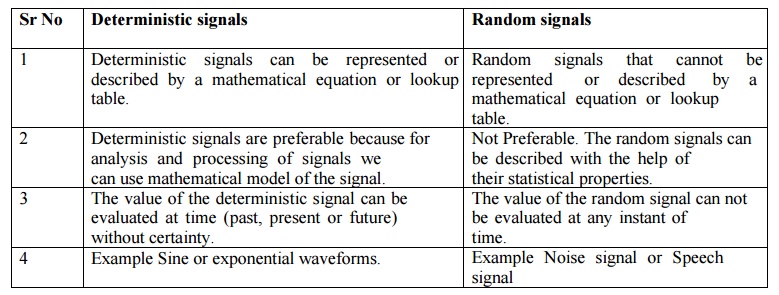
Deterministic signals
1.
Deterministic
signals can be
represented or described by a
mathematical equation or lookup table.
2.
Deterministic signals are preferable because for
analysis and processing of signals we can use mathematical model of the signal.
3.
The value of the deterministic signal can be
evaluated at time (past, present or future) without certainty.
4.
Example Sine or exponential waveforms.
Random signals
1.
Random
signals that cannot
be represented or described by a mathematical equation or lookup table.
2.
Not Preferable. The random signals can be described
with the help of their statistical properties.
3.
The value of the random signal can not be evaluated
at any instant of time.
4.
Example Noise signal or Speech signal
7. Periodic signal and
Non-Periodic signal
The
signal x(n) is said to be periodic if x(n+N)= x(n) for all n where N is the
fundamental period of the signal. If the signal does not satisfy above property
called as Non-Periodic signals.
Discrete
time signal is periodic if its frequency can be expressed as a ratio of two
integers. f= k/N where k is integer constant.

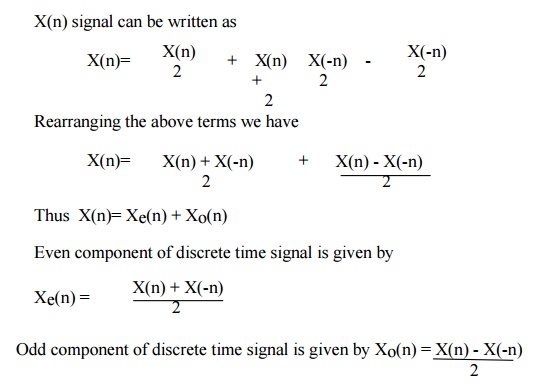
8. Symmetrical(Even) and
Anti-Symmetrical(odd) signal
Ex. 1.:Test whether the following CT waveforms is
periodic or not. If periodic find out the fundamental period.
a) 2 sin(2/3)t + 4 cos (1/2)t + 5 cos((1/3)t Ans: Period of x(t)= 12 b)
a) cos(t √2) + b
sin(t/4) Ans: Non-Periodic
Find out the even and odd parts of the discrete
signal x(n)={2,4,3,2,1}
Find out the even and odd parts of the discrete
signal x(n)={2,2,2,2}
9. Energy signal and Power signal
Discrete time signals are also classified as
finite energy or finite average power signals. The energy of a discrete time
signal x(n) is given by
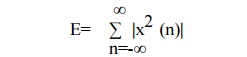
The average power for a discrete
time signal x(n) is defined as
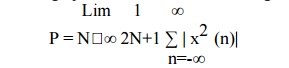
If Energy is finite and power is zero for x(n)
then x(n) is an energy signal. If power is finite and energy is infinite then
x(n) is power signal. There are some signals which are neither energy nor a
power signal.
a) Find the power and energy of u(n) unit step
function.
b) Find the power and energy of r(n) unit ramp
function.
c) Find the power and energy of an
u(n).
Related Topics