Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: Respiratory System
Changing Alveolar Volume
Changing Alveolar Volume
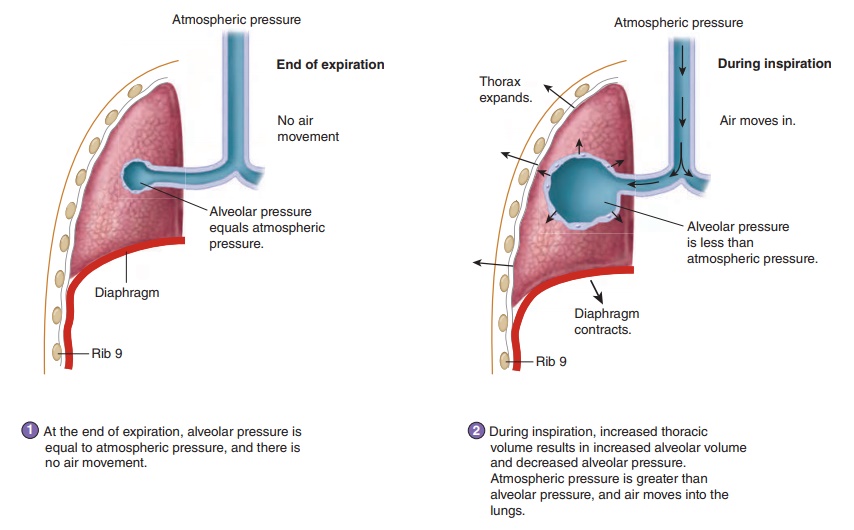
Changes in alveolar volume cause the changes in alveolar pressure that are responsible for moving air into and out of the lungs (see figure 15.11). Alveolar volume changes result from changes in pleural pressure. For example, during inspiration, pleural pressure decreases, and the alveoli expand. The decrease in pleural pressure occurs for two reasons:
1. Increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity results in a decrease in pleural pressure because a change in volume affects pressure.
2. As the lungs expand, lung recoil increases, increasing the suction effect and lowering the pleural pressure. The increased lung recoil of the stretched lung is similar to the increased force generated in a stretched rubber band.
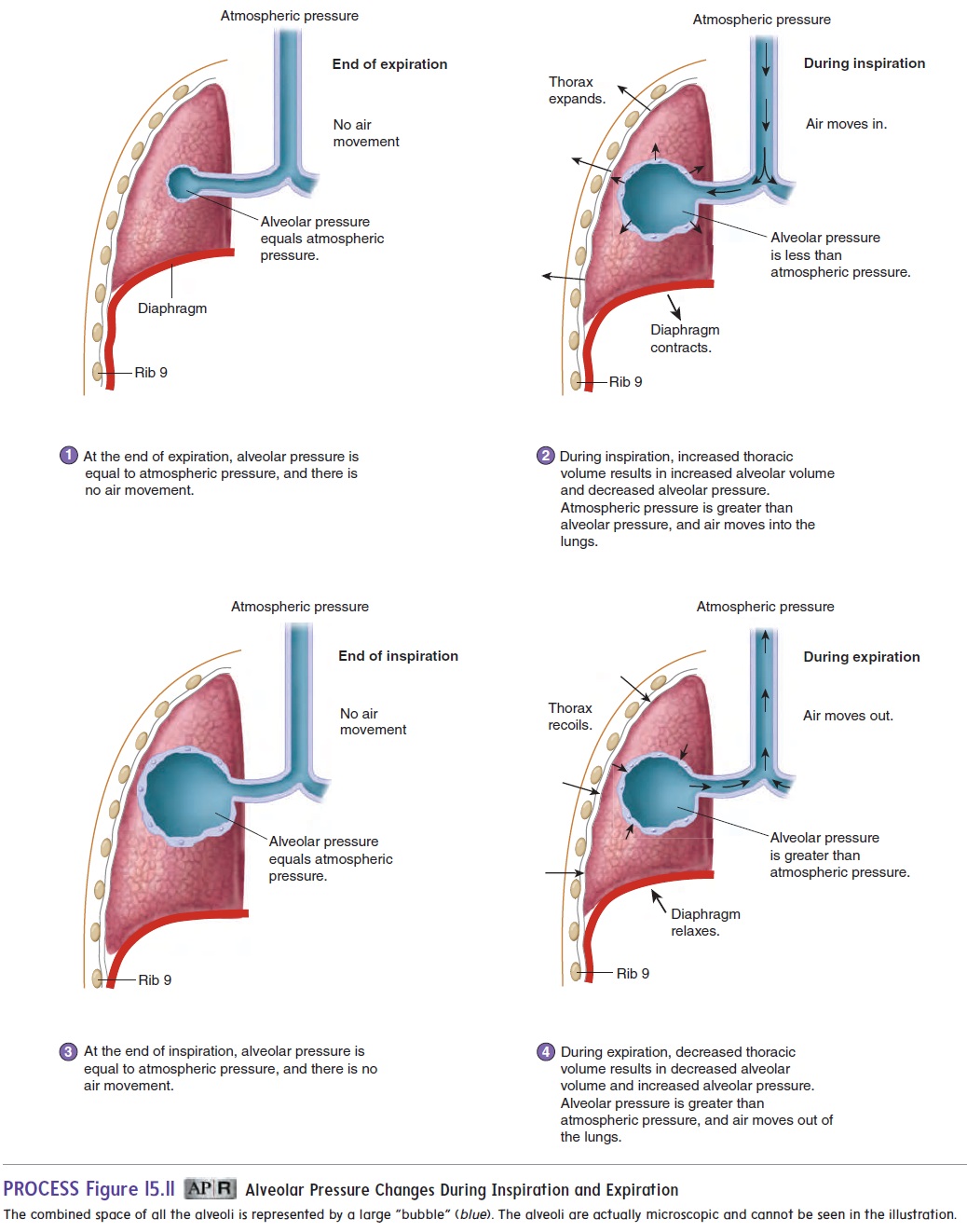
The events of inspiration and expiration can be summarized as follows:
1. During inspiration, pleural pressure decreases because of increased thoracic volume and increased lung recoil. As pleural pressure decreases, alveolar volume increases, alveolar pressure decreases, and air flows into the lungs.
2. During expiration, pleural pressure increases because of decreased thoracic volume and decreased lung recoil. As pleural pressure increases, alveolar volume decreases, alveolar pressure increases, and air flows out of the lungs.
Related Topics