Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Botanical description of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis
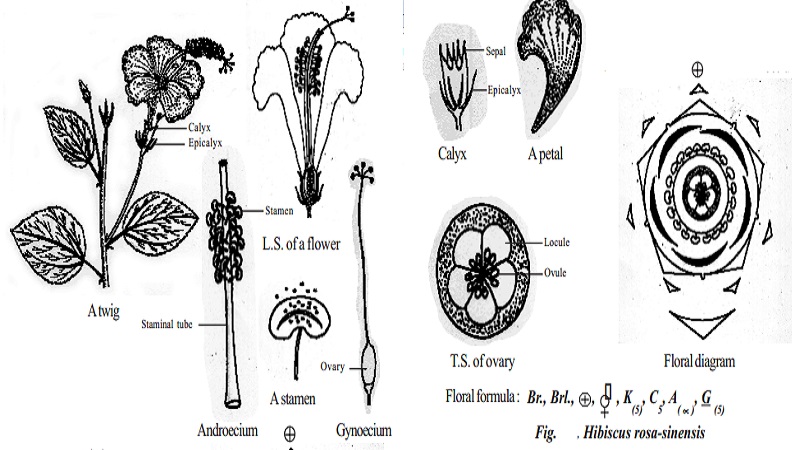
Botanical description of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis
Habit
Perennial shrub.
Root
Tap root system.
Stem
Aerial, erect, cylindrical, woody and branched.
Leaf
Simple, Alternate, petiolate, stipulate, serrate, glabrous, apex acuminate with multicostate reticulate venation.
Inflorescence
Solitary cyme and axillary.
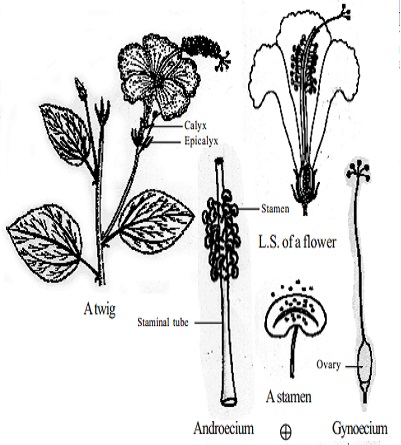
Flower
Pedicel jointed, bracteate, bracteolate, bisexual, large, showy, pentamerous, dichlamydeous, actinomorphic, complete and hypogynous and mucilage is present in floral parts.
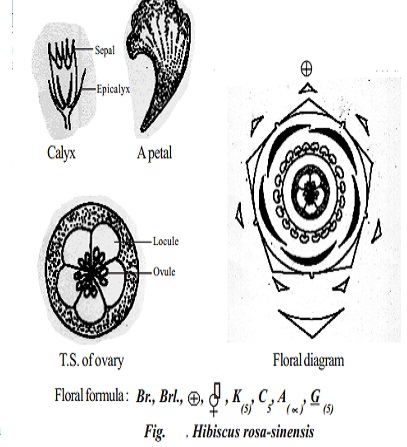
Epicalyx
5 to 8 bracteoles outer to the calyx. They are green and free.
Calyx
Sepals 5, green, gamosepalous showing valvate aestivation and odd sepal is posterior in position.
Corolla
Petals 5, variously coloured, polypetalous but fused at the base and showing twisted aestivation.
Androecium
Numerous stamens, monadelphous, filaments are fused to form a staminal tube around the style. Staminal tube is red. Anthers are monothecous, reniform, yellow, transversely attached to the filament, dehisce transversely and extrorse.
Gynoecium
Ovary superior, pentacarpellary and syncarpous. Ovary pentalocular with many ovules per locule on axile placentation. Style simple, long, slender and passes through the staminal tube. Stigma 5, capitate and coloured.
Fruit
Mostly abortive.
Floral Formula
Br., Brl., +, &, K(5), C5, A(x), G (5)
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE
1. Fibre plants
Gossypium barbadense (Egyptian cotton), G. hirsutum (American cotton), G. herbaceum (Cotton) and several other species of Gossypium yield cotton fibres of commercial value. The fibres are obtained from the surface of seeds.
Hibiscus cannabinus (Deccan hemp) yields bast fibres which are used for making ropes.
2. Food plants
The tender fruit of Abelmoschus esculentus (lady's finger) is used as vegetable. The leaves and sepals of Hibiscus sabdariffa (A kind of 'pulichai') are used for making pickles, jam and jelly. A delicious 'chutney' is prepared from the leaves and sepals of H. cannabinus (Pulichai keerai) and
H. sabdariffa.
3. Timber Plants
Timber obtained from Thespesia populnea (portia tree) is useful for making boat, furniture and agricultural implements.
4. Medicinal plants
Root and leaves of Abutilon indicum (Thuthi) and Malva sylvestris are used against fever. Roots of Malva sylvestris and Althaea rosea are used for treating whooping cough and dysentery respectively.
5. Ornamental plants
Althaea rosea (Hollyhock), Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (Shoe flower)
H. schizopetalus (A kind of shoe flower with dissected petals) are grown in gardens.
Related Topics