Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Botanical description and Economic importance of Datura metal
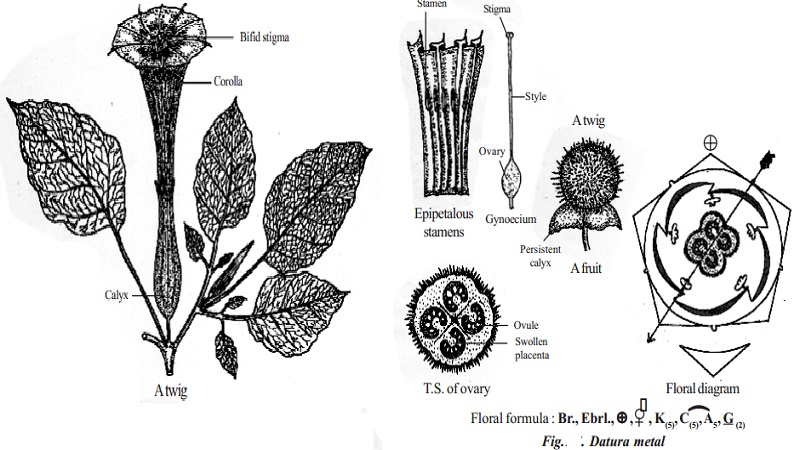
Botanical description of Datura metal
Habit
Large, erect and stout herb.
Root
Branched tap root system.
Stem
The stem is hollow, green and herbaceous with strong odour.
Leaf
Simple, alternate, petiolate, entire or deeply lobed, glabrous showing unicostate reticulate venation and exstipulate.
Inflorescence
Solitary and axillary cyme.
Flower
Flowers are large, greenish white, bracteate, ebracteolate, pedicellate, complete, dichlamydeous, pentamerous, regular, actinomorphic, bisexual and hypogynous.
Calyx
Sepals 5, green, gamosepalous showing valvate aestivation. Calyx is mostly persistent and odd sepal is posterior in position.
Corolla
Petals 5, greenish white, gamopetalous, plicate (folded like a fan) showing twisted aestivation, funnel shaped with wide mouth and 10 lobed.
Androecium
Stamens 5, free from one another epipetalous, alternate the petals and are inserted in the middle of the corolla tube. Anthers are basifixed, dithecous with long filament, introrse and longitudinally dehiscent.
Gynoecium
Ovary superior, bicarpellary and syncarpous. Ovary basically bilocular but tetralocular due to the formation of false septa. Carpels are obliquely placed and ovules on swollen axile placenta. Style simple, long and filiform. Stigma two lobed.
Fruit
Spinescent capsule opening by four apical valves with persistent calyx.
Seed
Endospermous.
ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE
1. Food plants
Tubers of Solanum tuberosum (potato) are used as common vegetable throughout the world. Tender fruits of S. melongena (brinjal) and ripened fruits of Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato) are used as delicious vegetables.
2. Medicinal plants
Roots of Atropa belladona yield powerful alkaloid 'atropine'. It is used for relieving muscular pain. Leaves and flowers of Datura stramonium are the sources of drug 'stramonium' used to treat asthma and whooping cough. Leaves, flowers, berries of Solanum trilobatum (thoodhuvalai) are used to treat cough. Roots and leaves of Withania somnifera (Amukkara) are used to treat nervous disorder and are diuretic apart from useful tonic.
3. Tobacco
Leaves of Nicotiana tabacum (tobacco) contain alkaloids nicotine, nornicotine and anabasine. Nicotine is considered to be the principal alkaloid in commercial tobaccos such as cigarette, bidi, pipes and hukkah as well as chewing and snuffing. It is also used as sedative, antispasmodic and insecticide.
4. Ornamental plants
Cestrum diurnum (day jasmine), C. nocturnum (night jasmine) and Petunia hybrida (pink flower) are grown in gardens for their beautiful flowers.
Related Topics