Chapter: 11 th 12th std standard Bio Botany plant tree Biology Higher secondary school College Notes
Botanical description and Economic importance of Cocos nucifera
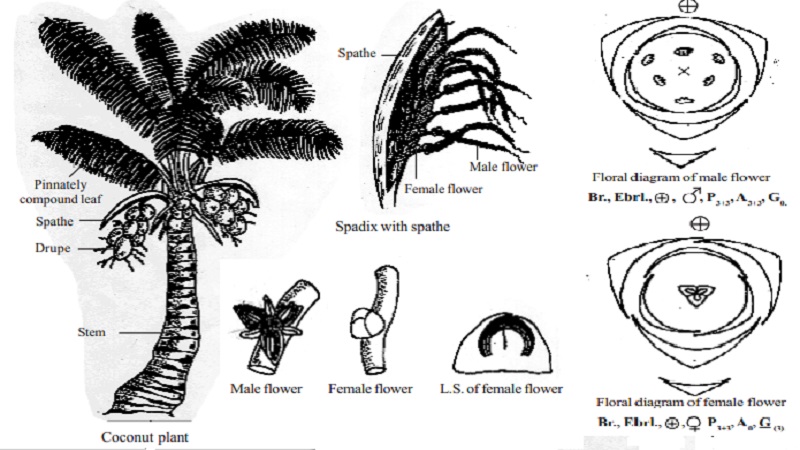
Botanical description of Cocos nucifera
Habit
Unbranched tree with arborescent stem and a crown of large leaves. It grows to a height of 60 to 100 feet.
Root
Fibrous and adventitious root system. As the stem increases in diameter, new roots are added at higher levels from the massive basal cushion and the youngest roots are visible above the soil surface.
Stem
Aerial, erect, unbranched and columnar, having prominent scars of leaf bases. Internodes are usually short.
Leaf
Exstipulate, petiolate, petiole long and very strong with sheathing leaf base, spiral and pinnately compound showing parallel venation.
Inflorescence
Large, lateral arising from the axils of leaves, compound spadix, enclosed by large woody bract called spathe. Each spike in the spadix bears 2 to 3 female flowers at the base and 200 to 300 male flowers at the top. Flowers are protandrous, the female flowers open, after the male flowers have withered.
Male flower
Bracteate, ebracteolate, sessile, staminate, incomplete, trimerous, actinomorphic and pistillodes are present.
Perianth
Tepals 6 arranged in two whorls of three each, persistent and polyphyllous showing valvate aestivation in both the whorls. Inner odd tepal is posterior in position.
Androecium
Stamens 6 arranged in two whorls of three each and antiphyllous. Anthers are dithecous, basifixed, introrse and dehiscing longitudinally.
Gynoecium
Absent but pistillode is present.
Female flower
Bracteate, ebracteolate, sessile, pistillate, incomplete, trimerous, actinomorphic and hypogynous.
Perianth
Tepals 6 arranged in two whorls of three each, persistent, and polyphyllous showing imbricate aestivation in both the whorls. The inner posterior tepal is completely outside.
Androecium
Absent but staminodes are present.
Gynoecium
Ovary superior, tricarpellary and syncarpous. Ovary trilocular with single ovule showing axile placentation. Style is absent and stigmas three. Out of three carpels, two become abortive.
Fruit
Fibrous drupe with stony endocarp.
Seed
With small embryo and abundant endosperm.
Economic importance
Edible products
The fluid of tender fruit of Cocos nucifera (kalpa vriksha - coconut palm) is sweet and refreshing drink. The boiled young seedlings of Borassus flabellifer (palmyra palm) are edible and its fruits are eaten raw.
Oil plants
The oil obtained from dried endosperm of Cocos nucifera is called cocoanut oil. It is used for cooking, for the preparation of vegetable fat (ghee) and as hair oil. The oil obtained from fleshy mesocarp of Elaeis guineansis is called palm oil. It is mainly used for the manufacture of soap.
Toddy
A sugary solution obtained by cutting young peduncles of Cocos nucifera, Borassus flabellifer and Phoenix sylvestris (Eechai) is used for manufacturing jaggery. This sugary solution on fermentation yields the beverage called 'toddy'. This sap is also used for manufacturing a number of commercially useful products such as palm sugar, alcohol and vinegar.
Timber plants
Dense stem wood of Borassus flabellifer and Cocos nucifera is used as timber.
Ornamental plants
Adonidia merilli (Manila palm) and Caryota urens (wine palm).
Related Topics