Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 2 : Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
Bohr atom model
Bohr atom model:
The work of Planck and Einstein showed that the energy of electromagnetic radiation is quantised in units of h╬Į (where ╬Į is the frequency of radiation and is Planck's constant 6.626 ├Ś 10-34 Js). Extending PlanckŌĆÖs quantum hypothesis to the energies of atoms, Niels Bohr proposed a new atomic model for the hydrogen atom. This model is based on the following assumptions:
1. The energies of electrons are quantised
2. The electron is revolving around the nucleus in a certain fixed circular path called stationary orbit.
3. Electron can revolve only in those orbits in which the angular momentum (mvr) of the electron must be equal to an integral multiple of h/2ŽĆ.
i.e. mvr = nh/2ŽĆ -------- (2.1)
where n = 1,2,3,...etc.,
4. As long as an electron revolves in the fixed stationary orbit, it doesnŌĆÖt lose its energy. However, when an electron jumps from higher energy state (E2) to a lower energy state (E1), the excess energy is emitted as radiation. The frequency of the emitted radiation is
E2 ŌĆō E1 = h╬Į
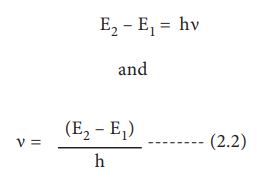
Conversely, when suitable energy is supplied to an electron, it will jump from lower energy orbit to a higher energy orbit.
Applying BohrŌĆÖs postulates to a hydrogen like atom (one electron species such as H, He+ and Li2+ etc..) the radius of the nth orbit and the energy of the electron revolving in the nth orbit were derived. The results are as follows:
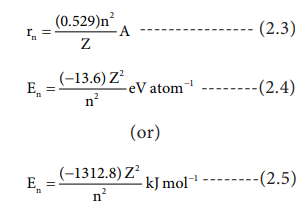
The detailed derivation of rn and En will be discussed in 12th standard atomic physics unit.
Limitation of Bohr's atom model:
The Bohr's atom model is applicable only to species having one electron such as hydrogen, Li2+ etc... and not applicable to multi electron atoms. It was unable to explain the splitting of spectral lines in the presence of magnetic field (Zeeman effect) or an electric field (Stark effect). BohrŌĆÖs theory was unable to explain why the electron is restricted to revolve around the nucleus in a fixed orbit in which the angular momentum of the electron is equal to nh/2ŽĆ and a logical answer for this, was provided by Louis de Broglie.
Related Topics