Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Genetic Engineering and Recombinant DNA
Arrest of Translation to Assay for DNA of a Gene
Arrest of Translation to Assay for DNA of a Gene
In vitro translation of mRNA forms the basis of one
technique foridentification of clones containing DNA of a particular gene. The
technique requires that the enriched messenger RNA of the gene, such as the
mRNA obtained from an oligo-dT column, be translatable in vitro to yield a detectable protein product of the desired gene.
To perform the identification, DNA for a candidate clone is denatured and
hybridized to the RNA used in the translation mixture. If the DNA contains
sequences complementary to the mRNA, the two will hybridize to-gether, the
messenger will become unavailable for in
vitro translation, and the gene product will not be synthesized (Fig.
9.15). DNA from a clone not possessing the DNA sequence of the gene will not
interfere
Figure
9.15 Hybridization arrest of
translation as an assay for DNA of a genewhose mRNA can be translated into
protein.
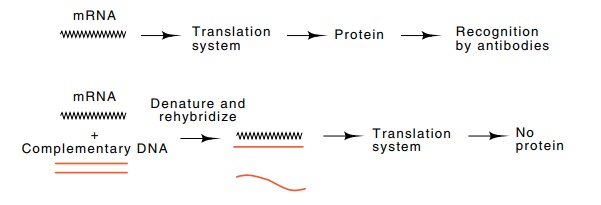
with translation of the messenger. Hence DNA
carrying sequences complementary to the messenger can be detected by
hybridization arrest of translation.
Related Topics