Chapter: Civil : Construction Planning And Scheduling
Additional resource constraints
Additional
resource constraints.
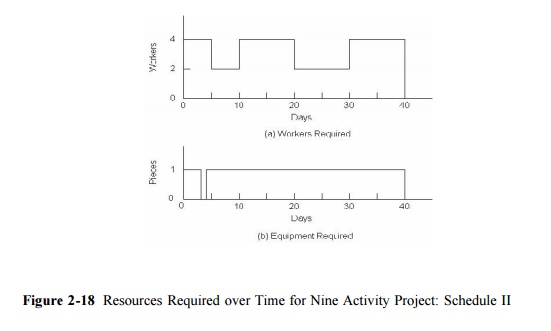
As another example, suppose that only one piece of equipment
was available for the project. As seen in Figure 2-17, the original schedule
would have to be significantly modified in this case. Application of the
resource constrained scheduling heuristic proceeds as follows as applied to the
original project schedule:
1. On day 4,
activities D and C are both scheduled to begin. Since activity D has a larger
value of late start time, it should be re-scheduled.
2. On day
12, activities D and E are available for starting. Again based on a later value
of late start time (15 versus 13), activity
D is deferred.
3. On day
21, activity E is completed. At this point, activity D is the only feasible
activity and it is scheduled for starting.
4. On day
28, the planner can start either activity G or activity H. Based on the later
start time heuristic, activity G is chosen to start.
5. On
completion of activity G at day 30, activity H is scheduled to begin.
The resulting profile of resource use is shown in Figure
10-18. Note that activities F and I were not considered in applying the
heuristic since these activities did not require the special equipment being
considered. In the figure, activity I is scheduled after the completion of
activity H due to the requirement of 4 workers for this activity. As a result,
the project duration has increased to 41 days. During much of this time, all
four workers are not assigned to an activity. At this point, a prudent planner
would consider whether or not it would be cost effective to obtain an
additional piece of equipment for the project.
Related Topics