Chapter: Clinical Anesthesiology: Perioperative & Critical Care Medicine: Acid-Base Management
Strong Ion Difference
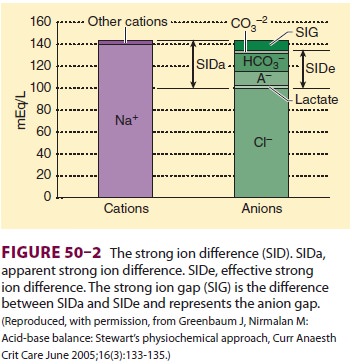
Strong Ion Difference
The SID is the sum of all the strong, completely or
almost completely dissociated, cations (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+) minus the strong
anions (Cl−, lactate−, etc.) ( Figure 50–2). Although we can calculate the SID,
because the laws of electroneutrality must be observed, if there is a SID,
other unmeasured ions must be present. Pco2 is an independent
variable, assuming ventilation is ongoing. The conjugate base of HA is A− and is composed mostly
of phosphates and proteins that do not change independent of the other two
variables. A− plus AH is an independent variable because its value is not determined
by any other variable. Note that [H+] is not a strong ion
(water does not completely dissociate), but it can, does, and must change in
response to any changein SID, Pco2, or ATOT to comply with the laws of
electroneutrality and conservation of mass. Strong ions cannot be made to
achieve electroneutrality, but hydrogen ions, H+, are created or consumed based
on changes in the dissociation of water.
Related Topics