Chapter: Clinical Dermatology: Regional dermatology
Squamous cell carcinoma
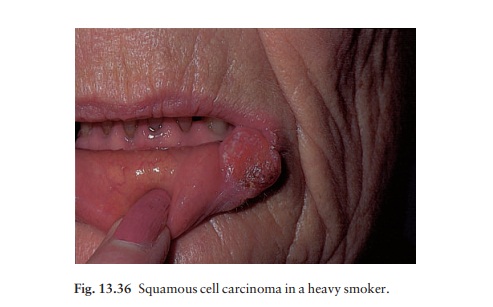
Squamous cell carcinoma (Fig.
13.36)
Cause
Predisposing
factors include smoking or chewing tobacco products, and the ‘straight-shot’
drinking of alcohol. Cancer can also occur in the plaques and ulcers of lichen
planus. Lip cancers may be sun-induced.
Presentation
A
thickening or nodule develops, usually on the lower lip, and often in a field
of actinic chelitis (rough scaling mucosa from sun damage). Inside the mouth,
the tongue is the most common site to be affected, often on its undersurface.
The cancer itself appears either as an indurated ulcer with steep edges, or as
a diffuse hardness or nodule. Red or white thickened plaques are common
precursors, and the cancer may be surrounded by these changes.
Course
Unfortunately,
cancer of the mouth often goes undetected. Its symptoms are excused by the
patient as aphthous ulcers or denture sores, and its signs are not seen by the
physicians who scan the skin. Cancers grow, and squamous cell carcinomas of the
mouth are no exception. Plaques and hard areas may ulcerate.
Differential diagnosis
Confusion
occurs with ulcerative lichen planus and other causes of white and red patches.
Biopsy will dif-ferentiate a squamous cell carcinoma from these other
conditions.
Treatment
Dermatologists
often treat lip cancers by a wedge excision through all layers of the lip, with
primary repair. Oral surgeons or otolaryngologists usually remove intraoral
cancers. Metastatic disease may require radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Complications
Squamous
cell carcinomas of the lip caused by sun exposure carry a much better prognosis
than the others. Left untreated, squamous cell carcinomas are prone to
metastasize to regional lymph nodes and elsewhere. The overall 5-year survival
for intraoral squamous cell carcinoma is about 40 –50%.
Related Topics