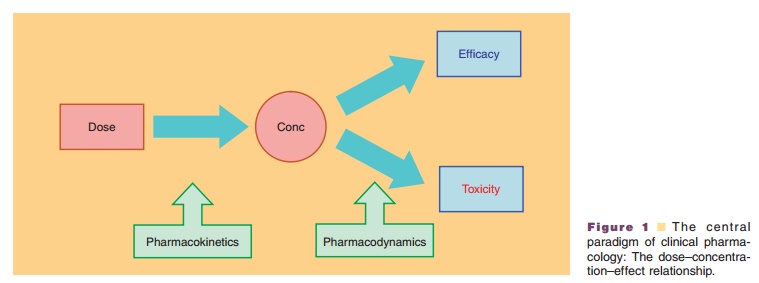
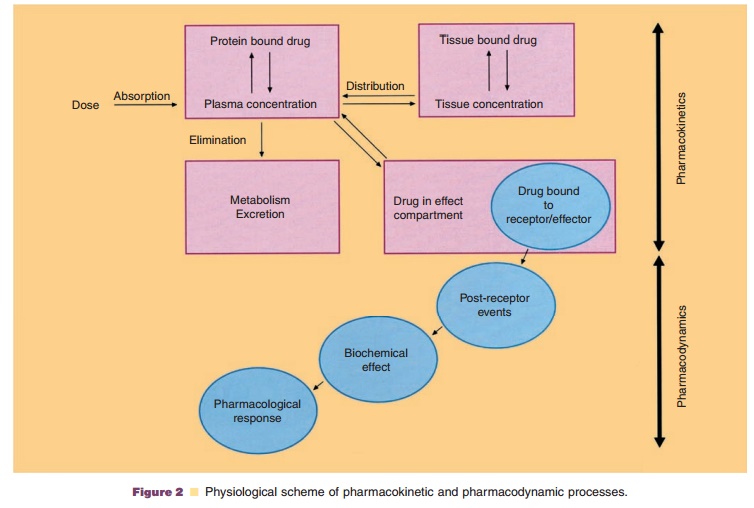
Chapter: Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: Fundamentals and Applications : Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Peptide and Protein Drugs
Pharmacokinetics of Protein Therapeutics
PHARMACOKINETICS OF PROTEIN THERAPEUTICS
The in vivo disposition of peptide and protein drugs may often be
predicted to a large degree from their physiological function (Tang and
Meibohm, 2006). Peptides, for example, which frequently have hormone activity,
usually have short elimination half-lives, which is desirable for a close
regulation of their endogenous levels and thus function. Insulin, for example
shows dose-dependent elimination with a relatively short half-life of 26 and 52
minutes at 0.1 and 0.2 U/kg, respectively. Contrary to that, proteins that have
transport tasks such as albumin or long-term
immunity functions such as immunoglobulins have elimination half-lives
of several days, which enables and ensures the continuous maintenance of
physio-logically necessary concentrations in the bloodstream (Meibohm and
Derendorf, 1994). This is for example reflected by the elimination half-life of
antibody drugs such as the anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody
cetuximab, an IgG1 chimeric antibody forwhich a half-life of approximately 7
days has been reported (Herbst and Langer, 2002).
Related Topics