Chapter: Environmental Science and Engineering
Non-Reneable Energy Sources
NON-RENEABLE ENERGY SOURCES
1 Coal
Coal is a
solid fossil fuel formed in several stages as buried remains of land plants
that lived 300-400 million years ago were subjected to intense heat and
pressure over millions of years.
Various stages of coal
3. The carbon content of Anthracite is 90% and its calorific value is 8700 k.cal.
2. The
carbon content of bituminous, lignite and peat are 80, 70 and 60% respectively
3. India
has about 5% of world’s coal. Indian coal is not good because of poor heat
capacity.
Disadvantages
3. When
coal is burnt it produces CO2 causes global warming
2. Since
coal contains impurities like S and N, it produces toxic gases during burning.
2 Petroleum
Petroleum
or crude oil = hydrocarbons +small amount S, O, N.
Occurrence
The
fossil fuel formed by the decomposition of dead animals and plants that were
buried under lake and ocean at high temperature and pressure for million years
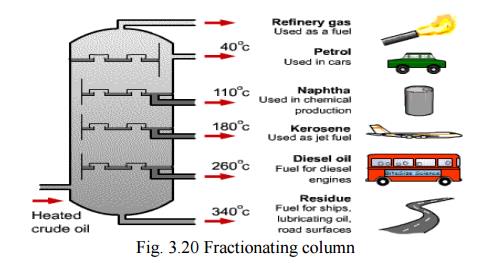
Fractional distillation
Hydrocarbons
are separated by fractioning the crude oil.
Petroleum World Scenario
3. 67%
oil reserves.
2. 25% of
the oil reserves in Saudi Arabia.
At the
present rate of usage, the world’s crude oil reserves are expected to get
exhausted in just 40 years.
3 LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)
1. The
petroleum gas, converted into liquid
under high pressure as LPG
2. LPG is
colorless and odorless gas.
3. During
bottling some mercaptans is added,
to detect leakage of LPG from the cylinder.
4 Natural Gas
3. Mixture
of 50-90% methane and small amount
of other hydrocarbons.
2. Its calorific
value ranges from 12,000-14,000 k-cal/m3.
(i)Dry gas
If the
natural gas contains lower hydrocarbons like methane and ethane, it is called
dry gas.
(ii)Wet gas
If the
natural gas contains higher hydrocarbons like propane, butane along with
methane it is called wet gas.
Occurrence
Formed by
the decomposition of dead animals and plants, those were buried under lake and
ocean, at high temperature and pressure for millions of years.
Related Topics