Chapter: Environmental Science and Engineering
Nuclear Energy
NUCLEAR ENERGY
India has 10 nuclear reactors, which produce 2% of India’s
electricity.
1 Nuclear Fission
Heavier
nucleus is split into lighter nuclei, on bombardment by fast moving neutrons,
and a large amount of energy is released.
Eg:
Fission
of U235
When U235
nucleus is hit by a thermal neutron, it undergoes the following reaction with
the release of 3 neutrons.
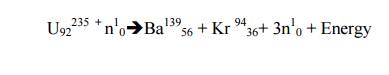
Each of
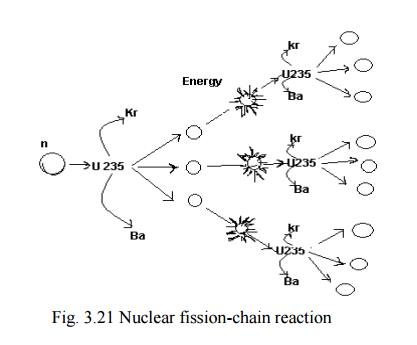
the above 3 neutrons strikes another U235 nucleus causing (3x3) 9
subsequent reactions. These 9 reactions further give rise to (3x9) 27
reactions.
This process of propagation of the reaction by multiplication in threes at each fission is called chain reaction.
Fission
reaction of U235 is given below.
92U235 +0n1 → 36Kr92 + 56Ba141 + 3 0n1 + energy
2 Nuclear fusion:
Lighter
nucleuses are combined together at extremely high temperatures to form heavier
nucleus and a large amount of energy is released.
Eg:
Fusion of
H21 .Two hydrogen-2 (Deuterium) atoms may fuse to form
helium at 1 billion0C with the release of large amount of energy
1H2+1H2 → 3He2+0n1+energy
Nuclear power of India
Tarapur(Maharashtra),
Ranapratap
Sagar (Rajasthan)
Kalpakkam
(Tamilnadu)
Narora
(U.P).
Why
Alternate (Renewable) Energy Sources are required?
The
importance of solar energy can be emphasized particularly in view of the fact
that fossil fuels and other conventional sources are not free from
environmental implications.
least pollution, safety and security snags and
are universally available have the
best enhance of large scale
utilization in future
Hydro-electric power generation
is expected to upset the ecological balance existing on earth Besides space heating, hydel power
plants critically pollute the aquatic and terrestrial biota. Radioactive pollutants released from
nuclear power plants are chronically hazardous.
The
commissioning of boiling water power reactors (BWRS) have resulted in the
critical accumulation of large number of long lived radionuclides in water\
The dangerous radiowaste cannot be buried
in land without the risk of polluting soil and underground water.
Nor the
waste can be dumped into the rivers without poisoning aquatic life and human
beings as well The burning of coal, oil,
wood, dung cakes and petroleum products has well debated environmental
problems. The smoke so produced causes respiratory and digestive problems
leading to lungs, stomach and eye diseases.
The disposal of fly ash requires large ash
ponds and may pose a severe problem considering the limited availability of
land. Thus the non-conventional sources of energy are needed.
Objectives
To
provide more energy to meet the requirements of increasing population.
To reduce
environmental pollution
To reduce
safety and security risks associated with the use of nuclear energy.
Related Topics