Chapter: Environmental Science and Engineering
Disaster Management
DISASTER MANAGEMENT
Hazard
It is a perceived natural event which threatens both life and property.
Disaster
ü A disaster is the realization of this hazard
ü It is defined as the geological process and it is an event concentrated in time and space in which a society or subdivision of a society undergoes severe danger and causes loss of its members and physical property.
Types
Natural disasters – refers to those disasters that are generated by natural phenomena. Man made disasters – refers to the disasters resulting from man made hazards.
1 FLOODS
Whenever the magnitude of water flow exceeds the carrying capacity of the channel within its banks the excess of water overflows on the surroundings causes floods.
Causes of floods
Ø Heavy rain, rainfall during cyclone causes floods
Ø Sudden snow melt also raises the quantity of water in streams and causes flood
Ø Sudden and excess release of impounded water behind dams
Ø Clearing of forests for agriculture has also increased severity of floods.
Flood Management
· Encroachment of flood ways should be banned.
· Building walls prevent spilling out the flood water over flood plains.
· Diverting excess water through channels or canals to areas like lake, rivers where water is not sufficient.
· Optical and microwave data from IRS is also used for flood management.
· Flood forecasts and flood warning are also given by the central water commission.
2 CYCLONES
It is a meteorological process, intense depressions forming over the open oceans and moving towards the land.
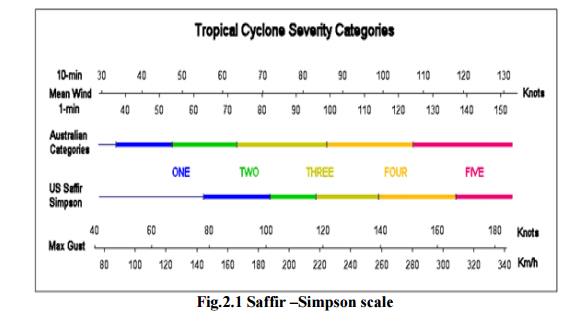
Cyclone is measured by Saffir-Simpson scale.
1 Effect
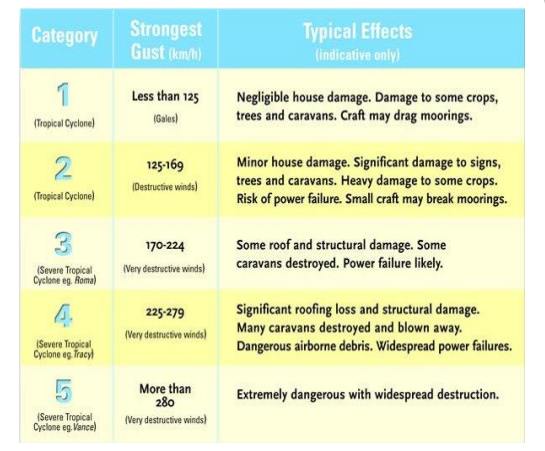
ü The damage depends on the intensity of cyclone the damage to human life, crops, roads, transport, could be heavy.
ü Cyclone occurrence slows down the developmental activities of the area.
Table 2.1 Classification of cyclones based on their speed
2 Cyclone management
Ø Satellite images are used by meteorological departments for forecasting the weather conditions which reveal the strength and intensity of the storm.
Ø Radar system is used to detect the cyclone and is being used for cyclone warning.
3 Case studies
Cyclone in Orissa – 1999
ü Two cyclones in Orissa occurred on 18th and 29th October 1999.In the coastal area of Orissa, a powerful cyclone storm hit with a wind velocity of about 260 km/hr. Nearly 14-30 districts of Orissa were in severe damage.
ü It has been reported that nearly 15 millions of people were affected and 90-95% of the crop yield was affected. About 11,500 local schools have been damaged.
3 LAND SLIDES
The movement of earthy materials like coherent rock, mud, soil and debris from higher to lower region to gravitational pull is called land slides.
1 Causes
v Movement of heavy vehicles on the unstable sloppy regions.
v Earthquake, shocks, vibrations and cyclone.
2 Effects of landslides
1. Block roads and diverts the passage.
2. Soil erosion increases.
2. Causes damages to houses, crops and live stock.
4 EARTH QUAKES
An earthquake is a sudden vibration caused on earth surface with the sudden release of tremendous energy stored in rocks under the earth’s crust.
1 Causes
1. Disequilibrium in any part of the earth crust
2. Underground nuclear testing
2. Decrease of underground water level.
2 Severity of an earthquake:
Generally it is measured by its magnitude on Richter scale.

3 Effect
· Damage the settlements and transport systems
· Collapses houses and their structures
· Deformation of ground surface
· Tsunami
4 Earthquake Management
ü Constructing earthquake resistant building
ü Wooden houses are preferred
ü Seismic hazard map should give the information about the magnitude of intensity of anticipated earthquakes.
5 TSUNAMI
A tsunami is a large wave that is generated in a water body when the seafloor is deformed by seismic activity. This activity displaces the overlying water in the ocean.
Causes of tsunami
v Seismic activities like earthquakes, landslides, volcanic eruptions, explosions, can generate tsunami.
v Deformation of the sea floor due to the movement of plates.
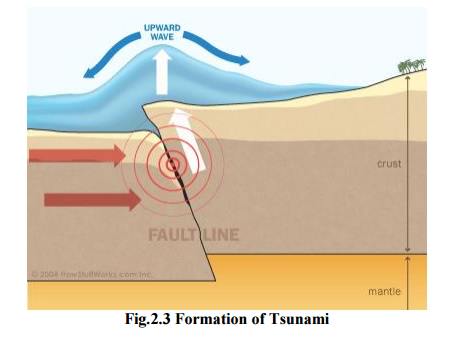
Concept of Tsunami
A tsunami is not a single wave but a series of waves like the ordinary waves which we see on
seas.
Effects on Tsunami
§ Tsunami attacks mostly the coastlines, causing devastating property, damage and loss of life.
§ Tsunami can kill lot of human beings, livestock’s.
§ Tsunami may also spread lot of water borne diseases.
Tsunami Management
ü Earthquakes under the water are monitored by sensors on the floor of the sea.
ü The sensors send the information of floating buoys on the surface, whenever they detect any changes in pressure of the sea.
ü The information is then relayed to satellites, which passes it on to the earth stations.
ü Finally the country make the people alert through the media to take all necessary precautions.
Case studies
Tsunami- Japan 2011, India 2004.
Related Topics