Chapter: Environmental Science and Engineering
Renewable Energy Resources and Methods of Harvesting
RENEWABLE ENERGY RESOURCES
Renewable
resources are parts of our natural environment and form our eco-system
SOLAR ENERGY
The
energy that we get directly from the sun is called solar energy.
The
nuclear fusion reactions occurring inside the sun release enormous amount of
energy in the form of heat and light.
The solar
energy received by the near earth space is approximately3.4 kJ/s/m2
known as solar constant.
Methods of Harvesting Solar Energy
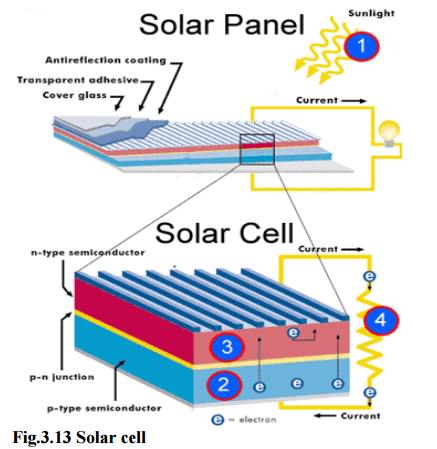
1. Solar cells (or) photovoltaic cells (or) PV
cells
Solar
cells consist of a p-type semiconductor (such as Si doped with B) and n-type
semi-conductor (Si doped with P).
They are
in close contact with each other.
When the
solar rays fall on the top layer of p-type semi-conductor, the electrons from
the valence band get promoted to the conduction band and cross the p-n junction
into n-type semi-conductor.
There by
potential difference between two layers is created, which causes flow of
electrons (ie.,an electric current)
cell Uses
Used in
calculators, electronic watches. Street lights, water pumps to run radios and
TVs.
Solar Battery
When a
large number of solar cells are connected in series it form a solar battery.
Solar
battery produce more electricity which is enough to run water pump, to run
street-light, etc., They are used in remote areas where conventional
electricity supply is a problem.
2. Solar heat collectors
Solar
heat collectors consists of natural materials like stones, bricks, (or)
materials like glass, which can absorb heat during the day time and release it
slowly at night.
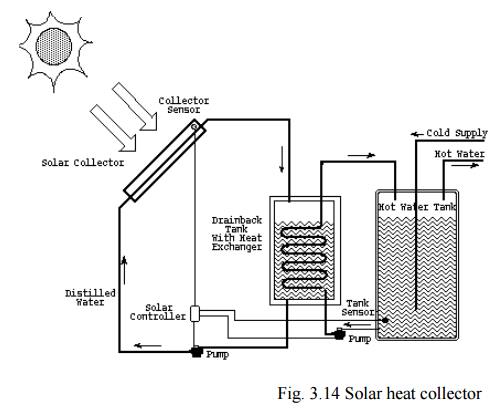
Uses
Used in
cold places, where houses are kept in hot condition using solar heat
collectors.
3. Solar water heater
It
consists of
An
insulated box inside of which is painted with black paint. Provided with a
glass lid to receive and store solar heat.
Inside
the box it has black painted copper coil, through which cold water is allowed
to flow in, which gets heated up and flows out into a storage tank.
From the
storage tank water is then supplied through pipes.
WIND ENERGY
Definition
Moving
air is called wind.
Energy
recovered from the force of the wind is called wind energy.
The
energy possessed by wind is because of its high speed.
The wind
energy is harnessed by making use of wind mills.
Harvesting of wind energy
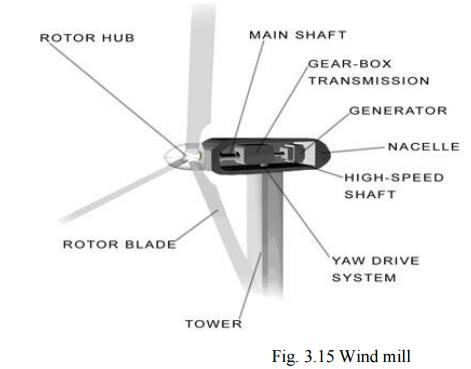
1. Wind Mills
The
strike of blowing wind on the blades of the wind mill makes it rotating
continuously.
The
rotational motion of the blade drives a number of machines like water pump,
flour mills and electric generators.
2. Wind farms
When a
large number of wind mills are installed and joined together in a definite
pattern it forms a wind farm.
The wind
farms produce a large amount of electricity.
Conditions
The
minimum speed required for satisfactory working of a wind generator is 15
km/hr.
Advantages
It does
not cause any air pollution
It is
very cheap.
OCEAN ENERGY
It can be
generated by following ways.
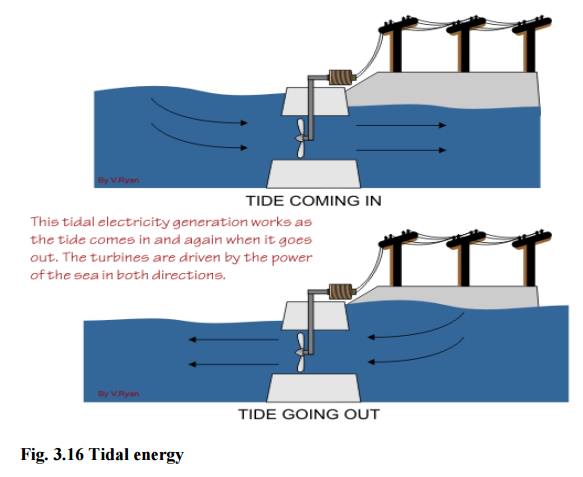
1. Tidal energy (or) Tidal power
Ocean
tides, produced by gravitational forces of sun and moon, contain enormous
amount of energy.
The “high
tide” and “low tide” refer to the rise and fall of water in the oceans.
The tidal
energy can be harnessed by constructing a tidal barrage.
During
high tide, the sea-water is allowed to flow into the reservoir of the barrage
and rotates the turbine, which intern produces electricity by rotating the
generators.
During
low tide, when the sea level is low, the sea water stored in the barrage reservoir
is allowed to flow into the sea and again rotates the turbine.
2. Ocean thermal energy (OTE)
There is
often large temperature difference between the surface level and deeper level
of the tropical oceans.
This
temperature difference can be utilized to generate electricity.
The
energy available due to the difference in temperature of water is called ocean
thermal energy.
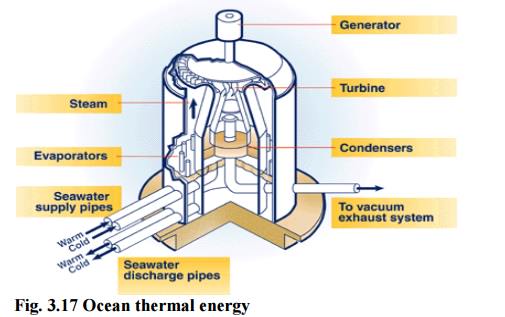
Fig. 3.17 Ocean thermal energy
Condition
The
temperature difference should be of 200C or more is required between
surface water and deeper water.
Process
The warm
surface water of ocean is used to boil a low boiling liquid like ammonia.
The high
vapour pressure of the liquid, formed by boiling is then to turn the turbine of
the generator and generates electricity.
The cold
water from the deeper ocean is pumped to cool and condense the vapour into
liquid.
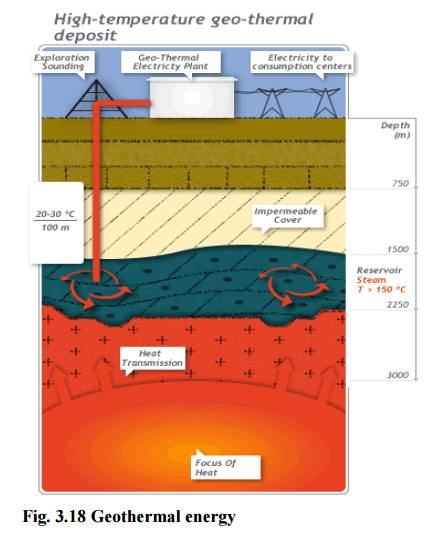
3. Geo-thermal Energy
3.
Temperature of the earth increases at a rate of 20-750C per km, when
we move down the earth surface.
2. High temperature
and high pressure steam fields exists below the earth’s surface in many places.
3. The
energy harnessed from the high temperature present inside the earth is called
geothermal energy.
3. Natural geysers
In some
places, the hot water (or) steam comes out of the ground through cracks
naturally in the form
2. Artificial geysers
In some
places, we can artificially drill a hole up to the hot region and by sending a
pipe in it, we can make the hot water or steam to rush out through the pipe
with very high pressure.
Thus, the
hot water (or) steam coming out from the natural (or) artificial geysers is
allowed to rotate the turbine of a generator to produce electricity.
BIOMASS ENERGY
Biomass
is the organic matter, produced by plants or animals, used as sources of
energy. Most of the biomass is burned directly for heating, cooling and
industrial purposes.
Eg: Wood,
crop residues, seeds, cattle dung, sewage, agricultural wastes.
Biogas
Mixture
of methane, carbondioxide, hydrogen sulphide, ete. It contains about 65% of
methane gas as a major constituent
Biogas is
obtained by the anaerobic fermentation
of animal dung or plant wastes in the presence of water.
2. Bio fuels
Biofuels
are the fuels, obtained by the fermentation
of biomass.
Eg:
Ethanol, Methanol
(a)Ethanol
Ethanol
can be easily produced from the sugarcane.
Its calorific value is less when compared to petrol, and produces much less
heat than petrol.
(b)Methanol
Methanol
can be easily obtained from ethanol or
sugar-containing plants.
Its
calorific value is also too low when compared to gasoline and diesel.
(c)Gasohol
Gasohol
is a mixture of ethanol+gasoline.
In India
trial is being carried out to use Gasohol in cars and buses.
Gasohol
is common fuel in Brazil and Zimbabwe for running cars and buses.
Methanol
is very useful since it burns at a lower temperature than gasoline or diesel.
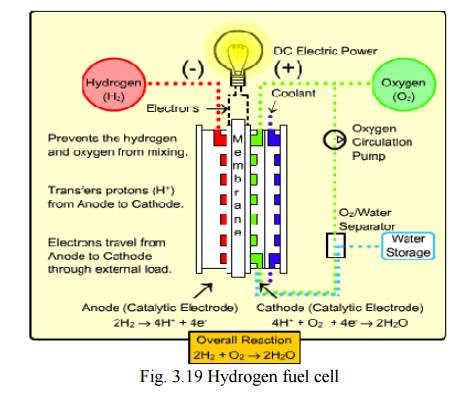
Due to its high calorific value, hydrogen can serve as an excellent fuel.
Moreover
it is non-polluting and can be easily produced.
Presently
H2 is used in the form of liquid hydrogen as a fuel in spaceships.
Hydrogen Fuel
Hydrogen can be produced by thermal dissociation or photolysis
or electrolysis of water. It
possesses high calorific value.
It is non polluting, because the combustion product
is water. 2H2+O2---->2H2O+150KJ
Disadvantages of hydrogen fuel
Hydrogen
is highly inflammable and explosive in nature
Safe
handling is required
It is
difficult to store and transport.
Related Topics