Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 5 : Hydrosphere
Fresh water
Fresh
water
Fresh water is defined as water with a salinity of
less than1% compared to that of the oceans (i.e. below 0.35%). Water with
salinity between 0.35‰ and 1‰ is typically referred to as marginal water
because it is marginal for many uses by humans and animals.
Considering the distribution of fresh water 68.6%
of it is locked in Glaciers and icecaps. About 30.1% is stored as ground water
and the remaining 1.5% is available as surface water.
Surface water includes ice and snow on the land and
sea, water in the lakes, rivers, swamps and marshes, moisture in soil,
atmosphere and biosphere. Rivers and lakes are the major sources of fresh water
around the world, and are vital to the communities they serve.
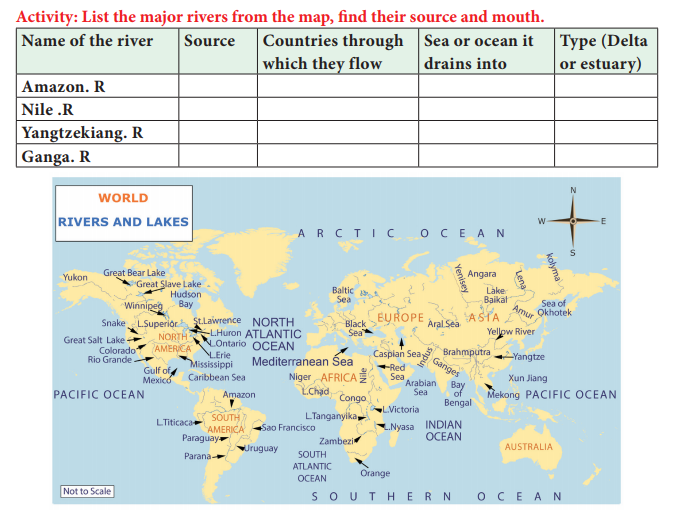
Rivers: Rivers generally have a source on a mountain either from a glacier, a
spring or a lake. River Ganga has its source from Gangotri glacier in the
Himalayas. River Cauvery has its source from a spring in Talacauvery located in
Kodagu district of Karnataka. River Nile has its source near Lake Victoria in
Uganda. The river flows through confined channel between two banks and ends up
at the mouth which is either on a sea or lake. When rivers drain their water
into a lake or an inland sea, it is said to be an inland drainage.
The Nile River in Africa is the longest river in
the world. The Nile River flows through Egypt, Uganda, Ethiopia, Kenya,
Tanzania, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, Burundi, Sudan and Eritrea
drains and into the Mediterranean Sea forming a delta to the north of Cairo
city.
The river Amazon in South America, is the second
longest river, and has the largest drainage basin of any river. The Amazon
River flows through Peru, Colombia, and Brazil and drains into the Atlantic
Ocean forming an estuarine delta.
The Yangtze River, which flows in China, is the
longest river in Asia, and the third longest river in the world. The longest
river system in the United States, the Mississippi-Missouri system is
considered the fourth longest river in the world.
The total volume of water in rivers in the world is
estimated at 2,120 km3. Asia excluding Middle East, has the largest
run off of 13,300 km3/year followed by North America with 12,000 km3
per year.
Lakes: Lakes are larger bodies of water with outlet through a river or stream.
Lakes may have their origin through tectonic activity,
volcanic activity, river, glacier and wave action or sometimes meteoric origin.
Caspian Sea, Lake Baikal and Wular Lake have been formed by earth movements.
Lake Baikal is the deepest freshwater lake in the world. Caspian Sea is the
largest salt water lake in the world.
Lagoon lakes are formed by wave deposition. Chilika
Lake is the largest lagoon lake in India. Lonar Lake in Maharashra is believed
to be formed by depression created by meteor impact which hit during
Pleistocene Epoch.
Wetlands:Wetlands are area of marsh, fen, peat land
or water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of
marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six metres. Marshes
are shallow wetlands around lakes, streams, or the ocean where grasses and
reeds are common, without trees. Rann of Kutch in India is a salt marsh. A
swamp is a wetland with lush trees and vines found in a low-lying area beside
slow-moving rivers. Pallikaranai wetland is fresh water swamp adjacent to the
Bay of Bengal situated in the southern part of Chennai.
Groundwater
Groundwater is the most valuable resource for any
country. The rain water that falls on the earth either runs off as surface
water or percolates into the ground to recharge the groundwater. The permeable
rocks that can hold water and allow water to pass through them are called
aquifers. The upper part of the saturated zone of the aquifer is called the
water table. The level of water table fluctuates according to seasons (Figure
5.1).

Fact
File
Tmc ft,
is the abbreviation for one thousand million cubic feet (1,000,000,000 = 1
billion), commonly used in India with reference to volume of water in a
reservoir or river flow.
Related Topics