Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Textiles And Dress Designing Cloth stitch Higher secondary school College practical steps methods Notes
Classification or Types of printing
PRINTING
Printing produces colourful effect on the fabrics Printing is application of colour in the form of a design. Printing can be done by hand or machine. The dyes used in printing are in the form of pastes.
Types of printing : Printing has been divided into,
A) Hand printing B) Machine printing
A) Hand printing
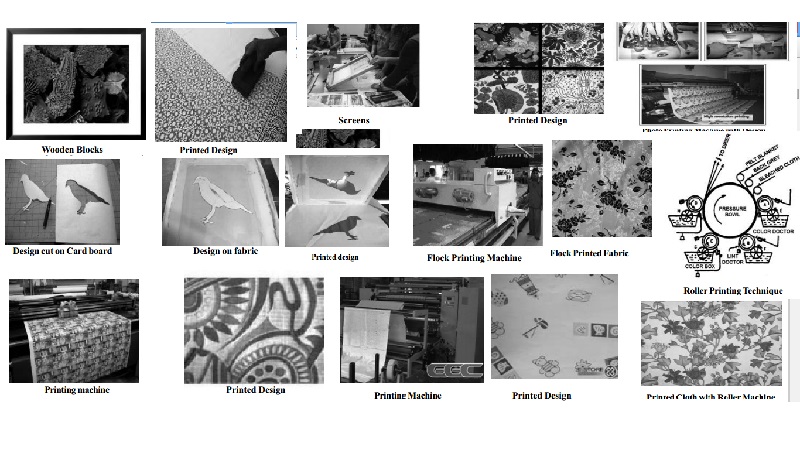
� Block Printing : Block printing was practiced by Chinese and Indians some two thousand years ago. Blocks are made of wood or wood and lino. The design is carved on line which is generally cut to a thickness of � inch. This cut piece of lino is struck to wooden piece of the same size. Many printers use only wooden blocks on which the design has been carved. These blocks are dipped in paste of colour and then pressed on the fabric, so that coloured pattern is produced on the fabric. First a block carrying the paste of one colour is stamped on the fabric and allowed to dry. Then another block carrying the paste of different colour is stamped over it to form the multi-coloured patterns. The process is repeated over the entire fabric surface to be printed.
It is a slow and costly process, uniform pressure is needed to transfer the colour. The intensity of colour cannot be uniform throughout.
� Stencil Printing : Stencil printing originated in Japan. Its high cost limits its use and importance. In this, printing, the design must be first cut in cardboard, wood or metal. The stencil may have a fine delicate design, or there may be large spaces through which a great amount of colour may be applied. A stencil design is usually limited to the application of one or two colours and generally used for narrow width of fabric like block printing. This method is very slow.
� Screen Printing : Originally, this technique was referred to as silk screen printing because the screens were made of fine, strong silk thread. Today they are also made of nylon, polyester, vinyl and metal. Screen printing is done with the use of either flat or cylindrical screens.
Each screen design may be drawn by hand and a coating of lacquer or other impermeable substance applied to all parts of the screen that are not part of its design. Today the design is photographed and a negative is used for each sensitized screen to opaque or block out, those areas not part of the screen's colour design. Each screen is then fitted into a wooden or metal frame.
The printing paste or dye is poured on the screen and forced through its unblocked areas onto the fabric with a rubber-edged squeeze. The frame is then raised and placed on the next section of the fabric and the operation is repeated until the entire length of the cloth is printed with that particular colour. This process must be repeated for each colour to be used in the design.
The hand screen printing is time-consuming and limited to relatively short lengths of 60 yards (58m) of fabric. Electronically controlled automatic machines can screen print long lengths of cloth at rates of upto 450 yards (400m) per hour.
B) Machine Printing
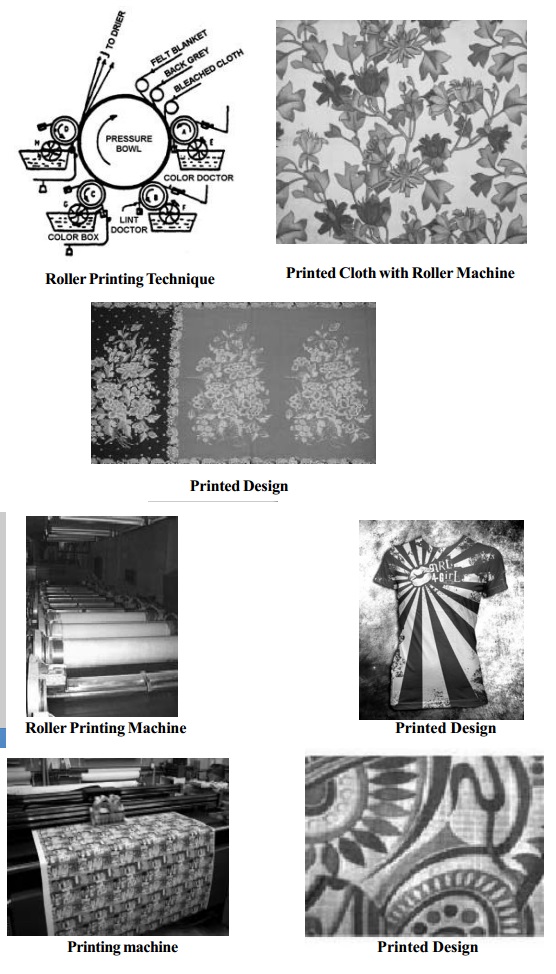
Machine printing includes Direct Roller printing, Duplex printing, discharge printing, resist printing, pigment printing, transfer printing, photo printing and flock printing.
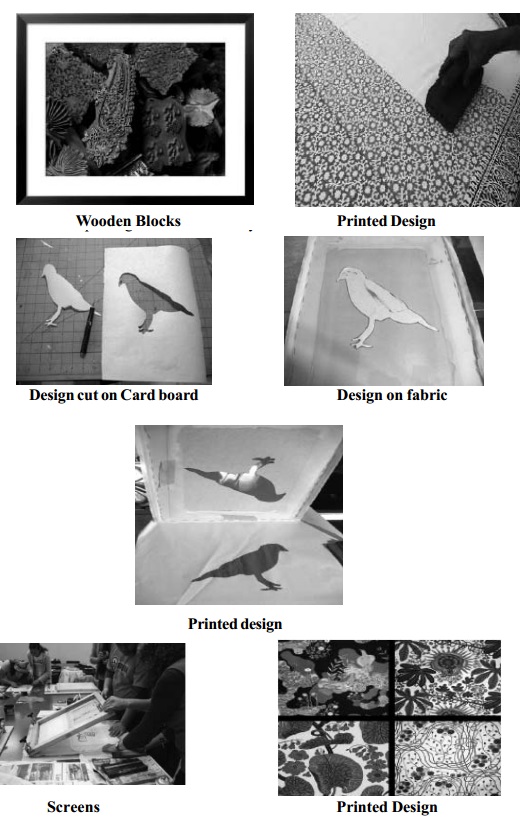
� Direct Roller Printing : Roller printing was developed in 1785. Thousands of yards of coloured designed fabrics are produced in an hour by this method of printing.
In this printing, several copper cylinders or rollers are engraved with design. Engraving the designs on the rollers is a hard and careful work lasting many days, but actual printing by this method takes very little time.
The roller is as wide as the cloth. The numbers of rollers required depends on the number of colours used in the design. One roller prints one colour only.
The roller printing machine comprises of a large central cylinder around which passes the fabric to be printed, this cylinder rotates with the moving fabric. Number of colour printing rollers, carrying different colours, press against the fabric and the central cylinder. Thus if there are five colours in the design there are five colour printing rollers. Each of these rollers is made of copper and engraved with the respective design. Furnished rollers which move at intervals, containing the colour or dye are placed close to the design rollers. The dye is absorbed by the brush like surface and transferred to the design engraved rollers.
Next to the design roller is a big iron cylinder or roller around which the cloth is drawn as it is printed. The cloth to be printed needs a rubberized blanket (for padding) and grey cloth pass between the engraved rollers and the cylinder. The blanket gives a good surface for sharp printing and the grey cloth protects the blanket besides absorbing the excess dye.
Printing machines of this kind can be provided with upto fourteen rollers, as they are able to produce patterns in fourteen colours. The roller printing machine prints only on one side of the fabric.
� Duplex Printing : In Duplex printing, the printing is done on both the sides. The fabric may be passed through the roller printing machine in separate operations. This printing forms clear outline on both sides of fabric.
� Discharge Printing : This type of printing is suitable for fabrics with dark backgrounds. The fabric is first dyed. A discharge paste which contains chemicals to remove the colour is then printed on the fabric, to produce a white pattern on a ground colour. This print is done on materials like cotton and rayon.
Resist Printing : This is just the opposite of discharge printing. In this type of printing, resist paste is printed first on the white fabric, and the fabric is then piece dyed. The resist materials used are resins, or clay or gum. It is put in a patterned form on fabric and is subsequently immersed in dye. The dye will affect only the parts that are not covered by the resist paste. The places where resist material has been put remain undyed. After fabric has been passed through subsequent dyeing processes, the resist paste is removed, leaving a pattern on dark background.
Pigment Printing : In this, dyes used are insoluble in water and very fast to light. These pigments are made into colour printing paste, using various ingredients especially resin to act as binder and the pigment to the printed fabric.
� Transfer Printing : In this process, certain substances can be made to pass from a solid state directly to a vapour state when heated and return directly to a solid when cooled. The design is printed to a paper, which is fed into a machine. This is brought into contact with heat zone, which vapourizes the dye on the paper. Thus the dye is absorbed by the fabric.
� Photo Printing : In this type, the fabric is coated with a chemical that is sensitive to light. The negative of the design is put against the fabric surface and the light is made to fall on it. The design on the negative gets printed on the fabric. The fabric is then washed. Black and white designs and coloured designs can be printed on the fabric.
� Flock Printing : This is a technique of adhering minute pieces of fibre, called flock, to form design on fabrics. Using a suitable adhesive, a design is roller printed onto the fabric. Then flock of cotton, wool, viscose rayon, nylon or acrylic are applied to the fabric in a manner that causes it to adhere in an upright position and produce a pile like, velvet - textured design.

CONCLUSION
Thus dyeing and printing methods are adopted to enhance the beauty of the textile materials.
Related Topics