Classification | Biomolecules | Chemistry - Vitamins | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Biomolecules
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Biomolecules
Vitamins
Vitamins:
Vitamins are small organic compounds that cannot be synthesised by our
body but are essential for certain functions. Hence, they must be obtained
through diet. The requirements of these compounds are not high, but their
deficiency or excess can cause diseases. Each vitamin has a specific function
in the living system, mostly as co enzymes. They are not served as energy
sources like carbohydrates, lipids, etc.,
The name ‘Vitamin’ is derived from ‘vital amines’, referring to the
vitamins earlier identified amino compounds. Vitamins are essential for the
normal growth and maintenance of our health.
Classification of vitamins
Vitamins are classified into two groups based on their solubility either
in water or in fat.
Fat
soluble vitamins: These vitamins absorbed best when taken with fatty
food and are stored in fatty tissues
and livers. These vitamins do not dissolve in water. Hence they are called fat
soluble vitamins. Vitamin A, D, E & K are fat-soluble vitamins.
Water
soluble vitamins: Vitamins B (B1, B2, B3,
B5, B6, B7, B9 and B12) and C are readily soluble in water. On the contrary to fat soluble vitamins, these can’t be
stored. The excess vitamins present will be excreted through urine and are not
stored in our body. Hence, these two vitamins should be supplied regularly to
our body. The missing numbers in B vitamins are once considered as vitamins but
no longer considered as such, and the numbers that were assigned to them now
form the gaps.
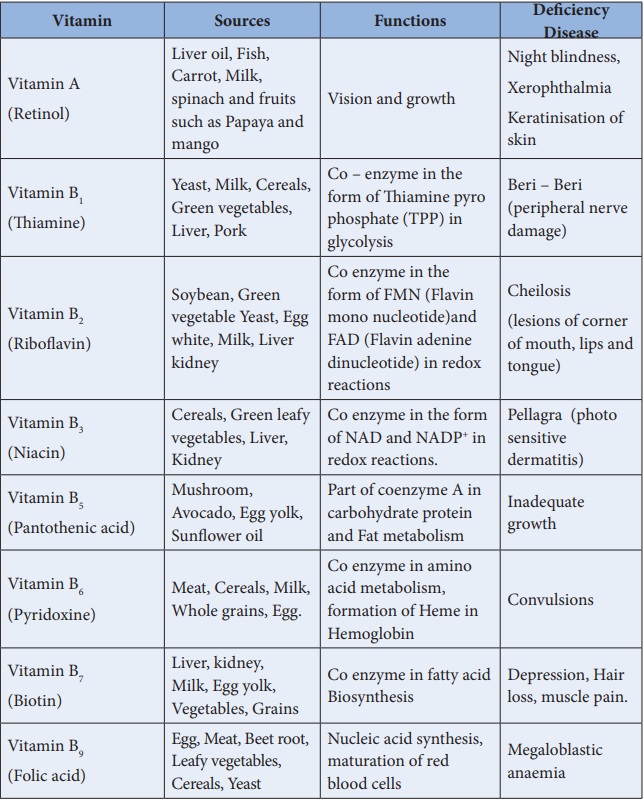
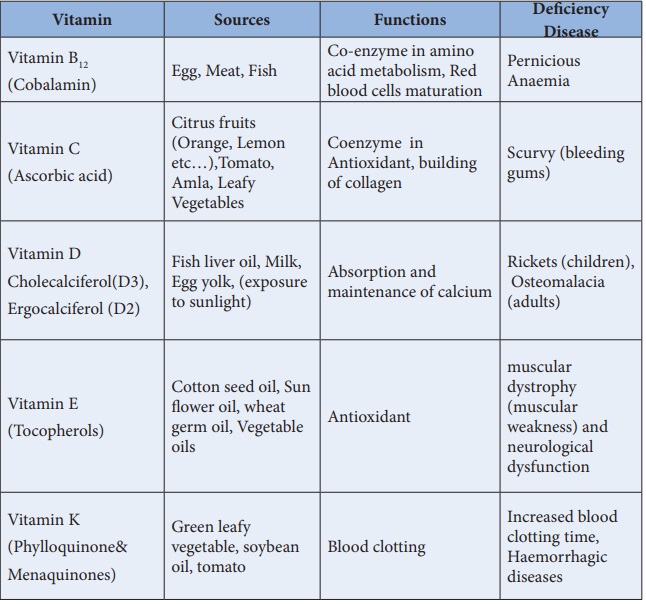
Table 14.2: Vitamins, their Sources, Functions and their
Deficiency disease
Related Topics