Biomolecules | Chemistry - Disaccharides | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Biomolecules
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Biomolecules
Disaccharides
Disaccharides
Disaccharides are sugars that yield two molecules of monosaccharides on
hydrolysis. This reaction is usually catalysed by dilute acid or enzyme.
Disaccharides have general formula Cn(H2O)n-1.In
disaccharides two monosaccharide’s are linked by oxide linkage called ‘glycosidic
linkage’, which is formed by the
reaction of the anomeric carbon of one monosaccharide reacts with a hydroxyl group of another
monosaccharide.
Example: Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose
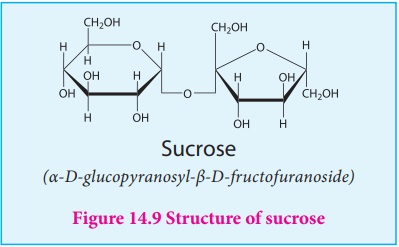
Sucrose: Sucrose,
commonly known as table sugar is the
most abundant disaccharide. It is obtained mainly from the juice of sugar cane
and sugar beets. Insects such as honey bees have the enzyme called invertases
that catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose to a glucose and fructose mixture.
Honey in fact, is primarily a mixture of glucose, fructose and sucrose.
On hydrolysis sucrose yields equal amount of glucose and fructose units.
Sucrose ----- Invertase → Glucose + Fructose
Sucrose (+66.6°) and
glucose (+52.5°) are
dextrorotatory compounds while fructose is levo rotatory (-92.4°). During
hydrolysis of sucrose the optical rotation of the reaction mixture changes from
dextro to levo. Hence, sucrose is also called as invert sugar.
Structure:
In sucrose, C1 of α-D-glucose is joined to C2 of β-D-fructose. The glycosidic bond thus formed is called α-1,2 glycosidic bond. Since, both the carbonyl carbons (reducing groups) are involved in the glycosidic bonding, sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
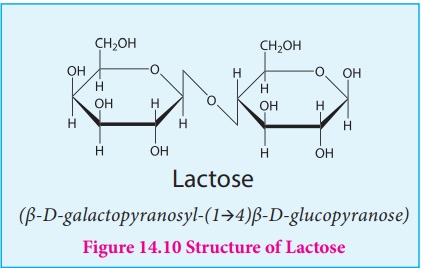
Lactose: Lactose is a disaccharide found in milk of mammals and hence it is referred to as milk sugar. On hydrolysis, it yields galactose and glucose. Here, the β-D–galactose and β-D–glucose are linked by β-1,4 glycosidic bond as shown in the figure 14.10 . The aldehyde carbon is not involved in the glycosidic bond hence, it retains its reducing property and is called a reducing sugar.
Maltose: Maltose
derives its name from malt from
which it is extracted. It is commonly called as malt sugar. Malt from sprouting
barley is the major source of maltose. Maltose is produced during digestion of
starch by the enzyme α-amylase.
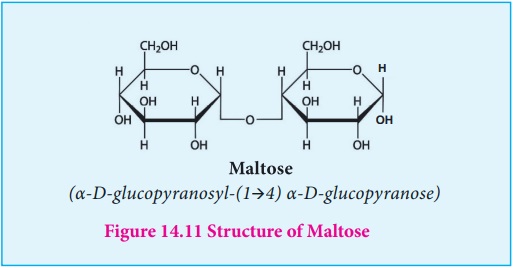
Maltose consists two molecules of α-D-glucose
units linked by an a-1,4
glycosidic bond between anomeric carbon of one unit and C-4 of the other unit.
Since one of the glucose has the carbonyl group intact, it also acts as a
reducing sugar.
Related Topics