Classification, Properties, Peptide bond formation | Proteins - Amino acids | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Biomolecules
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Biomolecules
Amino acids
Proteins
Proteins are most abundant biomolecules in all living organisms. The
term protein is derived from Greek word ‘Proteious’
meaning primary or holding first place. They are main functional units for the
living things. They are involved in every function of the cell including
respiration. Proteins are polymers of α-amino acids.
Amino acids
Amino acids are compounds which contain an amino group and a carboxylic
acid group. The protein molecules are made up α-amino acids which can be represented by the
following general formula.
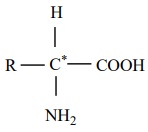
There are 20 α-amino
acids commonly found in the protein molecules. Each amino acid is given a
trivial name, a three letter code and a one letter code. In writing the amino
acid sequence of a protein, generally either one letter or three letter codes
are used.
Classification of α-amino acids
The amino acids are classified based on the nature of their R groups
commonly known as side chain. They can be classified as acidic, basic and
neutral amino acids. They can also be classified as polar and non-polar
(hydrophobic) amino acids.
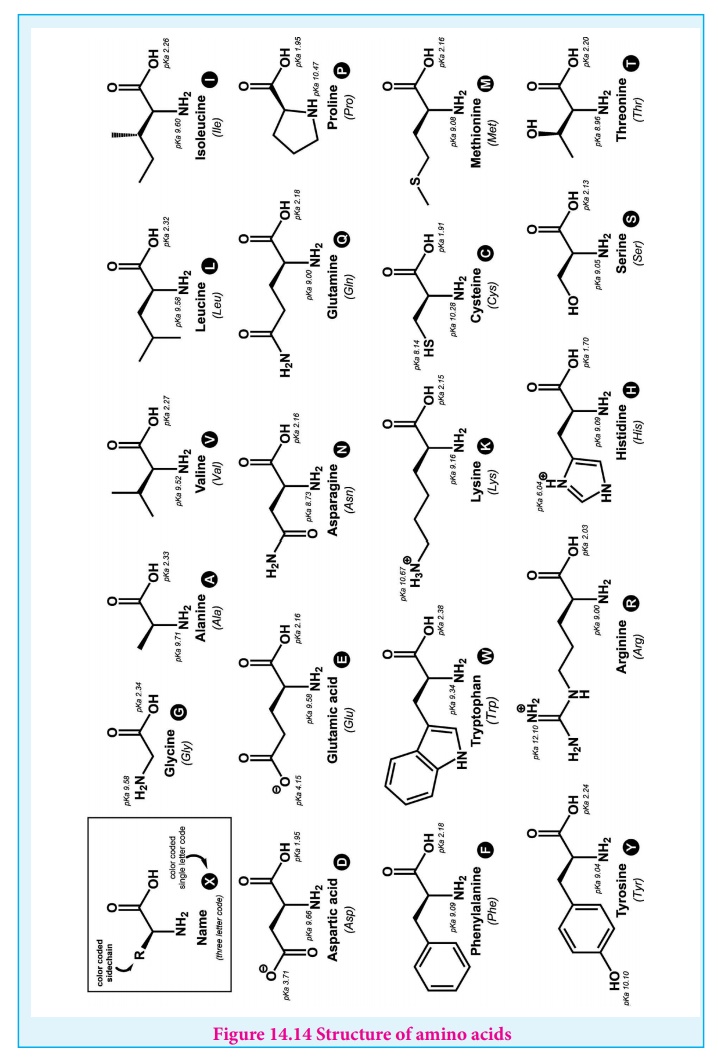
Amino acids can also be classified as essential and non-essential amino
acids based on the ability to be synthesise by the human. The amino acids that
can be synthesised by us are called non-essential amino acids (Gly, Ala, Glu,
Asp, Gln, Asn, Ser, Cys, Tyr & Pro) and those needs to be obtained through
diet are called essential amino acids (Phe, Val, Thr, Trp, Ile, Met, His, Arg,
Leu and Lys). These ten essential amino acids can be memorised by mnemonic
called PVT TIM HALL.
Although the vast majority of plant and animal proteins are formed by
these 20 α- amino
acids, many other amino acids are also found in the cells. These amino acids
are called as non–protein amino acids. Example: ornithine and citrulline
(components of urea cycle where ammonia is converted into urea)
Properties of amino acid
Amino acids are colourless, water soluble crystalline solids. Since they
have both carboxyl group and amino group their properties differ from regular
amines and carboxylic acids. The carboxyl group can lose a proton and become
negatively charged or the amino group can accept a proton to become positively
charged depending upon the pH of the solution. At a specific pH the net charge
of an amino acid is neutral and this pH is called isoelectric point. At a pH above the isoelectric point the amino
acid will be negatively charged and positively charged at pH values below the
isoelectric point.
In aqueous solution the proton from carboxyl group can be transferred to
the amino group of an amino acid leaving these groups with opposite charges.
Despite having both positive and negative charges this molecule is neutral and
has amphoteric behaviour. These ions are called zwitter ions.
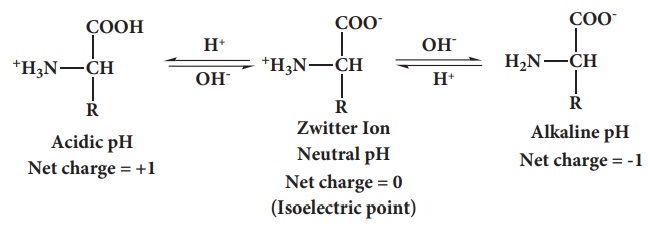
Except glycine all other amino acids have at least one chiral carbon
atom and hence are optically active. They exist in two forms namely D and L
amino acids. However, L-amino acids are used predominantly by the living
organism for synthesising proteins. Presence of D-amino acids has been observed
rarely in certain organisms.
Peptide bond formation
The amino acids are linked covalently by peptide bonds. The carboxyl
group of the first amino acid react with the amino group of the second amino
acid to give an amide linkage between these amino acids. This amide linkage is
called peptide bond. The resulting
compound is called a dipeptide. Addition an another amino acid to this
dipeptide a second peptide bond results in tripeptide. Thus we can generate
tetra peptide, penta peptide etc… When you have more number of amino acids
linked this way you get a polypeptide. If the number of amino acids are less it
is called as a polypeptide, if it has large number of amino acids (and
preferably has a function) then it is called a protein.
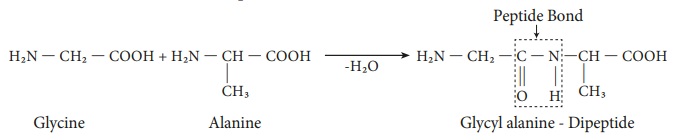
The amino end of the peptide is known as N-terminal or amino terminal
while the carboxy end is called C-terminal or carboxy terminal. In general
protein sequences are written from N-Terminal to C-Terminal. The atoms other
than the side chains (R-groups) are called main chain or the back bone of the
polypeptide.
Related Topics