Biomolecules | Chemistry - Polysaccharides | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Biomolecules
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 14 : Biomolecules
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides:
Polysaccharides consist of large number of monosaccharide units bonded
together by glycosidic bonds and are the most common form of carbohydrates.
Since, they do not have sweet taste polysaccharides are called as non-sugars.
They form linear and branched chain molecules.
Polysaccharides are classified into two types, namely, homopolysaccharides
and heteropolysaccharides depending upon the constituent monosaccharides.
Homopolysaccharides are composed of only one type of monosaccharides while the
heteropolysaccharides are composed of more than one. Example: starch, cellulose
and glycogen (homopolysaccharides); hyaluronic acid and heparin
(heteropolysaccharides).
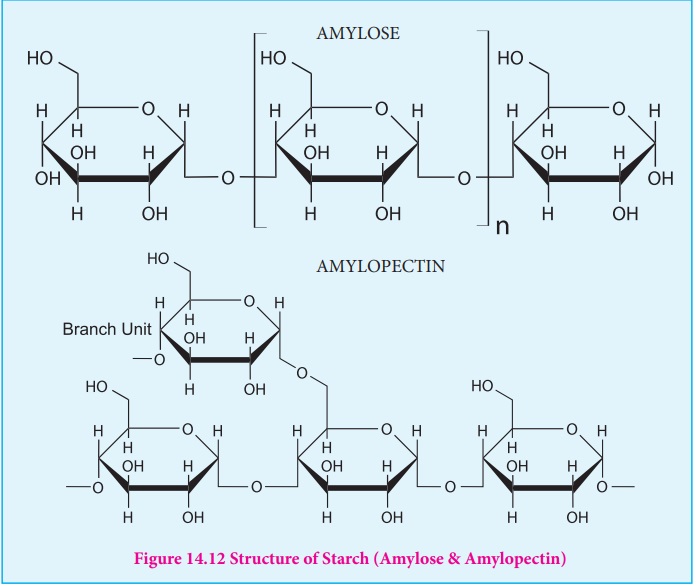
STARCH
Starch is used for energy storage in plants. Potatoes, corn, wheat and
rice are the rich sources of starch. It is a polymer of glucose in which
glucose molecules are lined by α (1,4)
glycosidic bonds. Starch can be separated into two fractions namely, water
soluble amylose and water insoluble amylopectin. Starch contains about 20 % of
amylose and about 80% of amylocpectin.
Amylose is composed of unbranched chains upto 4000 α-D-glucose
molecules joined by α(1,4)glycosidic
bonds. Amylopetin contains chains upto 10000 α-D-glucose molecules linked by α(1,4)glycosidic
bonds. In addition, there is a branching from linear chain. At branch points,
new chains of 24 to 30 glucose molecules are linked by α(1,6)glycosidic
bonds. With iodine solution amylose gives blue colour while amylopectin gives a
purple colour.
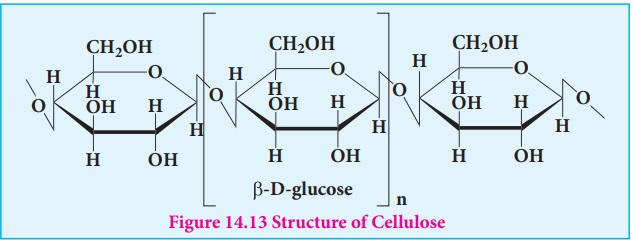
Cellulose
Cellulose is the major constituent of plant cell walls. Cotton is almost
pure cellulose. On hydrolysis cellulose yields D-glucose molecules. Cellulose
is a straight chain polysaccharide. The glucose molecules are linked by β(1,4)glycosidic
bond.
Cellulose is used extensively in the manufacturing paper, cellulose
fibres, rayon explosive, (Gun cotton – Nitrated ester of cellulose) and so on.
Human cannot use cellulose as food because our digestive systems do not contain
the necessary enzymes (glycosidases or cellulases) that can hydrolyse the
cellulose.
Glycogen:
Glycogen
is the storage polysaccharide of animals. It is present in the liver and muscles of animals. Glycogen is also
called as animal starch. On hydrolysis it gives glucose molecules.
Structurally, glycogen resembles amylopectin with more branching. In glycogen
the branching occurs every 8-14 glucose units opposed to 24-30 units in
amylopectin. The excessive glucose in the body is stored in the form of
glycogen.
Related Topics