Vermicomposting, Advantages of Using Vermicompost - Vermiculture | 11th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Trends in Economic Zoology
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Trends in Economic Zoology
Vermiculture
Vermiculture
Vermiculture
is the
process of using earthworms to decompose organic food waste, into a nutrient-rich material capable
of supplying necessary nutrients which helps to sustain plant growth. The aim
is to continually increase the number of worms to have a sustainable harvest.
The excess worms can either be used to expand a vermicomposting operation or
sold to customers. Vermicompost is the primary goal of vermiculture.
Technically, the worm castings are pure worm waste and are fine and nutrient
rich organic soil amendment. Vermicompost on the other hand, is comprised of
the castings, bits of bedding and other organic matter Essentially, though the
terms are used interchangeably, they are both worm manure and are valuable for
improving soil health. Applications of earthworm in technology of composting
and bioremediation of soils and other activities is called Vermitech (Sultan
Ismail, 1992).
The disposal of solid wastes (bio-degradable and
non- biodegradable) remains a serious challenge in most of the countries.
Earthworms play a vital role in maintaining soil fertility; hence these worms
are called as “farmer’s friends”.
These are also called as “biological
indicators of soil fertility”. The reason is that they support bacteria,
fungi, protozoans and a host of other organisms which are essential for
sustaining a healthy soil. The breakdown of organic matter by the activity of
the earthworms and its elimination from its body is called vermicast. It is a
finely divided granular material and is noted for its porosity, aeration,
drainage and moisture holding capacity and serves as rich organic manure.
Earthworms are divided into two major groups. The first group, the humus formers, dwell on the surface and feed on organic matter. They are generally darker in colour. These worms are used for vermicomposting. The second group, the humus feeders, are burrowing worms that are useful in making the soil porous, and mixing and distributing humus through out the soil.
There are different endemic
(native) species of earthworms cultured in India for vermicomposting such as Periyonyx excavatus, Lampito mauritii,
Octochaetona serrata. Some earthworm species
have been introduced from other countries and called as exotic species Eg. Eisenia
fetida, Eudrilus eugeniae.
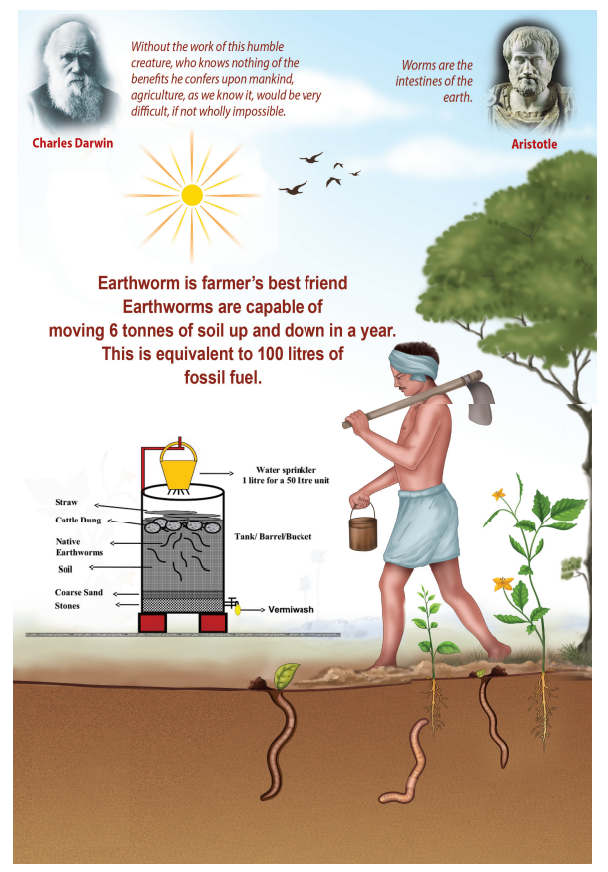
Vermicomposting
Vermicompost is the compost produced by the action
of earthworms in association with all other organisms in the compost unit.
Vermicompost bed may be selected on upland or an elevated level as it prevents
the stagnation of water. You may construct a cement pit of 3x2x1m size (LxWxD)
over ground surface using bricks. The size of pit may vary as per availability
of raw materials. Cement pot or well rings are practically good. Provision
should be made for excess water to drain. The vermibed should not be exposed to
direct sunlight and hence shade may be provided (Figure. 13.1). The first layer
of vermibed contains gravel at about 5 cm in height, followed by coarse sand to
a thickness of 3.5 cm, which will facilitate the drainage of excess water.

Earthworms collected from native soil prefer a
layer of local soil in their compost beds. If local soil earthworms are used,
add a layer of native loamy soil for about 15 cm on top of the gravel sand
layer and introduce earthworms into it. For exotic species such as Eisenia fetida and Eudrilus eugeniae, the layer of soil is not needed. The unit can
now be loaded with digested biomass or animal dung such as cow dung that has
lost its heat. The number of earthworms to be introduced in an unit depends on
the size of the vermibed prepared. Earthworms such as Periyonyx. excavatus, Eisenia fetida
or Eudrilus eugeniae are
introduced on the top. Jute bags or cardboards or broad leaves are used to cover the unit. As worms require moisture,
water management is most important for the survival of the earthworms. Too
little or too much of water is not good for the worms.
Earthworms release their castings on the surface.
One can start harvesting this from the surface on noticing the castings on the
surface. It may take several days for the entire biomass to be composted
depending on the amount of biomass.
When all the compost is harvested, earthworms can
be handpicked by creating small conical heaps of harvested compost and leaving
in sunlight for a few hours. The earthworms then move down and settle at the bottom
of the heap as a cluster. Earthworms from the lower layers of the compost can
be recovered and the worms can be transferred to new composting units.
Vermiwash is a liquid collected after the passage
of water through a column of vermibed. It is useful as a foliar spray to
enhance plant growth and yield. It is obtained from the burrows or drilospheres formed by earthworms.
Nutrients, plant growth promoter substances and some useful microorganisms are
present in vermiwash.
Earthworm Pests and Diseases
Earthworms are subjected to attack by a variety of
pests. Most outbreaks are the result of poor bed management. Earthworm enemies
include ants, springtails, centipedes, slugs, mites, certain beetle larvae,
birds, rats, snakes, mice, toads, and other insects or animals which feed on
worms. The earthworm has a number of internal parasites including numerous
protozoa, some nematodes, and the larvae of certain flies. Larger predators can be excluded from worm beds by proper
construction of the bins, and by use of screens or gratings at the bottom and
top of the beds.
Advantages of Using Vermicompost
People are aware about benefits of organic inputs
in farming. Vermicompost is excellent organic manure for sustainable
agro-practices. So, marketing vermicompost is now a potential and flourishing
industry. Retail marketing of vermicompost in urban areas is most promising.
Vermicompost is neatly packed in designed and printed packets for sale. People
of different age groups are involved in the production and selling of
vermicompost. Marketing of vermicompost can provide a supplementary income.
•
Vermicompost is rich in essential plant nutrients.
•
It improves soil structure texture, aeration, and
water holding capacity and prevents soil erosion
•
Vermicompost is a rich in nutrients and an
eco-friendly amendment to soil for farming and terrace gardening.
•
It enhances seed germination and ensures good plant
growth
Related Topics