Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Trends in Economic Zoology
Animal Husbandry and Management
Animal Husbandry and Management
Animal husbandry is the practice of breeding and
raising livestock cattles like cows, buffaloes, and goats and birds etc. that
are useful to human beings. Parameters such as adequate ventilation,
temperature, sufficient light, water and proper housing accommodation should be
taken into account to maintain dairy and poultry farms. Animals should be cared
and protected from diseases. Records should be maintained after the regular
visits by Veterinarian. More over the selection of good breeds with high
yielding potential combined and resistance to diseases is very important.
Animal Breeding
Human beings have been depending on animals and
animal products for food from very early times. Generally high yielding animals
produced by hybridization are reared in poultry and dairy farms. In earlier
days, animals were produced and selected based on specific characters. With the
gain in knowledge on the principles of heredity and genetics, human beings have
been successful in rearing animals with the superior qualities through
hybridization experiments. Complex issues are faced by the animal breeder
during hybridization experiments. Hence animals with maximum desirable characters
should be selected.
A group of animals related by descent and with
similar characters like general appearance, features, size etc., are said to
belong to a breed. Why should we breed animals? Through
animal breeding, improved breeds of animals can be produced by improving their
genotype through selective breeding.
Objectives of Animal breeding:
a)
To improve growth rate
b)
Enhancing the production of milk, meat. Egg etc.,
c)
Increasing the quality of the animal products
d)
Improved resistance to diseases
e)
Increased reproductive rate
Methods of Animal breeding:
There are two methods of animal breeding, namely
inbreeding and outbreeding
1. Inbreeding:
Breeding
between animals of the same breed for 4-6 generations is called inbreeding. Inbreeding increases homozygosity and exposes
the harmful recessive genes. Continuous inbreeding reduces fertility and even
productivity, resulting in “inbreeding depression”. This can be avoided by
breeding selected animals of the breeding population and they should be mated
with superior animals of the same breed but unrelated to the breeding
population. It helps to restore fertility and yield.
1.
Outbreeding:
The
breeding between unrelated animals is called outbreeding. Individuals produced do not have common ancestors for 4-6 generations.
Outbreeding helps to produce new and favourable traits, to produce hybrids with
superior qualities and helps to create new breeds. New and favourable genes can
be introduced into a population through outbreeding.
i. Out
crossing: It is the breeding between unrelated animals of the same breed
but having no common ancestry. The offspring of such a cross is called
outcross. This method is suitable for breeding animals below average in
productivity.
ii. Cross
breeding: Breeding between a superior male of one breed with a superior female of another breed. The cross
bred progeny has superior traits ( hybrid vigour or heterosis.)
iii. Interspecific hybridization:
In this method of breeding mating is between male
and female of two different species. The progeny obtained from such crosses are
different from their parents, and may possess the desirable traits of the
parents. Have you heard about Mule? It was produced by the process of
interspecific hybridization between a male donkey and a female horse.
Controlled breeding experiments
Artificial insemination:
Artificial insemination is a technique in which the
semen collected from the male is injected to the reproductive tract of the
selected female. Artificial insemination is economical measure where fewer
bulls are required and maximum use can be made of the best sire.
Advantages of artificial insemination
a.
It increases the rate of conception
b.
It avoids genital diseases
c.
Semen can be collected from injured bulls which
have desirable traits.
d.
Superior animals located apart can be bred
successfully.
Multiple ovulation embryo transfer technology (MOET)
It is another method of propagation of animals with
desirable traits. This method is applied when the success rate of crossing is
low even after artificial insemination. In this method Follicle stimulating
hormone (FSH) is administered to cows for inducing follicular maturation and
super ovulation. Instead of one egg per cycle, 6-8 eggs can be produced by this
technology. The eggs are carefully recovered non-surgically from the genetic
mother and fertilized artificially. The embryos at 8-32 celled stages are
recovered and transferred to a surrogate mother. For another round of
ovulation, the same genetic mother is utilized. This technology can be applied
to cattle, sheep and buffaloes. Advantage of this technology is to produce high
milk yielding females and high-quality meat yielding bulls in a short time.
Breeds of Dairy animals
Dairying is the production and marketing of milk
and its products. Dairy operation consists of proper maintenance of cattle, the
collection and processing the milk and its by products. There are 26 well
defined breeds of cattle and 6 breeds of buffaloes in India. Cattles are
classified under three groups based on the purpose they serve to man (Figure
13. 13). They are
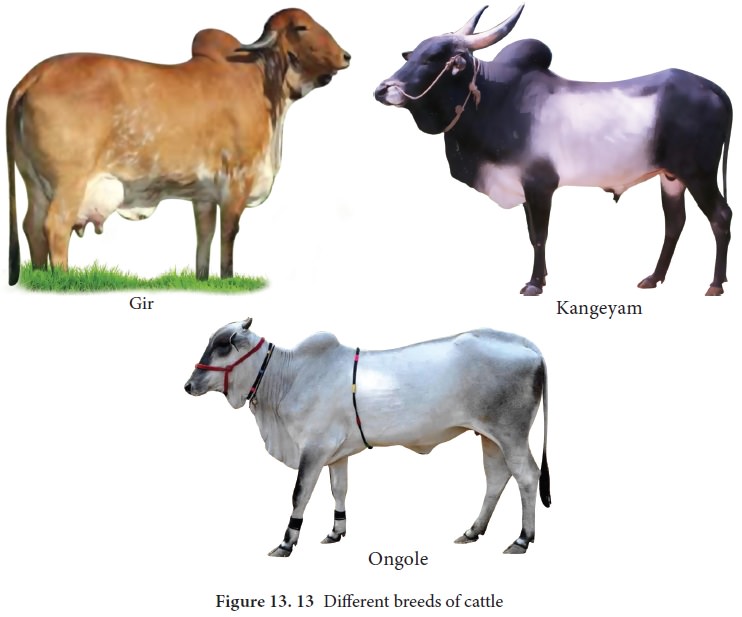
1.
Dairy
breeds or Milch breeds: They are high milk yielders with extended lactation. Eg., Sindhi, Gir,
Sahiwal, Jersy, Brown Swiss, Holstein cattle.
2.
Draught
purpose breeds: Bullocks are good for draught purpose. Eg. Kangayam, Malvi
3.
Dual
Purpose breeds: Cows are meant for yielding more milk and bullocks are used for better drought
purpose. Eg. Ongole, Hariana
To meet the milk demand of the growing population,
milk breeds are preferred by farmers in small scale farms. Goats are also used
all over India for supplementing deficiencies in milk production. Some of the
breeds of cattle that are good milkers are Jamunapari in Ganga-Jamuna riverine
tracts, Beetal in Punjab, Bar–bari in Uttarpradesh.
Common diseases of cattle: A healthy animal eat, drinks and sleeps well regularly. Healthy cattle appear bright, alert and active in their movement with a shiny coat. Cattle are affected by a large number of diseases.
Cattle in ill health appear dull,
restless and change posture frequently with drop in milk yield. The main
diseases of dairy cattle are rinderpest, foot and mouth disease, cow pox,
hemorrhagic fever, anthrax.
Uses of dairy products:
Milk
products: Milk is produced by dairy animals which is an emulsion of fat and lactose. Milk also contains enzymes
which are destroyed during pasteurization. Milk is a rich source of vitamin A,
B2 , B1 , and deficient in Vitamin C. Due to its high nutrition value, it
serves as a complete food for infants. Dairy products such as yoghurt, cheese,
butter, ice cream, condensed milk, curd, and milk powder processed from milk
make dairy, a highly farming attraction.
Meat: Meat is
rich in protein and also contains many minerals like iron, zinc, vitamins and selenium. It also contains
vitamins needed for human diet.
Land
management: Grazing of livestock is sometimes used as a way to
control weeds and undergrowth.
Manure: Manure
can be spread on agriculture fields to increase crop yields.
Poultry Farming
The word poultry refers to the rearing and
propagation of avian species such as chicken, ducks, turkeys, geese, quail and
guinea fowls. The most common and commercially farmed birds are chicken and
ducks. Poultry farming is essential for the purpose of meat, eggs and feather
production. Commercial poultry farming is also profitable. In this part we are
discussing about an overview of the chicken and duck breeds, farming practices
and its advantages.
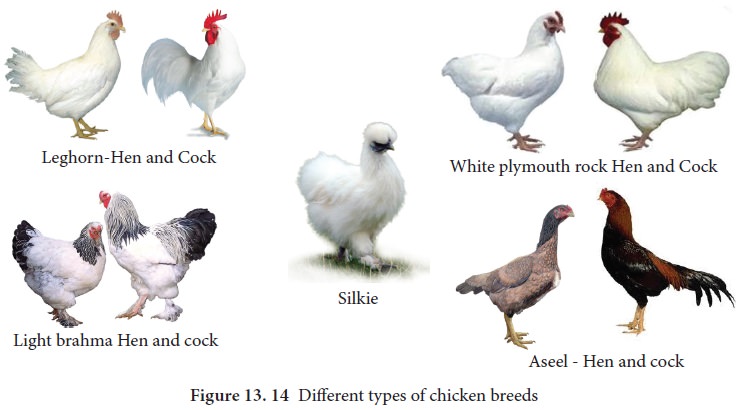

Types of
Chicken breeds: There are more than 100 breeds. The commonly farmed chicken breeds are categorized into
five based on the purpose for which it is farmed. They are egg layers, broiler
type, dual type, games and ornamental types (Figure 13.14).
![]()
1. Egg layers: These are farmed mainly for the production of egg.
Leghorn: This is
the most popular commercial breed in India and originated from Italy. They are small, compact with a
single comb and wattles with white, brown or black colour. They mature early
and begin to lay eggs at the age of 5 or 6 months. Hence these are preferred in
commercial farms. They can also thrive well in dry areas.
Chittagong:
It is the
breed chiefly found in West Bengal. They are golden or light yellow coloured. The beak is long and
yellow in colour. Ear lobes and wattles are small and red in colour. They are
good egg layers and are delicious.
2. Broiler type: These are well known for fast growth and soft quality meat.
White
Plymouth rock: They have white plumage throughout the body. It is commonly used in broiler production.
This is an American breed. It is a fast growing breed and well suitable for
growing intensively in confined farms.
3. Dual
purpose breeds: These are for both meat and egg production purpose.
Brahma: It is a
breed popularly known for its massive body having heavy bones, well feathered and proportionate body. Pea
comb is one of The important breed characters. It has two common varieties
namely, Light Brahma and Dark Brahma.
4. Game
breeds: Since ancient times, special breed of roosters have been used for the sport of cockfighting.
Aseel: This
breed is white or black in colour. The hens are not good egg layers but are good in incubation of eggs. It is
found in all states of India. Aseel is noted for its pugnacity, high stamina,
and majestic gait and dogged fighting qualities. Although poor in productivity,
this breed is well-known for their meat qualities.
5. Ornamental
breeds: Ornamental chicken are reared as pets in addition to their use for egg production and meat.
Silkie : It is a breed of chicken has a typical fluffy plumage, which is said to feel like silk and satin.
The breed has numerous additional special characters, such as
black skin and bones, blue earlobes, and five toes on each foot, while the
majority chickens only have four. They are exhibited in poultry shows, and come
out in various colours. Silkies are well recognized for their calm, friendly
temperament. Silkie chicken is especially simple to maintain as pets.
Types of
Poultry farming: There are different methods used to rear both broiler
and layer chicken. The types of
poultry farming are Free range farming, Organic method, Yarding method, Battery
cage method and Furnished cage method
Among these, Battery cage method is widely used in
large scale poultry farms. The Free range, Organic and Yarding methods are eco-
friendly and the eggs produced by such farming practices are preferred in the
market.
Stages involved in rearing:
There are some steps involved in rearing of
chicken.
1. Selection
of the best layer: An active intelligent looking bird, with a bright comb, not
obese should be selected.
2. Selection
of eggs for hatching: Eggs should be selected very carefully. Eggs should be
fertile, medium sized, dark brown shelled and freshly laid eggs are preferred
for rearing. Eggs should be washed, cleaned and dried.
3. Incubation
and hatching: The maintenance of newly laid eggs in optimum condition till
hatching is called incubation. The fully developed chick emerges out of egg
after an incubation period of 21 – 22 days. There are two types of incubation
namely natural incubation and artificial incubation.In the natural incubation
method, only a limited number of eggs can be incubated by a mother hen. In
artificial incubation, more number of eggs can be incubated in a chamber (Incubator).
3.
Brooding
Caring and management of young chicks for 4– 6
weeks immediately after hatching is called brooding. It can also be categorized
into two types namely natural and artificial brooding.
4.
Housing of Poultry
To protect the poultry from sun, rain and predators
it is necessary to provide housing to poultry. Poultry house should be
moisture- proof, rat proof and it should be easily cleanable and durable.
5 Poultry
feeding: The diet of chicks should contain adequate amount of water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats,
vitamins and minerals.
Poultry
products: The main products of poultry farming are eggs and meat. In India, the primary aim of poultry farming is
to obtain eggs. The eggs and poultry meat are the richest sources of proteins
and vitamins.
Poultry byproducts:
The feathers of poultry birds are used for making
pillows and quilts. Droppings of poultry can be used as manure in fields. The
droppings are rich in nitrogen, potash and phosphates.
A number of poultry byproducts like blood-meal,
feather meal, poultry by-product meal and hatchery by-product meal are used as
good sources of nutrients for meat producing animals and poultry. These
byproducts supply proteins, fats, vitamins and good amount of minerals.
Poultry
diseases: Ranikhet, Coccidiosis, and Fowl pox are some common poultry diseases.
Benefits of Poultry farming:
The advantages of poultry farming are
a)
It does not require high capital for construction
and maintenance of the poultry farming.
b)
It does not require a big space.
c)
It ensures high return of investment within a very
short period of time.
d)
It provides fresh and nutritious food and has a
huge global demand. It provides employment opportunities for the people.
Duck Farming
Duck is an aquatic bird and forms only 6% of our
country’s poultry population. There are about 20 breeds of ducks. The native
one includes Indian Runner and Syhlet meta. The exotic breeds include Muscori,
Pekin, Aylesbury and Campbell. Domesticated ducks have been derived from the
wild duck named Mallard (Anas boscas).
Farming ducks is profitable as it can be combined with aquafarming practices.
Peculiarity of ducks:
The body is fully covered with oily feathers. They
have a layer of fat under their skin which prevents it from getting wet. They
lay eggs at night or in the morning. The ducks feed on rice bran, kitchen
wastes, waste fish and snails.
Types of
breeds: There are three types of ducks depending on the purpose for which it is formed. They are meat productive duck
breeds, egg productive duck breeds, and breeds for both meat and egg
production.
Advantages of duck farming:
They can be reared in small backyards where water
is available and needs less care and management as they are very hardy. They
can adapt themselves to all types of environmental conditions and are breed for
feed efficiency, growth rate and resistance to diseases.
Related Topics