Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Trends in Economic Zoology
Fish culture
Fish culture
Characteristics of cultivable fishes
The special characteristic features of cultivable
fishes are:
i.
Fishes should have high growth rate in short period
for culture.
ii.
They should accept supplementary diet.
iii.
They should be hardy enough to resist some common
diseases and infection of parasites.
iv.
Fishes proposed for polyculture should be able to
live together without interfering or attacking other fishes.
v.
They should have high conversion efficiency so that
they can effectively utilize the food.
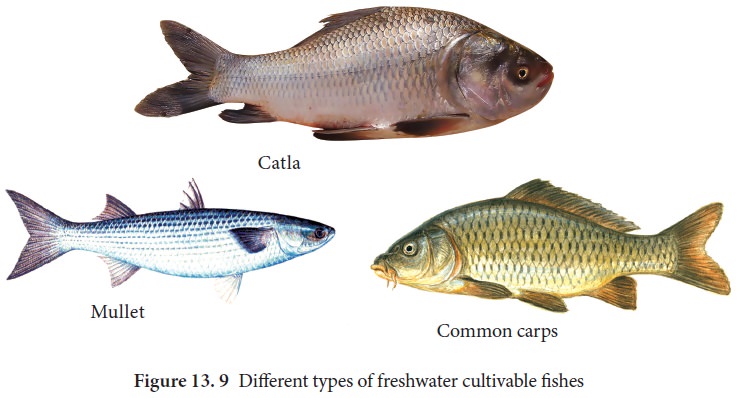
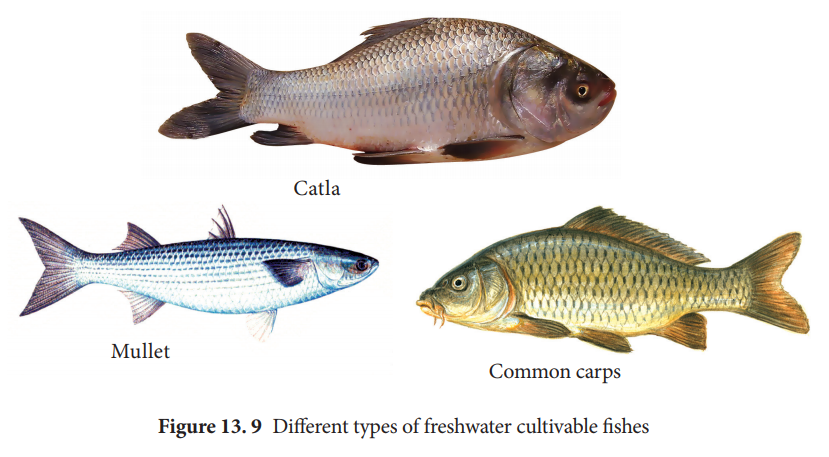
Types of cultivable fish
Cultivable fish are of 3 types(Figure 13. 9).
a)
Indigenous or native fresh water fishes (Major
carps, Catla, Labeo, Clarias)
b)
Salt water fishes acclimatized for fresh water (Chanos, Mullet).
c)
Exotic fishes or imported from other counties
(Common carps)
Among these, major carps have proved to be best
suited for culture in India, because the carps
1. Feed on
zooplanktons and phytoplanktons, decaying weeds, debris and other aquatic
plants.
2. They can
survive in turbid water with slightly higher temperature
3. Can
tolerate O2 variations in water.
4. Can be
transported from one place to other easily.
5. They are
highly nutritive and palatable.
External factors affecting fish culture
The factors that affect fish culture are temperature, light rain, water, flood, water current, turbidity of water, pH hardness, salinity and dissolved O2. Light and temperature also play an important role in fish breeding.
Management of fish farm
To culture fish, one should have an idea about
different stages of fish culture such as topographic situation, quality,
source, physical, chemical and biological factors of water. Breeding, hatching,
nursing, rearing and stocking fishes in ponds has to be managed properly.
Keeping in view the various stages of fishes, the following different types of
ponds have been recommended to manage them.
Breeding pond
The first step in fish culture is the breeding of
fishes, therefore, for proper breeding special types of ponds are prepared
called breeding ponds. These ponds are prepared near the rivers or other
natural water resources.
Types of breeding
Depending on the mode of breeding, they are divided into
1.Natural breeding (Bundh breeding)
These are special types of ponds where natural riverine
conditions or any natural water resources are managed for breeding of
culturable fishes. There bundhs are constructed in large low-lying areas that
can accommodate large quantity of rain water. The shallow area of such bundhs
is used as spawning ground.
2.Induced breeding
The fish seed is commonly collected from breeding
grounds but does not guarantee that all fish seeds belong to the same species.
Hence advanced techniques have been developed to improve the quality of fish
seed by artificial method of fertilization and induced breeding. Artificial
fertilization involves removal of ova and sperm from female and male by
artificial mechanical process and the eggs are fertilized. For artificial
fertilization the belly of mature female fish is held upward. Stripping is done
with the thumb of the right hand from the anterior to posterior direction for
the ejection of eggs due to force. In this way eggs are collected separately.
Further, the male fish is caught with its belly downwards. The milt of fish is
striped and collected separately, and then the eggs are fertilized.
Induced breeding is also done by hypophysation
(removal of pituitary gland). The gonadotropin hormone (FSH and LH) secreted by
the pituitary gland influences the maturation of gonads and spawning in fishes.
Pituitary gland is removed from a healthy mature fish.
Pituitary extract is prepared by homogenising in 0.3% saline or glycerine and
centrifuged for 15 minutes at 8000rpm. The supernatant is injected
intramuscularly at the base of the caudal fin or intra-peritonealy at the base
of pectoral fin. Male and female fishes start to spawn (release of gametes) and
eggs are fertilized. The fertilized eggs are removed from the spawning place
and kept into hatching hapas.
Fish seed
Fish seed is collected from breeding ponds. The
spawn collecting net is commonly called Benchijal (Shooting net) and
transferred to the hatching pits
Hatching pit
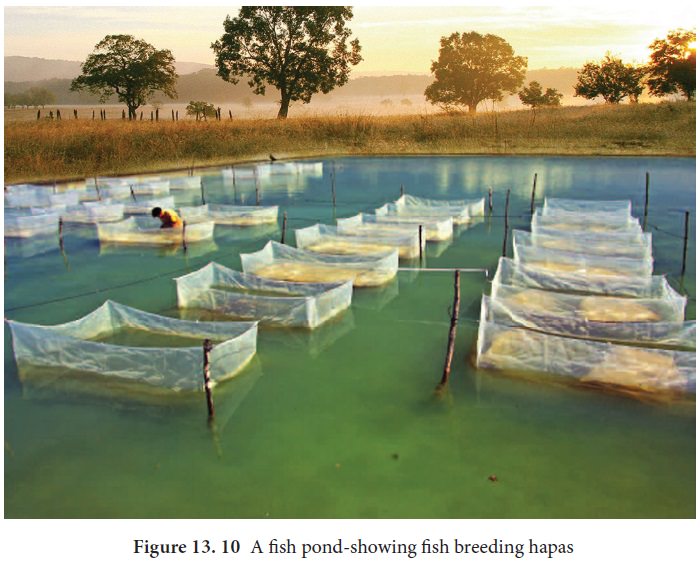
The fertilized eggs are kept in hatching pits. The hatching pits should be nearer to the breeding grounds, should be smaller in size with good quality water. There are two types of hatching pits, hatcheries are small sized pond in which unfertilized eggs are transferred and hatching happens.
Hatching hapas are rectangular trough shaped
tanks made up of mosquito net cloth supported by bamboo poles and fixed in the
river (Figure 13.10).

Nursery pond
The newly hatched fries are transported from the
hatching happa to nursery ponds where they grow into fingerlings.
Rearing pond
Fingerlings are transferred to rearing ponds that
is long and narrow and allows long distance swimming. The rearing pond should
be free from toxicants and predators. Antibiotics are used for washing the
fingerlings and then transferred to the stocking ponds.
Stocking ponds
Stocking ponds should be devoid of weeds and
predatory fishes. Proper organic manuring should be done to increase the
production with cow dung and chemical fertilizing should also be done.
Harvesting
Harvesting is done to capture the fishes from the
water. Well grown fishes are taken out for marketing. Small sized fishes are
again released into the stocking ponds for further growth. Different methods of
fishing are carried out to harvest fishes. These include Stranding, Angling,
Traps, Dipnets, Cast nets, Gill nets, Drag nets and purse nets. The harvested
fishes are preserved by refrigeration, Deep freezing, freeze drying, sun
drying, salting, smoking and canning.
Composite fish farming
Few selected fishes belonging to different species
are stocked together in proper proportion in a pond. This mixed farming is
termed composite fish farming or polyculture. The advantages include,
1.
All available niches are fully utilized.
2.
Compatible species do not harm each other.
3.
No competition among different species is found.
4.
Catla
catla, Labeo rohita and Cirrhinus
mrigala (surface feeder) are the commonly
used fish species for composite fish farming.
Exotic fishes
The fishes imported into a country for fish culture
are called exotic fishes and such fish culture is known as exotic fish culture.
Examples of such exotic fishes introduced in India are Cyprinus carpio and Oreochromis
mossambicus.
Disease Management
Diseases can be of viral or bacterial origin.
Regular monitoring of parameters like water quality, aeration, regular feeding,
observation for mortality should be checked. Parasitic infestations and
microbial infections should be observed periodically.
Economic importance of fish
Fishes frrm a rich source of protein food and
provide a good staple food to tide over the nutritional needs of man. Fish
species such as sardines, mackerel, tuna, herrings have high amino acids
concentrations particularly histidine which is responsible for the meaty flavor
of the flesh. It is rich in fat such as omega 3 fatty acids. Minerals such as
calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, iron, manganese, iodine and copper.
Some of the fish by - products are;
Fish oil is the
most important fish by product. It is derived from fish liver and from the fish body. Fish liver oil is
derived from the liver which is rich in vitamin A and D, whereas fish body oil
has high content of iodine, not suitable for human consumption, but is used in
the manufacture of laundry soaps, paints and cosmetics.
Fish meal
is
prepared from fish waste after extracting oil from the fish. The dried wastes are used to prepare food for
pig, poultry and cattle. The wastes obtained during the preparation of fish
meal are widely used as manure.
Isinglass
is a high
-grade collagen produced from dried air bladder or swim bladder of certain fishes viz. catfish and carps.
The processed bladder which is dissolved in hot water forms a gelatin having
adhesive property. It is primarily used for clarification of wine, beer and
vinegar.
Related Topics