Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Trends in Economic Zoology
Lac Culture
Lac Culture
The culture of lac insect using techniques for the
procurement of lac on large scale is known as Lac culture. Lac is produced by
the lac insect Tachardia lacca
previously known as Laccifer lacca.
It is a minute, resinous crawling scale insect which inserts its probosics into
the plant tissues and sucks juice, grows and secretes lac from the hind end of the body as a protective covering for its body.
Moreover the insect is a parasite on host plants i.e., Karanagalli (Acacia catechu), Karuvelai (Acacia nilotica) and Kumbadiri (Schleichera oleosa) . The quality of lac
depends upon the quality of the host plant. The female lac insect is
responsible for large scale production of lac, which is larger than the male
lac insect.
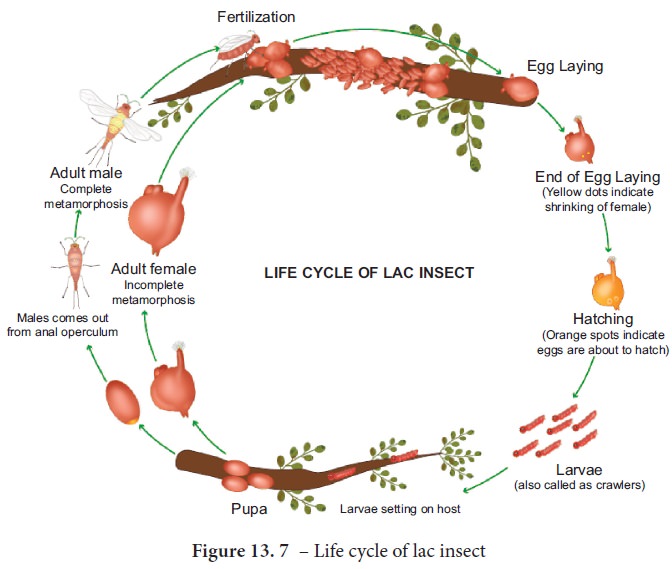
After copulation, the male insect dies. The female develops very rapidly after fertilization and lays about 200 to 500 eggs (Figure. 13. 7). Eggs hatch into larvae after six weeks. The mass emergence of larvae from the egg in search of a host plant is called ‘swarming’ . After settling on the host, the larvae start feeding continuously and the secretion of lac also starts simultaneously. Gradually the larvae become fully covered by lac. Then the larvae moult in their respective cells (chamber). The shapes of the cells are different for male and female insects, males are elongated whereas and the female are oval. Some insects are natural predators of lac insects. The caterpillars of these parasites feed upon lac insects showing hyper-parasitism.
Lac cultivation is a complicated process, so the
cultivators should know well about the inoculation, swarming period and
harvesting of lac. The process of introducing lac insect on the host plant is
called inoculation. Before inoculation, pruning of the host plant is done. The
twigs having brood lac, i.e., lac insect about 20 cm in length are attached to
fresh host plants. The lac insect then repeats its life cycle. The collection
of lac from the host plant is known as harvesting. Harvesting may be done
before swarming (immature) or after swarming (mature). Immature
harvesting produces ‘Ari lac’ whereas mature harvesting produces the mature
lac. Lac cut from the host plant is called ‘Stick lac’. The lac present on the
twig is scraped and collected. After grinding, the unnecessary materials like
dusts and fine particles are removed. The resultant lac is called ‘seed lac’.
The seed lac is sun dried and then melted to produce ‘shellac’.
Economic importance of Lac
· Lac is largely used as a sealing wax and adhesive
for optical instruments. It is used in electric industry, as it is a good
insulator.
· It is
used in preparations of shoe and leather polishes and as a protective coating
of wood.
· It is
used in laminating paper board, photographs, engraved materials and plastic
moulded articles.
· Used as
a filling material for gold ornaments
Related Topics