Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 13 : Trends in Economic Zoology
Animal Breeding
Animal
Breeding
Human beings have been depending on animals and
animal products for food from very early times. Generally high yielding animals
produced by hybridization are reared in poultry and dairy farms. In earlier
days, animals were produced and selected based on specific characters. With the
gain in knowledge on the principles of heredity and genetics, human beings have
been successful in rearing animals with the superior qualities through
hybridization experiments. Complex issues are faced by the animal breeder
during hybridization experiments. Hence animals with maximum desirable characters
should be selected.
A group of animals related by descent and with
similar characters like general appearance, features, size etc., are said to
belong to a breed. Why should we breed animals? Through
animal breeding, improved breeds of animals can be produced by improving their
genotype through selective breeding.
Objectives of Animal breeding:
a)
To improve growth rate
b)
Enhancing the production of milk, meat. Egg etc.,
c)
Increasing the quality of the animal products
d)
Improved resistance to diseases
e)
Increased reproductive rate
Methods of Animal breeding:
There are two methods of animal breeding, namely
inbreeding and outbreeding
1. Inbreeding:
Breeding
between animals of the same breed for 4-6 generations is called inbreeding. Inbreeding increases homozygosity and exposes
the harmful recessive genes. Continuous inbreeding reduces fertility and even
productivity, resulting in “inbreeding depression”. This can be avoided by
breeding selected animals of the breeding population and they should be mated
with superior animals of the same breed but unrelated to the breeding
population. It helps to restore fertility and yield.
1.
Outbreeding:
The
breeding between unrelated animals is called outbreeding. Individuals produced do not have common ancestors for 4-6 generations.
Outbreeding helps to produce new and favourable traits, to produce hybrids with
superior qualities and helps to create new breeds. New and favourable genes can
be introduced into a population through outbreeding.
i. Out
crossing: It is the breeding between unrelated animals of the same breed
but having no common ancestry. The offspring of such a cross is called
outcross. This method is suitable for breeding animals below average in
productivity.
ii. Cross
breeding: Breeding between a superior male of one breed with a superior female of another breed. The cross
bred progeny has superior traits ( hybrid vigour or heterosis.)
iii. Interspecific hybridization:
In this method of breeding mating is between male
and female of two different species. The progeny obtained from such crosses are
different from their parents, and may possess the desirable traits of the
parents. Have you heard about Mule? It was produced by the process of
interspecific hybridization between a male donkey and a female horse.
Controlled breeding experiments
Artificial insemination:
Artificial insemination is a technique in which the
semen collected from the male is injected to the reproductive tract of the
selected female. Artificial insemination is economical measure where fewer
bulls are required and maximum use can be made of the best sire.
Advantages of artificial insemination
a.
It increases the rate of conception
b.
It avoids genital diseases
c.
Semen can be collected from injured bulls which
have desirable traits.
d.
Superior animals located apart can be bred
successfully.
Multiple ovulation embryo transfer technology (MOET)
It is another method of propagation of animals with
desirable traits. This method is applied when the success rate of crossing is
low even after artificial insemination. In this method Follicle stimulating
hormone (FSH) is administered to cows for inducing follicular maturation and
super ovulation. Instead of one egg per cycle, 6-8 eggs can be produced by this
technology. The eggs are carefully recovered non-surgically from the genetic
mother and fertilized artificially. The embryos at 8-32 celled stages are
recovered and transferred to a surrogate mother. For another round of
ovulation, the same genetic mother is utilized. This technology can be applied
to cattle, sheep and buffaloes. Advantage of this technology is to produce high
milk yielding females and high-quality meat yielding bulls in a short time.
Breeds of Dairy animals
Dairying is the production and marketing of milk
and its products. Dairy operation consists of proper maintenance of cattle, the
collection and processing the milk and its by products. There are 26 well
defined breeds of cattle and 6 breeds of buffaloes in India. Cattles are
classified under three groups based on the purpose they serve to man (Figure
13. 13). They are
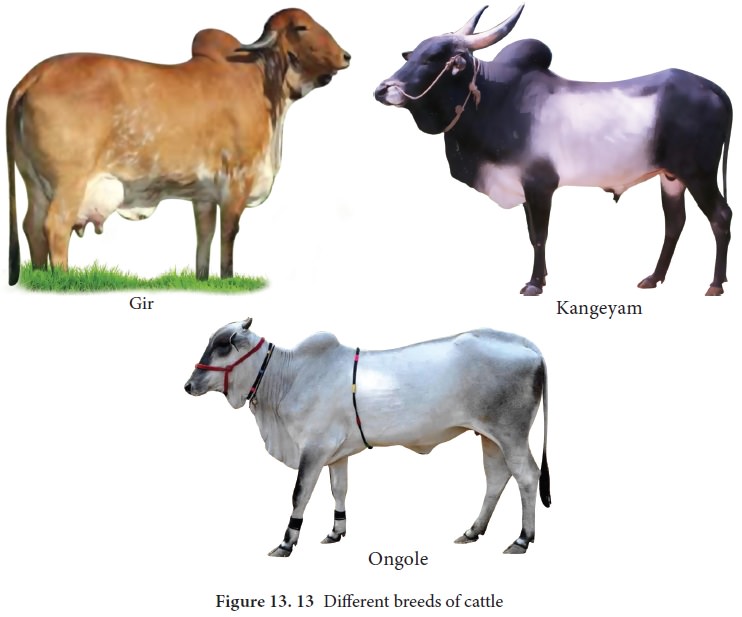
1.
Dairy
breeds or Milch breeds: They are high milk yielders with extended lactation. Eg., Sindhi, Gir,
Sahiwal, Jersy, Brown Swiss, Holstein cattle.
2.
Draught
purpose breeds: Bullocks are good for draught purpose. Eg. Kangayam, Malvi
3.
Dual
Purpose breeds: Cows are meant for yielding more milk and bullocks are used for better drought
purpose. Eg. Ongole, Hariana
To meet the milk demand of the growing population,
milk breeds are preferred by farmers in small scale farms. Goats are also used
all over India for supplementing deficiencies in milk production. Some of the
breeds of cattle that are good milkers are Jamunapari in Ganga-Jamuna riverine
tracts, Beetal in Punjab, Bar–bari in Uttarpradesh.
Common diseases of cattle: A healthy animal eat, drinks and sleeps well regularly. Healthy cattle appear bright, alert and active in their movement with a shiny coat. Cattle are affected by a large number of diseases.
Cattle in ill health appear dull,
restless and change posture frequently with drop in milk yield. The main
diseases of dairy cattle are rinderpest, foot and mouth disease, cow pox,
hemorrhagic fever, anthrax.
Uses of dairy products:
Milk
products: Milk is produced by dairy animals which is an emulsion of fat and lactose. Milk also contains enzymes
which are destroyed during pasteurization. Milk is a rich source of vitamin A,
B2 , B1 , and deficient in Vitamin C. Due to its high nutrition value, it
serves as a complete food for infants. Dairy products such as yoghurt, cheese,
butter, ice cream, condensed milk, curd, and milk powder processed from milk
make dairy, a highly farming attraction.
Meat: Meat is
rich in protein and also contains many minerals like iron, zinc, vitamins and selenium. It also contains
vitamins needed for human diet.
Land
management: Grazing of livestock is sometimes used as a way to
control weeds and undergrowth.
Manure: Manure
can be spread on agriculture fields to increase crop yields.
Related Topics