Chapter: Television and Video Engineering : Essentials of Color Television
Three Color Theory
THREE COLOR THEORY
All light
sensations to the eye are divided (provided there is an adequate brightness
stimulus on the operative cones) into three main groups. The optic nerve system
then integrates the different color impressions in accordance with the curve
shown in Fig.to perceive the actual color of the object being seen.
This is
known as additive mixing and forms the basis of any color television system. A
yellow color, for example, can be distinctly seen by the eye when the red and
green groups of the cones are excited at the same time with corresponding
intensity ratio.
Similarly
and color other than red, green and blue will excite different sets of cones to
generate the cumulative sensation of that color.
A white
color is then perceived by the additive mixing of the sensations from all the
three sets of cones. Mixing of Colors Mixing of colors can take place in two
ways subtractive mixing and additive mixing.
In
subtractive mixing, reflecting properties of pigments are used, which absorb
all wavelengths but for their characteristic color wavelengths.
When
pigments of two or more colors are mixed, they reflect wavelengths which are
common to both. Since the pigments are not quite saturated (pure in color) they
reflect a fairly wide band of wavelengths.
This type
of mixing takes place in painting and color printing. In additive mixing which
forms the basis of color television, light from two or more colors obtained
either from independent sources or through filters can create a combined
sensation of a different color.
Thus
different colors are created by mixing pure colors and not by subtracting parts
from white. The additive mixing of three primary colors red, green and blue in
adjustable intensities can create most of the colors encountered in everyday
life.
The
impression of white light can also be created by choosing suitable intensities
of these colors. Red, green and blue are called primary colors. These are used
as basic colors in television. By pairwise additive mixing of the primary
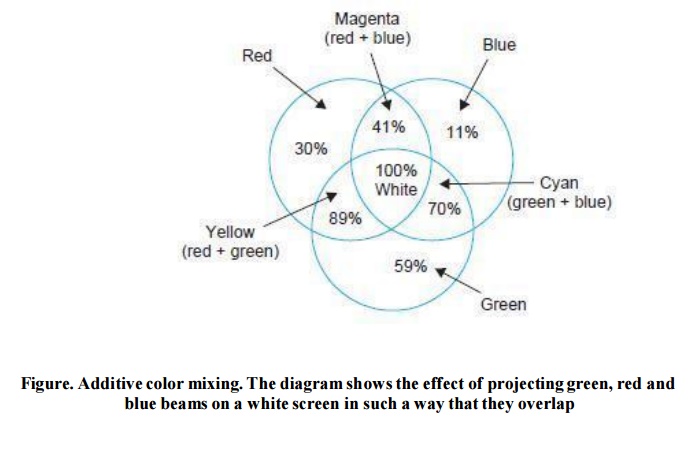
colors the following complementary colors are produced:
Red +
Green = Yellow
Red + Blue = Magenta (purplish red shade)
Blue + Green = Cyan (greenish blue shade)
Color
plate 1 depicts the location of primary and complementary colors on the color
circle. If a complementary is added in appropriate proportion to the primary
which it itself does not contain, white is produced.
This is
illustrated in Fig. where each circle corresponds to one primary color. Color
plate
2 shows
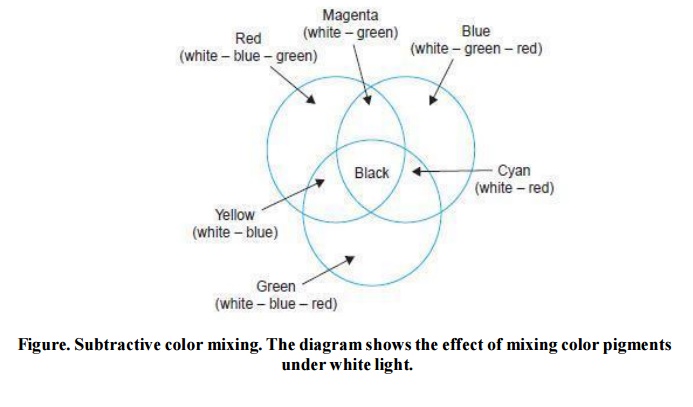
the effect of color mixing. Similarly Fig, illustrates the process of
subtractive mixing. Note that as additive mixing of the three primary colors
produces white, their subtractive mixing results in black.
(Research
has shown that the actual neural process of color perception is substantially
different from the tricolor process. However, all color reproduction processes
in television or printing use variations of this process and is found
satisfactory).
Related Topics