Chapter: Television and Video Engineering : Essentials of Color Television
Formation of the Chrominance Signal
FORMATION OF THE CHROMINANCE SIGNAL
Using the information of Table, Fig. illustrates the formation of the chroma signal for a color bar pattern after the color difference signals have been scaled down in accordance with corresponding weighting factors.
Note that new amplitudes of the chrominance subcarrier signals are 0.63 for red and cyan, 0.59 for green and magenta and 0.44 for blue and yellow.
These amplitudes will still cause over modulation to about 33%. This is permitted, because in practice, the saturation of hues in natural and staged scenes seldom exceeds 75 percent.
Since the amplitude of chroma signal is proportional to the saturation of hue, maximum chroma signal amplitudes are seldom encountered in practice.
Therefore, the weighted chroma values result in a complete color signal that will rarely, if ever, over modulate the picture carrier of a CTV transmitter. Hence it is not necessary to further decrease the signal amplitudes by employing higher weighting factors.
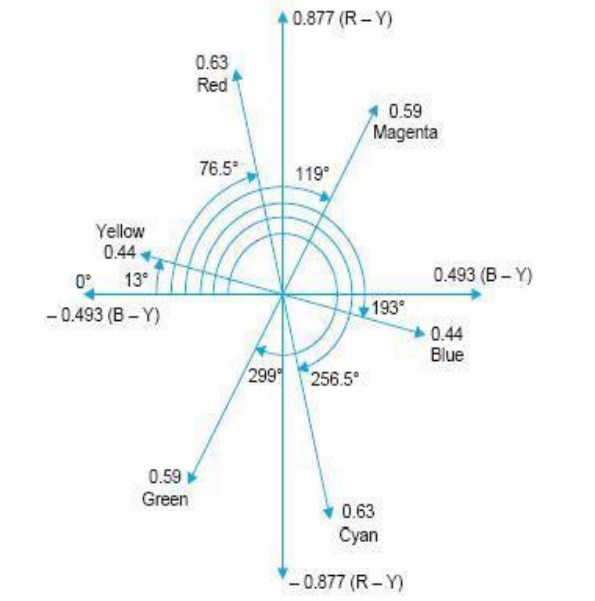
Chroma Signal Phasor Diagram
The compensation (readjustment) of chroma signal values results in a change of chroma phase angles. In the NTSC system it is a common practice to measure phase angles relative to the – (B–Y) phasor.
This location has been designated 0° or the reference phase position on the phasor diagram (see Fig.) because this is also the phase of the color burst that is transmitted on the back porch of each horizontal sync pulse.
Referring to Fig. the compensated color magenta is represented by a phasor at an angle of 119°. In the same manner the diagram indicates phase angles and amplitudes of other color signals. Note that primary colors are 120° apart and complementary colors differ in phase by 180° from their corresponding primary colors.
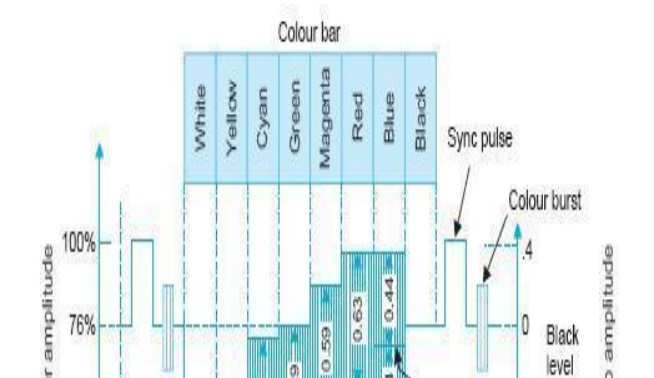
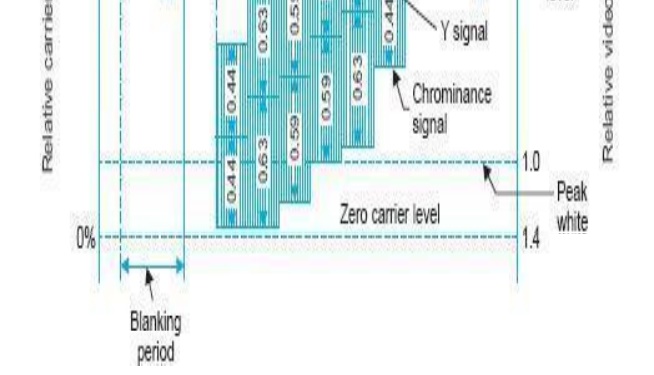
100% saturated, 100% amplitude color-bar signal in which the color difference signals are reduced by weighting factors to restrict the chrominance signal excursions to 33% beyond black and peak white levels.

Related Topics