Chapter: Mechanical : Total Quality Management (TQM) : Principles
The PDCA Cycle
THE PDCA CYCLE
PROBLEM
SOLVING METH OD
1. IDENTIFY THE OPPORT UNITY
├ś Identify
the Problem
┬¦ Pareto
analysis of external a larm signals.
┬¦ Pareto
analysis of internal alarm signals.
┬¦ Proposals
from key insiders.
┬¦ Proposals
from suggestion schemes.
┬¦ Field study
of userŌĆÖs needs.
┬¦ Comments
of key people ou tside the organization.
┬¦ Customer
surveys.
┬¦ Employee
surveys.
┬¦ Brainstorming
by work grou ps.
├ś Form the
Team
┬¦ Team
should be selected.
┬¦ Goals and
milestones are es tablished. ├ś Define
the Scope.
Criteria
for a good problem sta tement is as follows
┬¦ It
clearly describes the prob lem.
┬¦ It states
the effect.
┬¦ It
focuses on what is known, unknown etc.
┬¦ It
emphasizes the impact on the customer.
2. ANALYZE THE CURRENT PROCESS
The
objective is to understand the process and how it is currently performed.
Step 1 :
The team to develop a pr ocess flow diagram.
Step 2 :
The target performance m easures are defined.
Step 3 : Collection of all
available data and information.
Common items of data and
information are
1. Customer information
2. Design information
3. Process information
4. Statistical information
5. Quality information
6. Supplier information
3.
DEVELOP THE OPTIMAL SOLUTION(S)
This phase has the objective of establishing potential and
feasible solutions and recommending the best solution to improve the process.
├ś Creativity
plays the major role, and brainstorming is the principal technique.
├ś There are
three types of creativity:
┬¦ Create
new processes
┬¦ Combine
different processes
┬¦ Modify
the existing process
4.
IMPLEMENT CHANGES
This phase has the objective of preparing the implementation
plan, obtaining approval and implementing the process improvements.
├ś Approval
of the quality council.
├ś Obtain
the advice and consent of departments, functional areas, teams, individuals
etc.
├ś Monitor
the activity.
5. STUDY
THE RESULTS
This phase has the objective of monitoring and evaluating the
change by tracking and studying the effectiveness of the improvement efforts.
6.
STANDARDIZE THE SOLUTION
├ś Institutionalize by positive control of the
process.
├ś The quality peripherals ŌĆō the
system, environment and supervision must be certified. ├ś Operators must be certified.
7. PLAN
FOR THE FUTURE
The
objective is to achieve improved level of process performance.
├ś Regularly
conduct reviews of progress by the quality council.
├ś Establish
the systems to identify area for future improvements.
├ś Track
performance with respective internal & external customers.
├ś TQM tools
and techniques are used to improve quality, delivery and cost.
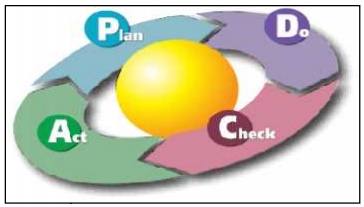
PDSA CYCLE (OR DEMING WHEEL)
The basic Plan ŌĆō Do ŌĆō Study ŌĆō Act cycle was originally developed by W alter A. Shewart. But it was popularized by Edward Deming and thatŌĆÖs why it is often called the Demi ng Cycle or Deming Wheel. It is an effective continuo us improvement technique.
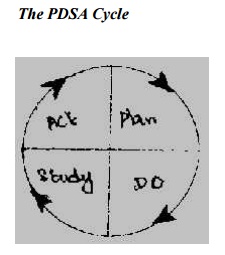
The PDSA Cycle
What is PDSA Cycle?
PDSA stands for Plan, D o, Study, and Act. It is a model for
testing ideas that you think may
create
improvement.
┬Ę
It is an extremely practical, common sense based
approach that is easy to understand.
┬Ę
It can be used to test ideas for improvement
quickly and easily based on existing ideas, research, feedback, theory, review,
audit, etc.
┬Ę
It encourages starting with small changes, which
can build into large improvements in the service through successive quick
cycles of change.
┬Ę
Illustrates the PDSA cycle.
Phases of PDSA Cycle
The four phases of PDSA cycle and their descriptions are
presented in Table.
Phases of PDSA Cycle
Phases : Description
1.
Plan
ŌĆó Define the
problem
ŌĆó Analyze the causes and draft an action plan for
solving the problem. ŌĆó Determine the quality objectives and the critical
factors.
ŌĆó Define the
performance indicators.
ŌĆó Collect and analyze the necessary process data. ŌĆó
Generate possible solutions
ŌĆó Select
the most feasible solution; and work it out.
2. Do
ŌĆó First,
implement the plan on a limited scale or conduct an experiment to test the
proposed improvement. Collection data is hereby essential.
ŌĆó Train all
involved employees in the use of quality improvement methods and techniques.
ŌĆó Describe
the process which is considered for improvement and form project teams to lead
the process.
3. Check
ŌĆó Evaluate
the trial project with the performance indicators.
ŌĆó Verify
whether the improvement has been successful or not.
4. Act
ŌĆó Act to
implement proven improvements. The choices are: introduce the plan, adjust or
reject it.
ŌĆó The
improvements are documented in standard procedures so all employees are well-informed
on how to handle in future.
ŌĆó Usually,
the cycle will be repeated under the different circumstances and conditions to
test how consistent the results are.
Continuous
Process Improvement Cycle Using PDCA
The relationship between the PDSA
cycle and eleven steps to continuous process improvement are illustrated in
figure.
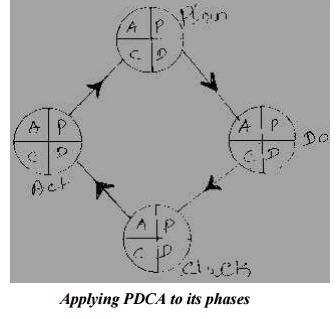
Each phase of the PDCA cycle must undergo its own PDCA cycle
for further improvements, as shown in figure.
Benefits
of the PDSA Cycle
The
benefits of the PDSA cycle can be experienced in the following areas:
┬Ę
Daily routine management ŌĆō for the
individual and / or the team.
┬Ę
Problem-solving process.
┬Ę
Project management
┬Ę
Continuous development
┬Ę
Vendor development
┬Ę
Human resources development
┬Ę
New product developmen t
┬Ę
Process trials
Related Topics