Chapter: Mechanical : Total Quality Management (TQM) : Principles
Motivation Concept of Motivation
MOTIVATION CONCEPT OF MOTIVATION
a. Scott defines, ŌĆ£Motivation means a process of
stimulating people to accomplish desired goals.ŌĆØ
b. Edwin B. Flippo defines, ŌĆ£Motivation is the
process of attempting to influence others to do your will through the
possibility of reward.ŌĆØ
a. In simple
words, motivation is the process of inducing people inner drives and action
towards certain goals and committing his energies to achieve these goals.
IMPORTANCE
OF MOTIVATION
a. Motivation
improves employee involvement.
b. Motivation
promotes job satisfaction and thus reduces absenteeism and turnover.
c. Motivation
helps in securing a high level of performance and hence enhances efficiency and
productivity.
d. Motivation
creates a congenial working atmosphere in the organization and thus promotes
interpersonal cooperation.
THEORIES
OF MOTIVATION
Though there are many theories of motivation, the
MaslowŌĆÖs
hierarchy of needs theory and HerzbergŌĆÖs two factor
theory are more important from our subject of view.
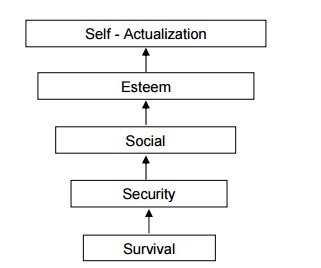
MASLOWŌĆÖS
HIERARCHY OF NEEDS
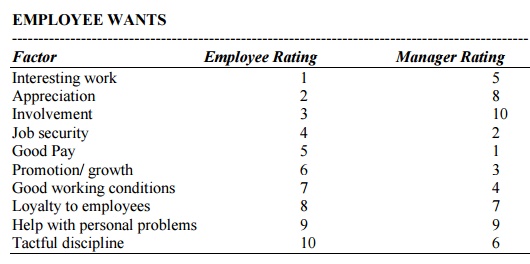
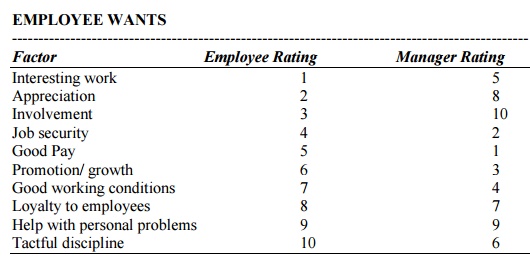
EMPLOYEE WANTS
Factor Employee Rating Manager Rating
Interesting work 1 5
Appreciation 2 8
Involvement 3 10
Job security 4 2
Good Pay 5 1
Promotion/ growth 6 3
Good working conditions 7 4
Loyalty to employees 8 7
Help with personal problems 9 9
Tactful discipline 10 6
HerzbergŌĆÖs Two Factor Theory
This theory is also called motivation-hygiene theory. This theory is based on two factors: 1. Motivation factors or satisfiers, and 2. Hygiene factors or dissatisfiers. Various motivation and hygiene factors are listed in Table.
Motivation and hygiene factors

Motivation Factors
Achievement
Recognition
The work itself
Responsibility
Advancement and growth
Hygiene Factors
Supervisors
Working conditions
Interpersonal relationships
Pay and security
Company policy and administration
According to Herzberg, maintenance or hygiene factors are necessary to maintain a reasonable level of satisfaction among employees. These factors do not provide satisfaction to the employees but their absence will dissatisfy them. Therefore these factors are called dissatisfiers.
On the other hand, motivational factors creates satisfaction to the workers at the time of presence but their absence does not cause dissatisfaction. It can be noted that HerzbergŌĆÖs dissatisfiers are roughly equivalent to MaslowŌĆÖs lower levels, and the motivators are similar to the MaslowŌĆÖs
upper levels.
Thus the knowledge of motivation is required for any organization to understand the utilization of employee involvement.
ACHIEVING A MOTIVATED WORK FORCE
The building of a motivated work force if for the most part an indirect process. Concepts to achieve a motivated work force are as follows:
1. Know thyself.
2. Know your employees.
3. Establish a positive attitude.
4. Share the goals.
5. Monitor progress.
6. Develop interesting work.
├ś Job rotation
├ś Job enlargement
├ś Job enrichment
7. Communicate effectively
8. Celebrate success.
EMPLOYEE SURVEYS
Employee surveys help managers assess the current state of employee relations, identify trends, measure the effectiveness of program implementation, identify needed improvements, and increase communication effectiveness.
STEP 1 The Quality Council to create a multifunctional team
STEP 2 The Team will develop survey instrument
STEP 3 Administer the survey
STEP 4 Results are compiled and analyzed
STEP 5 Determine areas for improvement
┬Ę Employee involvement is creating an environment in which people have an impact on decisions and actions that affect their jobs.
┬Ę Tell: the supervisor mak es the decision and announces it to staff. The supervisor provides complete direction.
┬Ę Sell: the supervisor makes the decision and then attempts to gain commitment from staff by "selling" the positive aspects of th e decision.
┬Ę Consult: the supervisor i nvites input into a decision while retaining a uthority to make the
final decision herself.
┬Ę Join: the supervisor inv ites employees to make the decision with the supervisor. The
supervisor considers her voice eq ual in the decision process.
To round out the model, I add the following.
┬Ę Delegate: the supervisor turns the decision over to another party.
Seven Rules of Motivation
#1 Set a major goal, but follow a path. The path has mini goals that go in m any directions. When you learn to succeed at mini goals, you will be motivated to challenge grand goals.

#2 Finish what you start. A half finished project is of no use t o anyone. Quitting is a habit. Develop the habit of finishing self-motivated projects.

#3 Socialize with others of similar interest. Mutual support is motivating. We will develop the attitudes of our five best friends. If they are losers, we will be a los er. If they are winners, we will be a winner. To be a cowboy we must associate with cowboys.

#4 Learn how t o learn. Dependency on others for knowledge supports the habit of procrastination. Man has the ability to learn without instructors. In fact, when we learn the art of s elf-education we will find, if not create, opportunity to find success beyond our wildest dreams.

#5 Harmonize natural talent w ith interest that motivates. Natural talent cr eates motivation, motivation creates persistence and persistence gets the job done.

#6 Increase knowledge of subjects that inspires. The more we know about a subject, the more we want to learn about it. A self-propelled upward spiral develops.

#7 Take risk. Failure and bouncing back are elements of motivation. Failure is alearning tool. No one has ever succeeded at anything worthwhile without a string of failures.
Related Topics